Abstract
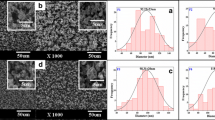
Electrospun fibers can be promising drug carriers for future biomedical applications. In this work, electrospun PLA fibers were developed as a new system for the delivery of ketoprofen which is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. For effective control of drug release, porous PLA fiber was prepared by phase separation during electrospinning. The release of various contents of ketoprofen from the electrospun PLA fiber was investigated at body temperature (37 °C) and at room temperature (20 °C). The release rates of the ketoprofen drug from the PLA/ketoprofen fibers showed a relatively higher release rate at 37 °C than at 20 °C. As the ketoprofen content increased, the release effect (cumulative drug released) increased. Thermal characteristic of PLA/ketoprofen fiber was also analyzed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kenawy E-R, Bowlin GL, Mansfield K et al (2009) Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J Control Release 81:57–64
Zong X, Kim K, Fang D et al (2002) Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 43:4403–4412
Zeng J, Xu X, Chen X et al (2003) Biodegradable electrospun fibers for drug deliver. J Control Release 92:227–231
Jiang H, Fang D, Hsiao BS et al (2004) Optimization and characterization of dextran membranes prepared by electrospinning. Biomacromolecules 5:326–333
Kenawy E-R, Abdely FI, El-Newehy MH et al (2007) Controlled release of ketoprofen from electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Mater Sci Eng, A 459:390–396
Giammona G, Carlisi B, Pitarrei G et al (1991) Hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymeric derivatives of anti-inflammatory agents such as alclofenac, ketoprofen, and ibuprofen. J Bioact Compat Polym 6:129–141
Langer R (1993) Polymer-controlled drug delivery systems. Acc Chem Res 26:537–542
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo WE et al (2005) An Introduction electrospinning and nanofibers. Word Scientific publishing Company, Singapore
Megelski S, Stephens JS, Chase DB et al (2002) Micro- and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules 35:8456–8465
Gibson P, Gibson HS, Rivin D (2001) Transport properties of porous membranes based on electrospun nanofibers. Colloids Surf A 187:469–481
McCann JT, Marquez M, Xia YJ (2006) Highly porous fibers by electrospinning into a cryogenic liquid. J Am Chem Soc 128:1436–1437
Fong H, Chun I, Reneker DH (1999) Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 40:4585–4592
Taepaiboon P, Rungsardthon U, Supaphol P (2006) Drug-loaded electrospun mate of poly(vinyl alcohol) fiberes and their release characteristics of four model drugs. Nanotechnology 17:2317–2329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JY., Lee, IH. Controlled release of ketoprofen from electrospun porous polylactic acid (PLA) nanofibers. J Polym Res 18, 1287–1291 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-010-9531-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-010-9531-0