Abstract
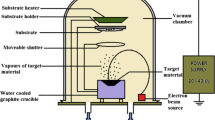
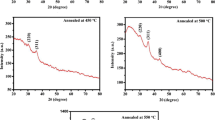
This paper is dedicated to deposit zinc substituted cobalt ferrite (Co0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4) thin films on glass substrate using electron beam deposition technique. The effect of post annealing temperature on structural, magnetic, and optical properties of thin films has been investigated. Thin films have been characterized using x-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), UV-VIS spectroscopy, and spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) analysis. The as-deposited thin films are amorphous in nature. After deposition, these thin films post annealed at different temperature ranges from 200 to 500 ∘C to enhance the crystallinity of films. The film post annealed at 200 ∘C is also amorphous in nature. As the post annealing temperature increases, the thin films become more crystalline. X-ray diffractometer and Raman analysis confirm the formation of cubical inverse spinel structure of thin films. The saturation magnetization of the thin films decreases with the annealing temperature due to the sites occupancy of cations between tetrahedral and octahedral. The reduction in coercivity is correlated with the anisotropy constant, but the anisotropy value is still high which is suitable to form stable magnetic storage memories. The band gap energy are decreased which is mainly attributed due to increase in grain size of the film. It is noted that the band gap energy of these thin films are higher than that of bulk material, so these may be suggested for use in wide band gap applications.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bragg, W. H.: Nature 95, 561 (1915)
Spaldin, N.A.: Magnetic materials: fundamentals and device applications, p. 119. Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom, (2003)
Jiles, D.C.: Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Chapman and Hall, USA 2nd edn, p. 89 (1998)
Cullity, B.D.: Introduction to Magnetic Materials, Wiley-IEEE Press, USA 2nd edn, p. 45 (2011)
Spaldin, N.A.: Magnetic Materials Fundamentals and Applications, Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom 2nd edn, p. 14 (2011)
Goldman, A.: Modern Ferrite Technology, Springer-Verlag New York Inc., United States 2nd edn, p 51 (2006)
Raj, K., Moskowitz, R., Casciari, R.: Advances in ferrofluid technology. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 149, 174–180 (1995)
Shahbaz Tehrani, F.: Structural, magnetic and optical properties of zinc and copper substituted nickel ferrite nanocrystals. Mater. Sci. 1–16 (2012)
Mathew, D.S.: An overview of structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. J. Chem. Eng. 129(3), 51–65 (2002)
Neelakanta, P.S.: Handbook of Electromagnetic Materials, CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 335 (1995)
Mathew, D.S.: An overview of structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsion. J. Chem. Eng. 129, 51–65 (2007)
Valenzuela, R.: Magneticceramics, pp 191–212. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1984)
Koseoglu, Y.: Effect of chromium addition on the structural, morphological and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline CoFe2O4 system. Ceram. Int. 38, 6671–6676 (2012)
Ding, J.: Magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed CoFe2O4. Solid State Commun. 95, 31–33 (1995)
Singhal, S.: Cation distribution and magnetic properties in Cr-substituted nickel ferrites prepared using aerosol route. J. Solid State Chem. 180, 296–300 (2007)
Sankpal, A.M.: Magnetization studies on aluminium and chromium substituted Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 186, 349 (1998)
Martin, P.M.: Handbook of Deposition Technologies for Films and Coatings, William Andrew Publishing, Boston 3rd edn (2009)
Pierson, H.O.: Handbook of Chemical Vapour Deposition, WILLIAM ANDREW PUBLISHING, LLC. Norwich, New York, U.S.A 2nd edn (1999)
Mattox, D.M.: Handbook of Physical Vapour Deposition Processing, William Andrew, United States of America 2nd edn (2010)
Barlow, F.: Film Deposition Techniques and Processes (2000)
Patil, V.: Effect of annealing on structural. Morphological, electrical and optical studies of nickel oxide thin films. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 25, 35–41 (2011)
Singhal, S., Namgyal, T.: Effect of Zn-substitution on the magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nano particles prepared via sol-gel route. J. Electromagn. Anal. Appl. 2, 376–381 (2010)
Arulmurugan, R., Jeyadevan, B.: Effects of zinc substitution on Co-Zn and Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 288, 470–477 (2005)
Sathishkumar, G.: Synthesis, structural and dielectric studies of nickel substituted cobalt zinc ferrite. Mater. Sci. Appl. 1, 19–24 (2010)
Dey, S., Ghose, J.: Synthesis, characterization and magnetic studies on nanocrystalline Co0.2Zn0.8Fe2O4. Mater. Res. Bull. 38, 1653–1660 (2003)
Kittel, C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics, Wiley India Pvt Ltd 7th edn (2007)
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-ray Diffraction. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1956)
Dixit, G.: Structural, magnetic and optical studies of NiFe2O4 thin films. Adv. Mater. Lett. 3(1), 21–28 (2012)
Ravindra, A.V., Padhan, P.: Electronic Structure and Optical Band Gap of CoFe2O4 Thin Films. Indian Institute of Technology, India (2012)
Koseoglu, Y.: Effect of Cr addition on the structural, morphological and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline cobalt ferrite system. Ceram. Int. 38, 6671–6676 (2012)
Mahesh Kumar, A., Appa Rao, P., Chaitanya Varma, M., Choudary, G.S.V.R.K., Rao, K.H.: Cation distribution in Co0.7Me0.3Fe2O4 (Me = Zn, Ni and Mn). J. Mod. Phys. 2, 1083–1087 (2011)
Ahmed, Y.M.Z., Hessien, M.M., Rashad, M.M., Ibrahim, I.A.: Nano crystalline copper ferrites from secondary iron oxide (Mill scale). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(16), 181–187 (2009)
Stoner Wohlfarth, E.C.: Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 240, 599 (1948). Reprinted by IEEE Trans. Magn. 27, 3475 (1991)
George, M., Nair, S.S., John, A.M., Joy, P.A., Anantharamam, M.R.: Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of the sol-gel prepared Li0.5Fe2.5O4 fine particles. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, 900–910 (2006)
Faruk, Y.O., Haluk, S., Mehmet, S., Basol, B.M.: Phys. Scr. 71, 221–224 (2005)
Khoshman, J.M., Ingram, D.C., Kordesch, M.E.: J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354(19), 2783–2786 (2008)
Benno, G., Joachi, K.: Optical properties of thin semiconductor films October, 2003
Rancour, J.: Optical Thin Films User’s Handbook. McGraw-Hill, New York (1987)
Abdelmoneim, H.M.: Optical properties of Ti0:5Li0.5La0.1Fe1.9O4 ferrite thin films. Phys. B J. 405, 1551–1557 (2010)
Faruk, Y.O., Haluk, S., Mehmet, S., Basol, B.M.: Phys. Scr. 71, 221–224 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anjum, S., Fayyaz, J., Khurram, R. et al. Tuning of Magnetic and Optical Properties of Co0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 Spinel Ferrite Thin Films Based on Post Annealing Temperature. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 4095–4106 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4662-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4662-3