Abstract
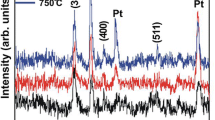
A comparative study between cobalt ferrite films deposited by pulsed laser deposition as a function of the laser sources, 355 nm (Nd:YAG) and 248 nm (KrF excimer), on amorphous quartz (AQ) and < 100 > -oriented silicon wafer (SW) at different temperatures (650–800 ∘C) is presented. Also, a quantitative estimation of the preferential crystalline growth orientation as laser source function was made by means of Lotgering factor and Harris texture coefficient, which were obtained from XRD patterns. The inversion degree in spinel-type structure for cobalt ferrite films was calculated through a deconvolution in Raman spectra, where the band A1g vibrating modes in tetrahedral sites were associated with Fe and Co sites (687 and 611 cm−1, respectively). Additionally, saturation magnetization was also calculated from the inversion degree obtained from deconvolution of the Raman spectra in CoFe2O4 films, being compared with experimental results, which is in a good agreement with cobalt ferrite bulk, and we also correlated the preferential growth and the particle size with increment of the coercive field.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to magnetic materials. Cullity. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(09)70091-4 (2009)
Khaja Mohaideen, K., Joy, P.A.: High magnetostriction and coupling coefficient for sintered cobalt ferrite derived from superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4745922 (2012)
Caltun, O.F., Rao, G.S.N., Rao, K.H., Rao, B.P., Kim, C., Kim, C. -O., Dumitru, I., Lupu, N., Chiriac, H.: High magnetostrictive cobalt ferrite for sensor applications. Sens. Lett. 5, 45–47 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1166/sl.2007.027
Suzuki, Y., Hu, G., van Dover, R.B.B., Cava, R.J.J.: Magnetic anisotropy of epitaxial cobalt ferrite thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 191, 1–8 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00364-3
Ramos, A.V., Guittet, M.J., Moussy, J.B., Mattana, R., Deranlot, C., Petroff, F., Gatel, C.: Room temperature spin filtering in epitaxial cobalt-ferrite tunnel barriers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2787880 (2007)
Nlebedim, I.C., Jiles, D.C.: Suitability of cation substituted cobalt ferrite materials for magnetoelastic sensor applications. Smart Mater Struct. 24. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/24/2/025006 (2015)
Giri, A.K., Kirkpatrick, E.M., Moongkhamklang, P., Majetich, S.A., Harris, V.G.: Photomagnetism and structure in cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 2341–2343 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1464661
Stichauer, L., Gavoille, G., Simsa, Z.: Optical and magneto-optical properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite films. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 3645–3650 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.361192
Scott, B.L., Radu, C., Smith, D.A., Stokes, K.L.: Magneto-optical study of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. In: Tms 2008 annual meeting supplemental proceedings, vol 3 Gen. Pap. Sel., pp 399–404 (2008)
Raghunathan, A., Nlebedim, I.C., Jiles, D.C., Snyder, J.E.: Growth of crystalline cobalt ferrite thin films at lower temperatures using pulsed-laser deposition technique. J. Appl. Phys. 107. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3357315(2010)
Zheng, H.: Multiferroic BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 nanostructures. Science (80). 303, 661–663 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094207
Ferreira, T.A.S., Waerenborgh, J.C., Mendonça, M.H.R.M., Nunes, M.R., Costa, F.M.: Structural and morphological characterization of FeCo2O4 and CoFe2O4 spinels prepared by a coprecipitation method. Solid State Sci. 5, 383–392 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1293-2558(03)00011-6
Na, J.G., Lee, T.D., Park, S.J.: Effects of cation distribution on magnetic properties in cobalt ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 12, 961–962 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00455632
Haneda, K., Morrish, A.H.: Noncollinear magnetic structure of CoFe2O4 small particles. J. Appl. Phys. 63, 4258–4260 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.340197
Sawatzky, G.A., Van Der Woude, F., Morrish, A.H.: Mössbauer study of several ferrimagnetic spinels. Phys. Rev. 187, 747–757 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.187.747
Sawatzky, G.A., Van Der Woude, F., Morrish, A.H.: Cation distributions in octahedral and tetrahedral sites of the ferrimagnetic spinel CoFe2O4. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 1204–1205 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1656224
Hassan, R.S., Viart, N., Ulhaq-Bouillet, C., Loison, J.L., Versini, G., Vola, J.P., Crégut, O., Pourroy, G., Muller, D., Chateigner, D.: Structural properties of cobalt ferrite thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition: effect of the reactive atmosphere. Thin Solid Films 515, 2943–2948 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2006.08.033
Madhav Kumar, V., Srinivas, A., Talapatra, A., Asthana, S., Mohanty, J., Kamat, S.: Effect of deposition temperature on structural microstructural and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition (2016)
Shirsath, S.E., Liu, X., Yasukawa, Y., Li, S., Morisako, A.: Switching of magnetic easy-axis using crystal orientation for large perpendicular coercivity in CoFe2O4 thin film. Sci. Rep. 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30074(2016)
Ning, M., Li, J., Ong, C.K., Wang, S.J.: High perpendicular coercive field of (100)-oriented CoFe2O4 thin films on Si (100) with MgO buffer layer. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 13911 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2828040
Lotgering, F.K.: Topotactical reactions with ferrimagnetic oxides having hexagonal crystal structures-I. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 9, 113–123 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1902(59)80070-1
Furushima, R., Tanaka, S., Kato, Z., Uematsu, K.: Orientation distribution–Lotgering factor relationship in a polycrystalline material—as an example of bismuth titanate prepared by a magnetic field. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 118, 921–926 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj2.118.921
Pham-Thi, M., Hemery, H., Dammak, H.: X ray investigation of high oriented (1 - x)PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3–(x)PbTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25, 2433–2435 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2005.03.077
Harris, G.B.: X. Quantitative measurement of preferred orientation in rolled uranium bars, London, Edinburgh, Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 43, 113–123 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440108520972
Thompson, C.V., Carel, R.: Grain growth and texture evolution in thin films. Mater. Sci. Forum 204–206, 83–98 (1996)
Sagar, E.S., Liu, X., Yusakawa, Y., Li, S., Morisako, A.: Sci. Rep. 1–9.https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30074 (2016)
Thompson, C.V., Carel, R.: J. Mech. Phys. Solids 44(5), 657–673 (1996)
Terzzoli, M.C., Duhalde, S., Jacobo, S., Steren, L., Moina, C.: High perpendicular coercive field of CoFe2O4 thin films deposited by PLD. J. Alloys Compd. 209–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2003.09.086 (2004)
Mishra, R.K., Thomas, G.: Surface energy of spinel. J. Appl. Phys. 48, 4576–4580 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.323486
Schnittger, S., Jooss, C., Sievers, S.: Magnetic and structural properties of cobalt ferrite thin films and structures. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/200/7/072086 (2010)
Delmdahl, R., Pätzel, R.: Pulsed laser deposition with excimer lasers. Phys. Stat. Sol (c) 5(10), 3276–3279 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssc.200779515
Milutinović, A., Lazarević, Z., Jovalekić, .̌ C. , Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I., Romčević, M., Kostić, S., Romčević, N.: The cation inversion and magnetization in nanopowder zinc ferrite obtained by soft mechanochemical processing. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 4759–4768 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.08.020
Shebanova, O.N., Lazor, P.: Raman study of magnetite (Fe3O4): laser-induced thermal effects and oxidation. J. Raman Spectrosc. 34, 845–852 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.1056
Ahlawat, A., Sathe, V.G.: Raman study of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles, bulk and films: effect of laser power. J. Raman Spectrosc. 42, 1087–1094 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2791
Chandramohan, P., Srinivasan, M.P., Velmurugan, S., Narasimhan, S.V., distribution, Cation: particle size effect on Raman spectrum of CoFe2O4. J. Solid State Chem. 184, 89–96 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2010.10.019
Nakagomi, F., da Silva, S.W., Garg, V.K., Oliveira, A.C., Morais, P.C., Franco, A.: Influence of the Mg-content on the cation distribution in cubic MgxFe3-xO4 nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 182, 2423–2429 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2009.06.036
Skomski, R.: Nanomagnetics. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 15, R841 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/15/20/202
Rana, K., Thakur, P., Sharma, P., Tomar, M., Gupta, V., Thakur, A.: Improved structural and magnetic properties of cobalt nanoferrites: influence of sintering temperature. Ceram. Int. 41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.11.143 (2015)
Gorter, E.W.: Magnetization in ferrites: saturation magnetization of ferrites with spinel structure. Nature 165, 798–800 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1038/165798a0
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the LUCE for the Raman measurements, and Carlos Flores Morales (IIM-UNAM) and Adriana Tejeda Cruz (IIM-UNAM) for the AFM and GIXRD measurements, respectively. We like to thank C. Sanchez-Aké for providing the PLD system and R. Sato for the discussion. Finally, E. López-Moreno thanks the CONACyT, Mexico, for the scholar grant no. 255468.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the DGAPA-UNAM, through the PAPIIT grant no. IG100517.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Moreno, E., Montiel, H., Conde, A. et al. Laser Source Influence on the Preferential Growth and the Inversion Degree in Pulsed Laser CoFe2O4 Films. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 599–607 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4740-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4740-6