Abstract
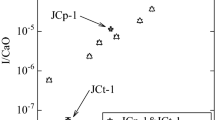
Five corals belonging to common scleractinian reef-building species, and collected from Gulf of Suez, Egypt were subjected to neutron activation analysis. The content of 26 elements: Na, Mg, Cl, Ca, Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn, As, Br, Rb, Sr, Sb, I, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Gd, Hf, Th, and U was experimentally determined. Ca and Sr have the highest content i.e. 38.4–39.5% and 0.73–0.78% respectively while, the content of all other elements was within the ranges reported for the worldwide corals. For a better understanding of the coral exoskeleton elemental content, the partition coefficient calculated for all determined elements showed a wide range of values varying from 2 × 10−4 in the case of Cl to 2 × 103 for Ce and other insoluble elements. Although all corals were collected in the vicinity of the Port Suez no traces of anthropogenic contamination were evidenced.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zinke J, Dullo WC, Heiss GA et al (2004) ENSO and Indian Ocean subtropical dipole variability is recorded in a coral record off southwest Madagascar for the period 1659 to 1995. Earth Planet Sci Lett. doi:10.1016/jepsl200409028
Al-Taani AA, Rashdan, Khashashneh S (2015) Atmospheric dry deposition of mineral dust to the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea: rate and trace elements. Mar Pollut Bull. doi:10.1016/jmarpolbul201411047
Royle SH, Andrews JE, Turner J et al (2015) Environmental and diagenetic records from trace elements in the Mediterranean coral Cladocora caespitosa. Palaeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. doi:10.1016/jpalaeo201510010
Thresher RE, Fallon SJ, Townsend AT (2016) A ”core-top” screen for trace element proxies of environmental conditions and growth rates in the calcite skeletons of bamboo corals (Isididae). Geochim Cosmochim Acta. doi:10.1016/jgca201607033
Fallon S, White JC, McCulloch M (2010) Porites corals as recorders of mining and environmental impacts: Misima Island. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00715-3
Carriquiry JD, Horta-Puga G (2010) The Ba/Ca record of corals from the Southern Gulf of Mexico: contributions from land-use changes, fluvial discharge and oil-drilling muds. Mar Pollut Bull. doi:10.1016/jmarpolbul201006007
Chen TR, Yu KF, Li S, et al. (2010) Heavy metal pollution recorded in Porites corals from Daya Bay, northern South China Sea Mar Envir Res DOI 10.1016/jmarenvres201006004
Liu Y, Peng Z, Wei G et al (2011) Interannual variation of rare earth element abundances in corals from northern coast of the South China Sea and its relation with sea-level change and human activities. Mar Envir Res 71:62–69. doi:10.1016/jmarenvres201010003
Metian M, Hedouin L, Ferrier-Pages C et al (2015) Metal bioconcentration in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: investigating the role of different components of the holobiont using radiotracers. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4383-z
Hedouin LS, Wolf RE, Phillips J et al (2016) Improving the ecological relevance of toxicity tests on scleractinian corals: Influence of season, life stage, and seawater temperature. Environ Pollut. doi:10.1016/jen-vpol201601086
Le Tissier MDAA, Clayton B, Brown BE et al (1994) Skeletal correlates of coral density banding and an evaluation of radiography as used in sclerochronology. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 110:29–44
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1961)72[175:DOTEIS]20CO;2
Livingstone HD, Thompson G (1971) Trace elements concentrations in some modern corals. Limnol Ocean. doi:10.4319/lo19711650786
Li Y (1991) Distribution patterns of the elements in the ocean: a synthesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(91)90485-N
Balling HW, Janse M, Sondervan PJ (2008) Trace elements, functions, sinks and replenishmentin reef aquaria, Advances in Coral Husbandry in Public Aquariumsin Coral Husbandry in Public Aquariums Public Aquarium Husbandry Series vol 2 RJ Leewis and M Janse (eds) Burgers Zoo Arnhem pp 143-156 https://www.burgerszoocom/media/560526/chapter-15pdf (accessed 30 06 2017)
Knoema (2017) Suez canal traffic statistics. https://www.knoemacom/mrrisdf/suez-canal-traffic-statistics. Accessed 05 May 2017
Al-Rousan S, Al-Shloul RN, Al-Horani FA et al (2007) Heavy metal contents in growth bands of Porites corals: record of anthropogenic and human developments from the Jordanian Gulf of Aqaba. Mar Pollut Bull. doi:10.1016/jmarpolbul200708014
Mohammed TAAA, Dar M (2010) Ability of corals to accumulate heavy metals, Northern Red Sea, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0138-x
Ali AAM, Hamed MA, Abd El-Azim H (2011) Heavy metal distribution in the coral reef ecosystem of the Northern Red Sea. Helgoland Mar Res. doi:10.1007/s10152-010-0202-7
Furby KA, Apprill A, Cervino JM et al (2014) Incidence of lesions on Fungiidae corals in the eastern Red Sea is related to water temperature and coastal pollution. Mar Environ Res 98:2938. doi:10.1016/jmarenvres201404002
Barakat SA, Al-Rousan S, Al-Trabeen MS (2015) Use of scleractinian corals to indicate marine pollution in the northern Gulf of Aqaba, Jordan. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4275-2
Frontasyeva MV (2011) Neutron activation analysis in the life sciences. Phys Part Nucl. doi:10.1134/S1063779611020043
Keller NB, Demina LL, Oskina NS (2007) Variation in the chemical composition of the skeletons of the non-zooxanthellate scleractinian (Anthozooa: Scleractinia) corals. Geochem Int 45:832–839. doi:10.1134/S0016702907080095
Zinicovscaia I, Duliu OG, Culicov OA et al (2017) Geographical origin identification of Moldavian wines by neutron activation analysis. Food Anal Met. doi:10.1007/s12161-017-0913-3
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2004) Composition of the continental crust. In: Holland H, Turekian K (eds) Treatise in geochemistry. Esevier, Oxford. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00301-6
Yamada G, Fujimori K, Yamada MO et al (1998) Trace elements found to be variable in two coral reef species, Heliofungia actiniformis and Galaxea fascicularis, collected from the Ryukyu Islands. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/BF02784268
Song Y, Yu K, Zhao J et al (2014) Past 140-year environmental record in the northern South China Sea: evidence from coral skeletal trace metal variations. Environ Pollut. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.024
Cole C, Finch A, Hintz C et al (2016) Understanding cold bias: Variable response of skeletal Sr/Ca to sea-water pCO2 in acclimated massive Porites corals. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep26888
Saha N, Webb GE, Zhao JX (2016) Coral skeletal geochemistry as a monitor of inshore water quality. Sci Total Environ. doi:10.1016/jscitotenv201605066
Al-Shawafi AN, Al-Khol A, Al-Jabal OA (2009) Heavy meta content in coral reef sediments from Red Sea of Yemen and its significance on marine environment. Glob Geol. doi:10.13969/j1issn1167329736120091021006
Nguyen AD, Zhao JX, Feng YX, Hu WP, Yu KF, Gasparon M, Pham TB, Clark TR (2013) Impact of recent coastal development and human activities on Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam: evidence from a Porites lutea geochemical record. Coral Reefs. doi:10.1007/s00338-012-0962-4
Brown BE, Howard LS (1985) Assessing the effects of stress on reef corals. Adv Mar Biol. doi:10.1016/S0065-2881(08)60049-8
Runnalls LA, Coleman ML (2003) Record of natural and anthropogenic changes in reef environments (Barbados West Indies) using laser ablation ICP-MS and sclerochronology on coral cores. Coral Reefs. doi:10.1007/s00338-003-0349-7
Jupiter SD (2008) Coral rare earth element tracers of terrestrial exposure in nearshore corals of the Great Barrier Reef. In: Bernhard R, Dodge RF (eds) Proceedings of the 11th international coral reef symposium, 7–11 July, Ft Lauderdale, Florida. http://www.nsuworksnovaedu/cgi/viewcontentcgi?article=1000&context=occicrs. Accessed 10 Jan 2017
Geich MA, Schleicher H (1990) Absolute age determination, Springer ISBN: 978-3-540-51276-9
Kumar SK, Chandrasekar N, Seralathan P (2010) Trace elements contamination in coral reef skeleton, Gulf of Mannar, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00128-009-9905-3
Krishnakumar S, Ramasamy S, Magesh NS et al (2015) Metal concentrations in the growth bands of Porites sp.: a base-line record on the history of marine pollution in the Gulf of Mannar, India. Mar Pollut Bull. doi:10.1016/jmarpolbul201510
Acknowledgements
The project was partially accomplished within the protocol no 4322-4-14/16 between the University of Bucharest and the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research Dubna Russian Federation. We would wish to thank two anonymous reviewers for their useful remarks and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdo, S.Y., Duliu, O.G., Zinicovscaia, I. et al. Epithermal neutron activation analysis of major and trace elements in Red Sea scleractinian corals. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314, 1445–1452 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5511-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5511-8