Summary
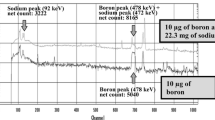
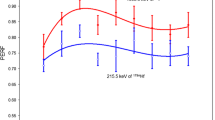
The thermal neutron prompt gamma-ray activation analysis (PGAA) facility, operated by the US Food and Drug Administration and National Institute of Standards and Technology Center for Neutron Research, has been redesigned to lower background radiation levels and improved analytical capabilities. Analysis of 22 element standards and food and botanical certified reference materials revealed significant sensitivity increases and lower limits of detection for H, B, C, N, Na, Al, P, S, Cl, K, Ca, Fe, and Cd. Mass fractions for these elements, as well as Mg, Al, Si, Ti, Mn, Fe, Cu, I, Zn, Sm, and Gd, were determined for 6 dietary supplements.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, D., Mackey, E. Improvements in food analysis by thermal neutron capture prompt gamma-ray spectrometry. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263, 683–689 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0643-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0643-7