Abstract
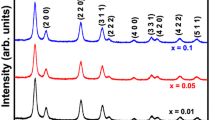
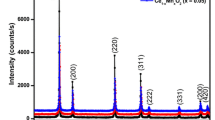
Nowadays, oxide-based diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles are the most reliable compounds, wherein they accommodate both spin as well as charge of the electron in single domain, means most preferable for the fabrication of spintronic devices. In this view, we report on new Ce1−xNixO2 (x = 0.00, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, and 0.08) nanoparticles prepared by precipitation method via polyethylene glycol as a surfactant. XRD analysis revealed that all the synthesized nanoparticles were crystallized in distinct FCC fluorite structure as that of CeO2 host lattice. Transmission electron microscopy analysis confirmed that all the synthesized samples were in spherical shape with average particle size of 8–10 nm, which is well concord with the grain size estimated from the Scherrer formula. The vibrating sample magnetometer evaluations suggested that pristine host lattice shows signals of paramagnetism; meanwhile, Ni substitution CeO2 nanoparticles exhibits strong ferromagnetism at room temperature. Particularly, 4% Ni-doped CeO2 samples shows enhanced ferromagnetism and which is suppressed with raising dopant concentration. The perceived magnetization with respect to the Ni dopant concentration is well anticipated by F-center exchange mechanism. We expect that the observations in this research suggest suitable path for preparing of various oxide-based diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles and their applications in fabrication of spintronic devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sato, K., Katayama-Yoshida, H.: Hyperfine Interact. 136, 737–742 (2001)
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J.M., Von Molnar, S., Roukes, M.L., Chtchelkanova, A.Y., Treger, D.M.: Science 294, 1488–1495 (2001)
Coey, J.M.D., Venkatesan, M., Fitzgerald, C.B.: Nat. Mater. 4, 173–179 (2005)
Prinz, G.A.: Science 282, 1660–1663 (1998)
Ohno, H.: Science 281, 951–956 (1998)
Zhao, L., Zhang, B., Pang, Q., Yang, S., Xixiang, Z., Ge, W.: vol. 89 (2006)
Matsumoto, Y., Murakami, M., Shono, T., Hasegawa, T., Fukumura, T., Kawasaki. M., Ahmet. P., Chikyow, T., Koshihara, S.Y., Koinuma, H.: Science 291, 854–6 (2001)
Ueda. K., Tabata, H., Kawai, T.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 988–990 (2001)
Fitzgerald, C.B., Venkatesan, M., Douvalis, A.P., Huber, S., Coey, J.M.D., Bakas, T.: J. Appl. Phys. 95, 7390–7392 (2004)
Saini, H.S., Singh, M., Reshak, A.H., Kashyap, M.K.: Science 74, 114–118 (2013)
Anupriya, K., Vivek, E., Subramanian, B.: J. Alloys Compd. 590, 406–410 (2014)
Yu, L., Xi, J.: Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 37, 15938–15947 (2012)
Zhang, X., Long, E., Li, Y., Guo, J., Zhang, L., Gong, M., Wang, M., Chen, Y.: J. Nat. Gas Chem. 18, 139–144 (2009)
Feng, T., Wang, X., Feng, G.: Mater. Lett. 100, 36–39 (2013)
Prestgard, M.C., Siegel, G., Ma, Q., Tiwari, A.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 102409–4 (2013)
Parveen, I.M., Asvini, V., Saravanan, G., Ravichandran, K., KalaiSelvi, D.: Ionics 23, 1285–1291 (2017)
Thurber, A., Reddy, K.M., Shutthanandan, V., Engelhard, M.H., Wang, C., Hays, J., Punnoose, A.: Phys. Rev. B 76, 165206–8 (2007)
Murugan, R., Vijayaprasath, G., Mahalingam, T., Ravi, G.: Mater. Lett. 162, 71–74 (2016)
Abbas, F., Jan, T., Iqbal, J., Ahmad, I., Haider Naqvi, M.S., Malik, M.: Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 931–936 (2015)
Devaraju, M.K., Shu, Y., Tsugio, S.: Cryst. Eng. Comm. 13, 741–746 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors (K. Subramanyam and N. Sreelekha) are grateful to the RAGHU engineering college, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India, for providing financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhav, P.L., Teja, K.R., Sreelekha, N. et al. Transition of Magnetic Characteristics from Paramagnetic State to Ferromagnetic Phase in Ce1−xNixO2 Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 1631–1636 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4375-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4375-z