Abstract
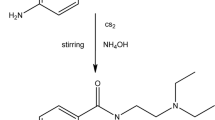
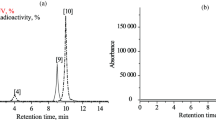
[111In]-DTPA-Amlodipine complex ([111In]-DTPA-AMLO) was prepared starting high purity [111In]indium chloride and conjugated DTPA-AMLO in 30 min at room temperature in acetate buffer in high radiochemical purity (>99 %, RTLC/HPLC; specific activity: 8–10 GBq/mmol). The log P, stability, biodistribution studies and imaging studies in untreated and amlodipine-pretreated rats were determined. The tracer is mostly washed out through kidneys as expected for a dihydropyridine compound. Blocking studies demonstrated high specific binding of the tracer in calcium channel-rich organs including intestine, heart and colon. SPECT images fully supported above results in normal and treated rats.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catterall WA, Perez-Reyes E, Snutch TP, Striessnig J (2005) International union of pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacol Rev 57:411–425
Terada K, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H (1987) Blocking actions of Ca+2 antagonists on the Ca+2 channels in the smooth muscle cell membrane of rabbit small intestine. Pflügers Arch 408:552–557
Wagner JA, Sax FL, Weisman HF et al (1989) Calcium-antagonist receptors in the atrial tissue of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 320:755–761
Mukherjee R, Hewett KW, Walker JD, Basler CG, Spinale FG (1998) Changes in L-type calcium channel abundance and function during transition to pacing-induced congestive heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 37:432–444
Sadeghpour H, Jalilian AR, Shafiee A, Akhlaghi M, Miri R, Mirzaei M (2008) Radiosynthesis of dimethyl-2-[18F]-(fluoromethyl)-6-methyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate for L-type calcium channel imaging. Radiochim Acta 96:849–853
Valette H, Dollé F, Guenther I, Fuseau C, Coulon C, Hinnen F, Péglion JL, Crouzel C (2002) In vivo quantification of myocardial dihydropyridine binding sites: a PET study in dogs. J Nucl Med 43(9):1227–1233
Ke AB, Eyal S, Chung FS, Link JM, Mankoff DA, Muzi M, Unadkat JD (2013) Modeling cyclosporine A inhibition of the distribution of a P-glycoprotein PET ligand, 11C-verapamil, into the maternal brain and fetal liver of the pregnant nonhuman primate: impact of tissue blood flow and site of inhibition. J Nucl Med 54(3):437–446
Sadeghpour H, Jalilian AR, Akhlaghi M, Kamali-dehghan M, Mirzaii M (2008) Preparation and biodistribution of [111In]-rHu Epo for erythropoietin receptor imaging. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:117–122
Hnatowich DJ, Layne WW (1983) Child RL radioactive labeling of antibody: a simple and efficient method. Science 220:613–619
McDaid DM, Deasy PB (1996) Formulation development of a transdermal drug delivery system for amlodipine base. Int J Pharm 133:271–283
Wang S, Luo J, Lantrip DA, Waters DJ, Mathias CJ, Green MA, Fuchs PL, Low PS (1997) Design and synthesis of [111In]DTPA-folate for use as a tumor-targeted radiopharmaceutical. Bioconjug Chem 8:673–679
Packard AB, Kronauge JF, Barbarics E, Kiani S, Treves ST (2002) Synthesis and biodistribution of a lipophilic Cu-64-labeled monocationic copper(II) complex. Nucl Med Biol 29:289–294
United States Pharmacopoeia 28 (2005) NF 23, p 1009
United States Pharmacopoeia 28 (2005) NF 23, p 1895
Chhabra G, Chuttani K, Mishra AK, Pathak K (2011) Design and development of nanoemulsion drug delivery system of amlodipine besilate for improvement of oral bioavailability. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 37(8):907–916
Beresford AP, McGibney D, Humphrey MJ, Macrae PV, Stopher DA (1988) Metabolism and kinetics of amlodipine in man. Xenobiotica 18(2):245–254
Firouzyar T, Jalilian AR, Fazaeli Y, Shafiee-Ardestani M, Aboudzadeh MR, Khalaj A (2014). Preparation and preliminary biological evaluation of radiogallium-labeled DTPA-amlodipine complex for possible L-type calcium channel imaging. Radiochim Acta. doi:10.1515/ract-2014-2260
Veeraveedu PT, Watanabe K, Ma M, Gurusamy N, Palaniyandi SS, Wen J, Prakash P, Wahed MI, Kamal FA, Mito S, Kunisaki M, Kodama M, Aizawa Y (2006) Comparative effects of pranidipine with amlodipine in rats with heart failure. Pharmacology 77(1):1–10
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank Ms F. Bolourinovin for chromatography experiments. This study has been funded and supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; Grant No. 18308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Firouzyar, T., Jalilian, A.R., Shafiee-Ardestani, M. et al. Development of an 111In-labeled dihydropyridine complex for L-type calcium channel imaging. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303, 2361–2369 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3656-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3656-2