Abstract
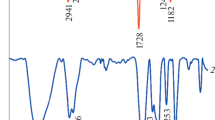
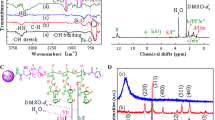
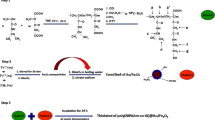
A novel pH-responsive Fe3O4/poly(2-succinyloxyethylmethacrylate-co-methylmethacrylate) (poly(SEMA-co-MMA)) nanocomposite was designed for anticancer drug delivery applications. For this propose, poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-methylmethacrylate) (poly(HEMA-co-MMA)) was synthesized via reversible addition-fragmentation transfer (RAFT) method. Then, poly(SEMA-co-MMA) was prepared by the esterification of poly(HEMA-co-MMA) copolymer through the reaction with an excess amount of succinic anhydride. The synthesized copolymers with acidic functional groups were adsorbed onto the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and Fe3O4/poly(SEMA-co-MMA) nanocomposite was developed. The pH-sensitivity of Fe3O4/poly(SEMA-co-MMA) nanocomposite was confirmed via dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements. The Doxorubicin (DOX) encapsulation efficiency was 92.6%. The release rates at pHs of 5.4 and 4 (37 °C) reached 55.7 and 62.4 wt%, respectively, and at pH = 7.4, it possessed a minimum amount around 38.3 wt% after 15 days. The synthesized nanocomposite may be find the drug delivery applications, in part thanks to their smart physicochemical properties.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhowmick A, Saha A, Pramanik N, Banerjee S, Das M, Kundu PP (2015) Novel magnetic antimicrobial nanocomposites forbone tissue engineering applications. RSC Adv 5:25437–25445
Massoumi B, Mousavi-Hamamlu SV, Ghamkhari A, Jaymand M (2017) A novel strategy for synthesis of polystyrene/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: RAFT polymerization, functionalization, and coordination techniques. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 56:873–882
Zhu L, Wang D, Wei X, Zhu X, Li J, Tu C, Su Y, Wu J, Zhu B, Yan D (2013) Multifunctional pH-sensitive superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanocomposites for targeted drug delivery and MR imaging. J Control Release 169:228–238
Wang W, Zhang Z (2007) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of carbohydrate microspheres coated with magnetic nanoparticles. J Dispers Sci Technol 28:557–561
Cheng R, Meng F, Deng C, Klok H-A, Zhong Z (2013) Dual and multi-stimuli responsive polymeric nanoparticles for programmedsite-specific drug delivery. Biomaterials 34:3647–3657
Hergt R, Dutz S, Muller R, Zeisberger M (2006) Magnetic particle hyperthermia: nanoparticle magnetism and materials development for cancertherapy. J Phys Condens Matter 18:S2919–S2934
Karumanchi RS, Doddamane SN, Sampangi C, Todd PW (2002) Field-assisted extraction of cells, particles and macromolecules. Trends Biotechnol 20:72–78
Jiang Y, Guo C, Xia H, Mahmood I, Liu C, Liu H (2009) Magnetic nanoparticles supported ionic liquids for lipase immobilization: Enzyme activity in catalyzing esterification. J Mol Catal B Enzym 58:103–109
Caoa J, Wanga Y, Yu J, Xiaa J, Zhanga C, Yina D, Hafeli UO (2004) Preparation and radiolabeling of surface-modifiedmagnetic nanoparticles with rhenium-188 formagnetic targeted radiotherapy. J Magn Magn Mater 277:165–174
Zhang X, Yang P, Dai Y, Ma P, Li X, Cheng Z, Hou Z, Kang X, Li C, Lin J (2013) Multifunctional up-converting nanocomposites with smart polymer brushes gated mesopores for cell imaging and thermo/pH dual-responsive drug controlled release. Adv Funct Mater 23:4067–4078
Oha JK, Park JM (2011) Iron oxide-based superparamagnetic polymeric nanomaterials: design, preparation, and biomedical application. Prog Polym Sci 36:168–189
Sivudu KS, Rhee KY (2009) Preparation and characterization of pH-responsive hydrogel magnetite nanocomposite. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 349:29–34
Lee JE, Lee DJ, Lee N, Kim B, Choi SH, Hyeon T (2011) Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanocomposite nanoparticles for pH controlled drug release and dual modal imaging. J Mater Chem 21:16869–16872
Poorgholy N, Massoumi B, Jaymand M (2017) A novel starch-based stimuli-responsive nanosystem for theranostic applications. Int J Biol Macromol 97:654–661
Pietsch C, Hoogenboom R, Schubert US (2010) PMMA based soluble polymeric temperature sensors based on UCST transition and solvatochromic dyes. Polym Chem 1:1005–1008
Chi W, Liu S, Yang J, Wang R, Ren H, Zhou H, Chenb J, Guo T (2014) Evaluation of the effects of amphiphilic oligomers in PEI based ternary complexes on the improvement of pDNA delivery. J Mater Chem B 2:5387–5396
Fran J, Lutz C (2006) Solution self-assembly of tailor-made macromolecular building blocks prepared by controlled radical polymerization techniques. Polym Int 55:979–993
Delaittre G, Save M, Gaborieau M, Castignolles P, Rieger J, Charleux B (2012) Synthesis by nitroxide-mediated aqueous dispersion polymerization, characterization, and physical core-crosslinking of pH- and thermoresponsive dynamic diblock copolymer micelles. Polym Chem 3:1526–1538
Beers KL, Boo S, Gaynor SG, Matyjaszewski K (1999) Atom transfer radical polymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate. Macromolecules 32:5772–5776
Ahmed M, Narain R (2013) Progress of RAFT based polymers in gene delivery. Prog Polym Sci 38:767–790
Davaran S, Ghamkhari A, Alizadeh E, Massoumi B, Jaymand M (2017) Novel dual stimuli-responsive ABC triblock copolymer: RAFT synthesis, Schizophrenic” micellization and its performance as an anticancer drug delivery nanosystem J Colloid Interface Sci 488:282–293
Yang C, Guo W, Cui L, An N, Zhang T, Lin H, Qu F (2014) pH-Responsive magnetic core-shell nanocomposites for drug delivery. Langmuir 30:9819–9827
Bastakoti BP, Guragain S, Nakashima K, Yamauchi Y (2015) Stimuli-induced core–corona inversion of micelle of poly(acrylic acid)-block-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and its application in drug delivery. Macromol Chem Phys 216:287–291
Huang G, Zhang K-L, Chen S, Li S-H, Wang L-L, Wang L-P, Liu R, Gao J, Yang H-H (2017) Manganese-iron layered double hydroxide: a theranosticnanoplatform with pH-responsive MRI contrast enhancement and drug release. J Mater Chem B 5:3629–3633
Ghamkhari A, Massoumi B, Jaymand M (2017) Novel ‘schizophrenic’ diblock copolymer synthesized via RAFT polymerization: Poly(2-succinyloxyethyl methacrylate)-b-poly[(N-4-vinylbenzyl),N,N-diethylamine]. Des Monomers Polym 20:190–200
Ma WF, Wu KY, Tang J, Li D, Wei C, Guo J, Wang SL, Wang CC (2012) Magnetic drug carrier with a smart pH-responsive polymer network shell for controlled delivery of doxorubicin. J Mater Chem 22:15206–15214
Li PY, Lai PS, Hung WC, Syu WJ (2010) Poly(L-lactide)-vitamin E TPGS nanoparticles enhanced the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin in drug-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 11:2576–2582
Massoumi B, Ghamkhari A, Agbolaghi S (2017) Dual stimuli-responsive poly(succinyloxyethylmethacrylate-b-N-Isopropylacrylamide) block copolymers as nano-carriers and respective application in Doxorubicin delivery. Int J Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2017.1300901
Salehi R, Rasouli S, Hamishehkar H (2015) Smart thermo/pH responsive magnetic nanogels for the simultaneous delivery of doxorubicin and methotrexate. Int J Pharm 487:274–284
Bol’bukha YN, Tertykha VA, Yurkovb GY, Ovchenkov EA (2011) Synthesis and properties of nanocomposites based on magnetite and biocompatible polymers. Russ J Appl Chem 84:847–853
Rahimi M, Shojaei S, Safa KD, Ghasemi Z, Salehi R, Yousefi B, Shafiei-Irannejad V (2017) Biocompatible magnetic tris(2-aminoethyl)amine functionalized nanocrystalline cellulose as a novel nanocarrier for anticancer drug delivery of methotrexate. New J Chem 41:2160–2168
Massoumi B, Poorgholy N, Jaymand M (2017) Multi-stimuli responsive polymeric nanosystems for theranostic applications. Int J Polym Mater 66:38–47
Shivakumar HG, Fathima SJ, Radha V, Khanum F (2016) pH and thermosensitive 5-fluorouracil loaded poly (NIPAM-co-AAc) nanogels for cancer therapy. RSC Adv 6:105495–105507
Bawa P, Pillay V, Choonara YE, du Toit LC (2009) Stimuli-responsive polymers and theirapplications in drug delivery. Biomed Mater 4:022001
Cheng R, Wang X, Chen W, Meng F, Deng C, Liuband H, Zhong Z (2012) Biodegradable poly(3-caprolactone)-g-poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)graft copolymer micelles as superior nano-carriers for “smart” doxorubicinrelease. J Mater Chem 22:11730–11738
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the Payame Noor University for supporting this project.
Funding
This study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghamkhari, A., Agbolaghi, S., Poorgholy, N. et al. pH-responsive magnetic nanocomposites based on poly(2-succinyloxyethyl methacrylate-co-methylmethacrylate) for anticancer doxorubicin delivery applications. J Polym Res 25, 37 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1431-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1431-0