Summary
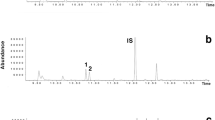
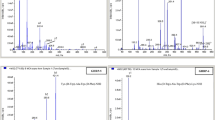
This paper describes an analytical method using a nuclear-related technique for the detection of forbidden doping substances in the urine of race horses. The proposed method, adapted from the Méthode Alcaline Sur C-18 developed by the French Laboratoire de Contrôle Antidopage, is based on gas chromatography separation followed by mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The method was validated for caffeine, identified as the most frequent doping substance in the Brazilian horseracing activity. This validation is also a major requirement to achieve ISO/IEC 17025 laboratory accreditation. The validation has led to several metrological challenges because the decisions are largely based on qualitative results (“false-positive” and/or “false-negative”) and the degree of accuracy, as well as the traceability had to be determined in the absence of certified matrix reference materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, I., Frota, M., Fernandes, E. et al. Assuring the reliability of mass spectrometry for the routine determination of traces of doping in horse-urine. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 269, 389–396 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-0397-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-006-0397-x