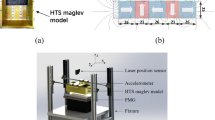
Abstract
The high-temperature superconducting (HTS) maglev system is characterized with self-stable levitation, low energy consumption, and pollution-free operation, and it has been considered as a promising technology for implementing high-speed transport systems. But the previous studies have shown that the damping of such system is relatively low, which indicates the large-amplitude nonlinear vibration may occur easily under external disturbances and affect the long-term motion stability, operation safety, and comfort of HTS maglev in rail transit application. In order to suppress the harmful vibration, an electromagnetic shunt damper (EMSD) was designed and incorporated into the HTS maglev system. Compared with other systems which employ the EMSD to diminish the vibration, the HTS maglev system does not need to set up external devices to supply magnetic field for the damper, because the permanent magnet guideway (PMG) in this system is directly taken advantages of. The natural frequency of the damper is adjusted to a value close to that of the maglev system. In this way, the damper becomes most effective because the moving vehicle body and the circuit resonate simultaneously. The feasibility of the damper was demonstrated through systematic experiments, and the effects of different field cooling heights (FCHs) of the HTS maglev system on EMSD’s performance were experimentally studied as well. Also, how the change of resistors in the EMSD circuit affects its working efficiency was preliminarily explored in this work. The results show that under the definite external disturbance, the damper can effectively attenuate the acceleration of vibration, furthermore, and it is found that the damper works better in condition of lower FCH. Within the scope of our experiments, the EMSD with a resistor in lower resistance performs better as results have shown. This investigation indicates that the vehicle will run in a more smooth and comfortable way along the track with this damper. The work is important for the further practical application of the technology.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hull, J.R.: Superconducting bearings. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 13(2), R1–R15 (2000)
Werfel, F.N., Floegel-Delor, U., Rothfeld, R., Goebel, B., Wippich, D., Schirrmeister, P.: Superconductor bearings, flywheels and transportation. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 25(1), 014007 (2012)
Wang, J.S., Wang, S.Y., Zeng, Y.W., Huang, H.Y., Luo, F., Xu, Z.P., Tang, Q.X., Lin, G.B., Zhang, C.F., Ren, Z.Y., Zhao, G.M., Zhu, D.G., Wang, S.H., Jiang, H., Zhu, M., Deng, C.Y., Hu, P.F., Li, C.Y., Liu, F., Lian, J.S., Wang, X.R., Wang, L.H., Shen, X.M., Dong, X.G.: The first man-loading high temperature superconducting maglev test vehicle in the world. Physica C. 378-381, 809–814 (2002)
Deng, Z.G., Zhang, W.H., Zheng, J., Ren, Y., Jiang, D.H., Zheng, X.X., Zhang, J.H., Gao, P.F., Lin, Q.X., Song, B., Deng, C.Y.: A high-temperature superconducting maglev ring test line developed in Chengdu, China. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 26(6), 3602408 (2016)
Deng, Z.G., Zhang, W.H., Zheng, J., Wang, B., Ren, Y., Zheng, X.X., Zhang, J.H.: A high-temperature superconducting maglev-evacuated tube transport (HTS maglev-ETT) test system. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 27(6), 3602008 (2017)
Schultz, L., de Haas, O., Verges, P., Beyer, C., Rohlig, S., Olsen, H., Kuhn, L., Berger, D., Noteboom, U., Funk, U.: Superconductively levitated transport system—the SupraTrans project. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 15(2), 2301–2305 (2005)
Sotelo, G.G., de Oliveira, R., Costa, F., Dias, D., de Andrade Jr., R., Stephan, R.: A full scale superconducting magnetic levitation (MagLev) vehicle operational line. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 25(3), 3601005 (2015)
Kovalev, K.L., Koneev, S.M.-A., Poltavec, V.N., Gawalek, W.: Magnetically levitated high-speed carriages on the basis of bulk HTS elements, in Proc. 8th Int. Symp. Magn. Suspension Technol., Dresden, Germany (2005) p. 51.
D’Ovidio, G., Crisi, F., Lanzara, G.: A V shaped superconducting levitation module for lift and guidance of a magnetic transportation system. Physica C. 468(14), 1036–1040 (2008)
Stephan, R.M., de Andrade, R., dos Santos, G.C., Neves, M.A., Nicolsky, R.: Levitation force and stability of superconducting linear bearings using NdFeB and ferrite magnets. Physica C. 386, 490–494 (2003)
Yang, W.J., Liu, Y., Wen, Z., Chen, X.D., Duan, Y.: Hysteresis force loss and damping properties in a practical magnet-superconductor maglev test vehicle. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 21(1), 015014 (2008)
Arai, Y., Seino, H., Nagashima, K.: Levitation properties of superconducting magnetic bearings using superconducting coils and bulk superconductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 23(11), 115011 (2010)
Teshima, H., Tanaka, M., Miyamoto, K., Nohguchi, K., Hinata, K.: Effect of eddy current dampers on the vibrational properties in superconducting levitation using melt processed YBaCuO bulk superconductors. Physica C. 274(1–2), 17–23 (1997)
Teshima, H.: Combination of additional noncontact dampers and superconducting levitation using melt-processed YBaCuO bulk superconductors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36(1A), 68–75 (1997)
Zheng, J., Deng, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Wang, S.Y., Wang, J.S.: Performance improvement of high temperature superconducting maglev system by eddy current damper. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 19(3), 2148–2151 (2009)
Jiang, Z.F., Gou, X.F.: Eddy damping effect of additional conductors in superconducting levitation systems. Physica C. 519, 112–117 (2015)
Behrens, S., Fleming, A.J., Moheimani, S.O.R.: Passive vibration control via electromagnetic shunt damping. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 10(1), 118–122 (2005)
Pei, Y.L., Liu, Y.L., Zuo, L.: Multi-resonant electromagnetic shunt in base isolation for vibration damping and energy harvesting. J. Sound Vibr. 423, 1–17 (2018)
Sun, H.X., Luo, Y.F., Wang, X.Y., Zuo, L.: Seismic control of a SDOF structure through electromagnetic resonant shunt tuned mass-damper-inerter and the exact H-2 optimal solutions. J. Vibroeng. 19(3), 2063–2079 (2017)
Stabile, A., Aglietti, G.S., Richardson, G., Smet, G.: A 2-collinear-DoF strut with embedded negative-resistance electromagnetic shunt dampers for spacecraft micro-vibration. Smart Mater. Struct. 26(4), 045031 (2017)
Jung, J.H., Cheng, T.H., Oh, I.K.: Electromagnetic synchronized switch damping for vibration control of flexible beams. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 13(6), 1031–1038 (2012)
Cheng, T.H., Oh, I.K.: Vibration suppression of flexible beam using electromagnetic shunt damper. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 45(6), 2758–2761 (2009)
Sasaki, M., Sugiura, T.: Vibration reduction of rotor supported by superconducting magnetic bearing utilizing electromagnetic shunt damper. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 26(3), 8801204 (2016)
Sasaki, M., Sugiura, T.: Effect of parameters of an electromagnetic shunt damper on whirling amplitude reduction of a rotor supported by a superconducting magnetic bearing. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 27(4), 3601005 (2017)
Sasaki, M., Kimura, J., Sugiura, T.: Vibration suppression in high-T-c superconducting levitation system utilizing nonlinearly coupled electromagnetic shunt damper. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond., Vol. 25(3), 3700605 (2015)
Inoue, T., Ishida, Y., Sumi, M.: Vibration suppression using electromagnetic resonant shunt damper. J. Vibration Acoust. 130(4), 041003 (2008)
Deng, Z.G., Li, J.P., Zhang, W.H., Gou, Y.F., Ren, Y., Zheng, J.: High-temperature superconducting magnetic levitation vehicle: dynamic characteristics while running on a ring test line. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 12(3), 95–102 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Science and Technology Partnership Program, Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51875485), the Sichuan Youth Science and Technology Fund (2016JQ0039), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2682018CX72), and the State Key Laboratory of Traction Power at Southwest Jiaotong University (2018TPL_T06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Deng, Z., Li, H. et al. Vibration Suppression of High-Temperature Superconducting Maglev System via Electromagnetic Shunt Damper. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 2819–2828 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-5050-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-5050-3