Abstract
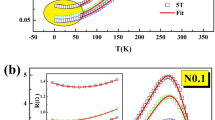
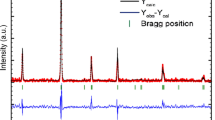
Structural, magnetic, magnetocaloric, electrical properties, and spin-polarized tunneling effect in La0.5Ca0.3Te0.2MnO3 polycrystalline were studied in details. The temperature dependence of the inverse of the magnetic susceptibility indicates the presence of ferromagnetic exchange interaction between the nearest neighbors at the Weiss temperature θp = 265.32 ± 0.109. Based on the magnetic field dependence of magnetization, M(H), and employing the thermodynamic Maxwell equation, the magnetic entropy change |ΔSM| of the studied sample was determined. The maximum entropy change value of the system was around 4.99 J kg−1 K−1 under a magnetic field of 5 T. Electrically, the upturned region of resistivity was observed at low temperature. The recovery of the resistivity was found to be strongly affected by the external magnetic field. The electrical data were analyzed considering various models. Interestingly, the exception of the spin-polarized tunneling (SPT) model is in good agreement with the experimental data among other models. In the current work, the SPT is the dominant mechanism leading to the rise of resistivity, while decreasing the temperature values. Magnetotransport analysis was successfully carried out using percolation model in the temperature range between around 50 K to nearly 300 K under different magnetic fields up to 8 T. The isothermal field dependence of magnetoresistance was recorded fairly well via a phenomenological model based on the spin-polarized tunneling model.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doshi, R.R., Solanki, P.S., Khachar, U., Kuberkar, D.G., Krishna, P.S.R., Banerjee, A., Chaddah, P.: J Phys. B. 406, 4031 (2011)
Dhiman, I., Das, A., Mishra, P.K., Lalla, N.P., Kumar, A.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 748 (2011)
Zener, C.: J. Phys. Rev. 82(3), 403 (1951)
Bourouina, M., Krichene, A., Chniba Boudjada, N., Khitouni, M., Boujelben, W.: J. Ceram. Int. 03, 138 (2017)
Mandal, P., Das, S.: J. Phys. Rev. B. 56(23), 15073 (1997)
Smari, M., Walha, I., Dhahri, E., Hlil, E.K.: J. Alloys Compd. 579, 564 (2013)
Smari, M., Walha, I., Dhahri, E., Hlil, E.K.: Chem. Phys. Lett. 607, 25 (2014)
Smari, M., Hamouda, R., Walha, I., Dhahri, E., Mompean, F., Hernández, M.G.: J. Alloys Compd. 05, 026 (2015)
Smari, M., Hamdi, R., Dhahri, E., Hlil, E.K., Bessais, L.: J. Ceram. Int. 03, 182 (2016)
Smari, M., Felhi, H., Hamdi, R., Nouri, K., Dhahri, E., Bessais, L.: J. Chem. Phys. Lett. 684, 72 (2017)
Felhi, H., Smari, M., Walha, I., Dhahri, E., Valente, M.A., Bessais, L.: J. Chem. Phys. Lett. 691, 262 (2018)
Ehsani, M.H., Kameli, P., Razavi, F.S., Ghazi, M.E., Aslibeiki, B.: J. Alloys Compd. 579, 406 (2013)
Munirathinam, B., Krishnaiah, M., Devarajan, U., EsakkiMuthu, S., Arumugam, S.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 73, 925 (2012)
Collado, J.A., Frontera, C., Garcıa-Munoz, J.L., Aranda, M.A.G.: J. Solid State Chem. 178, 1949 (2005)
Taguchi, H., Matsuda, D., Nagano, M., Tanihata, K., Miyamoto, Y.: J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 201 (1992)
Sanchez, R.D., Rivas, J., Vazquez-Vazquez, C., Lopez-Quintela, A., Causa, M.T., Tovar, M., Oseroff, S.: J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 134 (1996)
Browning, V.M., Stroud, R.M., Fuller-Mora, W.W., Byers, J.M., Osofsky, M.S., Knies, D.L., Grabowski, K.S., Koller, D., Kim, J., Chrisey, D.B., Horwitz, J.S.: J. Appl. Phys. 83, 7070 (1998)
Ming, Y., Hong-Guo, Z., Dan-Min, L., Jiu-Xing, Z.: Chin. Phys. B. 24, 17505 (2015)
Jin, S., Tiefel, T.H., McCormack, M., Fastnacht, R.A., Ramesh, R., Chen, L.H.: Science. 264, 413 (1994)
Von Helmolt, R., Wecker, J., Holzapfel, B., Schultz, L., Samwer, K.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 2331 (1993)
Moreo, A., Yunoki, S., Dagotto, E.: Science. 283, 2034 (1999)
Salamon, M.B., Jaime, M.: J. Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 583 (2001)
Fäth, M., Freisem, S., Menovsky, A.A., Tomioka, Y., Aarts, J., Mydosh, J.A.: Science. 285, 1540 (1999)
de Andres, A., et al.: Phys. Rev. B. 60, 7328 (1999)
Zhang, S., Yang, Z.: J. Appl. Phys. 79, 7398 (1996)
Coey, J.M.D., Viret, M., Ranno, L., Ounadjela, K.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3910 (1995)
Ju, H.L., Gopalakrishnan, J., Peng, J.L., Li, Q., Xiong, G.C., Venkatesan, T., Greene, R.L.: Phys. Rev. B. 51, 6143 (1995)
Li, X.W., Gupta, A., Xiao, G., Gong, G.Q.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 1124 (1997)
Hwang, H.Y., Cheong, S.W., Ong, N.P., Batlogg, B.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2041 (1996)
Pecharsky, V.K., Gschneidner, K.A.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200, 44 (1999)
Wang, Z.M., Ni, G., Xu, Q.Y., Sang, H., Du, Y.W.: J. Appl. Phys. 90(11), 5689–5691 (2001)
Foldeaki, M., Chahine, R., Bose, T.K.: J. Appl. Phys. 77(7), 3528 (1995)
Amaral, J.S., Reis, M.S., Amaral, V.S., Mendonca, T.M., Araujo, J.P., Sa, M.A., Tavares, P.B., Vieira, J.M.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 290, 686 (2005)
Inoue, J., Shimizu, M.: J. Phys. Lett. A. 90, 85 (1982)
Amaral, V.S., Amaral, J.S.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272–276, 2104 (2004)
Anwar, M.S., Kumar, S., Ahmed, F., Arshi, N., Kim, G.W., Koo, B.H.: J. Korean Phys. Soc. 60, 1587 (2012)
Jaime, M., Lin, P., Salamon, M.B., Han, P.D.: Phys. Rev. B. 58, R5901 (1998)
Zhao, G., Smolyaninova, V., Prellier, W., Keller, H.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 6086 (2000)
Jeffrey Snyder, G., Hikes, R., DiCarolis, S., Beasley, M.R., Geballe, T.H.: J. Phys. Rev. B. 53, 14434 (1996)
Kubo, K., Ohata, N.A.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 33, 21 (1972)
Goodenough, J.B., Zhou, J.S.: Nature. 386, 229 (1997)
Das, S., Dey, T.K.: Solid State Commun. 134, 837 (2005)
Das, S., Dey, T.K.: J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 294, 338 (2005)
Rozenberg, E., Auslender, M., Felner, I., Gorodetsky, G.: J. Appl. Phys. 88, 2578 (2000)
Mukhopadhyay, S., Das, I.: Euro. J. Phys. Lett. 79, 67002 (2007)
Garcia-Hermandez, M., Guinea, F., de Andres, A., Martinez, J.L., Prieto, C., Vazquez, L.: J. Phys. Rev. B. 61, 9549 (2000)
Helman, J.S., Abeles, B.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 37, 1429 (1976)
Auslender, M.I., Rozenberg, E., Karlin, A.E., Chaudhuri, B.K., Gorodetsky, G.: J. Alloys Compd. 326, 81 (2001)
Ciftja, O., Luban, M., Auslender, M., Luscombe, J.H.: Equation of state and spin-correlation functions of ultrasmall classical Heisenberg magnets. Phys. Rev. B. 60, 10122–10133 (1999)
Li, G., Zhou, H.D., Feng, S.L., Fan, X.J., Li, X.G.: J. Appl. Phys. 92, 1406 (2002)
Raychaudhuri, P., Nath, T.K., Nigam, A.K., Pinto, R.: J. Appl. Phys. 84, 2048 (1998)
Das, K., Satpati, B., Das, I.: RSC Adv. 5, 27338 (2015)
Raychaudhuri, P., Sheshadri, K., Taneja, P., Bandyopadhyay, S., Ayyub, P., Nigam, A.K., Pinto, R.: J. Phys. Rev. B. 59, 13919 (1999)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research and the Moroccan, Algerian and French Ministries of Higher Education and Research of PHC Morocco 15MAG07 collaboration, within the framework of Franco-Moroccan collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
In the present study, the polycrystalline La0.5Ca0.3Te0.2MnO3 was prepared by sol-gel method. The maximum of the magnetic entropy change (\( -\triangle {S}_M^{\mathrm{max}} \)) was calculated using the isothermal magnetization curves M (H) under magnetic field change of 5 T and is found to be 4.99 J kg−1 K−1 for our sample. The electrical data were analyzed considering various models. It is noteworthy that the exception of the spin-polarized tunneling (SPT) model is in good agreement with the experimental data among other models. In the current work, the SPT is the dominant mechanism leading to the rise of resistivity while decreasing the temperature values. The isothermal field dependence of magnetoresistance was recorded honestly well via a phenomenological model based on the spin-polarized tunneling model.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felhi, H., Smari, M., Hamdi, R. et al. Investigation of the Structural, Magnetic, Magnetocaloric, Electrical Properties, and Spin-Polarized Tunneling Effect of the La0.5Ca0.3Te0.2MnO3 System. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 463–473 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4906-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4906-2