Summary
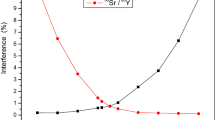
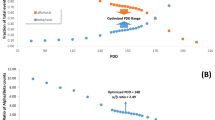
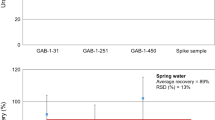
The standard procedure for analyzing gross alpha and gross beta in water is evaporation of the sample and radioactivity determination of the resultant solids by proportional counting. This technique lacks precision, and lacks sensitivity for samples with high total dissolved solids. Additionally, the analytical results are dependent on the choice of radionuclide calibration standard and the sample matrix. Direct analysis by liquid scintillation counting has the advantages of high counting efficiencies and minimal sample preparation time. However, due to the small sample aliquants used for analysis, long count times are necessary to reach required detection limits. The procedure proposed consists of evaporating a sample aliquant to dryness, dissolving the resultant solids in a small volume of dilute acid, followed by liquid scintillation counting to determine radioactivity. This procedure can handle sample aliquants containing up to 500 mg of dissolved solids. Various acids, scintillation cocktail mixtures, instrument discriminator settings, and regions of interest (ROI) were evaluated to determine optimum counting conditions. Precision is improved and matrix effects are reduced as compared to proportional counting. Tests indicate that this is a viable alternative to proportional counting for gross alpha and gross beta analyses of water samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perera, S. Gross alpha/beta analyses in water by liquid scintillation counting. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 264, 357–363 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0721-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0721-x