Abstract
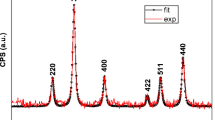
In this work, we aimed to develop stable usnic acid (UA)-conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) as a potential drug carrier for in vitro analysis of MCF-7 (breast cancer cell line), HeLa (cervix cancer cell line), L929 (mouse fibroblast cell line), U87 (glioblastoma cell line, brain cancer), and A549 (human lung cancer cell line) cell lines. SPIONs were synthesized via the polyol method and functionalized with APTES using the Stöber method. Carboxylated polyethylene glycol (PEG-COOH), folic acid (FA), and carboxylated luteolin (CL) were conjugated on the surface via a carboxylic/amine group using the nanoprecipitation method, respectively. X-ray powder diffraction analysis confirmed the purity of the product with crystallite size of around 11 nm. Fourier-transformed infrared spectrophotometer (FT-IR) analyses explained the conjugation of all functional groups to the surface of SPIONs. The percentages of inorganic and organic content in the products were investigated via thermal gravimetric analyzer (TGA). For morphological analysis, a transmission electron microscope (TEM) was used. The superparamagnetic property of the product was also confirmed by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avendano, C., Menendez, J.C.: Medicinal Chemistry of Anticancer Drugs, 1st edn, p. 1 (Chapter 1). Elsevier, Amsterdam (2008)
Jemal, A., Bray, F., Center, M.M., Ferlay, J., Ward, E., Forman, D.: Global, cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61, 69–90 (2011)
Wang, P., Cai, J., Chen, J.Q., Li, L.S., Sun, C.L., Xue, B., Ji, M.: 3D-QSAR and docking studies of piperidine carboxamide derivatives as ALK inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 23, 2576–2583 (2014)
Gilchrest, B.A., Eller, M.S.: Cancer therapeutics: smart and smarter. Drugs Future 34, 205–216 (2009)
Kamel, M.M., Abdo Megally, N.Y.: Synthesis of novel 1,2,4-triazoles, triazolothiadiazines and triazolothiadiazoles as potential anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 86, 75–80 (2014)
La Regina, G., Bai, R., Coluccia, A., Famiglini, V., Pelliccia, S., Passacantilli, S., Rew, Y., Sun, D.: Discovery of a small molecule MDM2 inhibitor (AMG 232) for treating cancer. J. Med. Chem. 57, 6332–6341 (2014)
Valente, S., Trisciuoglio, D., De Luca, T., Nebbioso, A., Labella, D., Lenoci, A., Bigogno, C., Dondio, G., Miceli, M., Brosch, G., Del Bufalo, D., Altucci, L., Mai, A.: 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-containing histone deacetylase inhibitors: anticancer activities in cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 57, 6259–6265 (2014)
Varbanov, H.P., Goschl, S., Heffeter, P., Theiner, S., Roller, A., Jensen, F., Jakupec, M.A., Berger, W., Galanski, M., Keppler, B.K.: A novel class of bis- and tris-chelate diam (m) inebis(dicarboxylato) platinum(IV) complexes as potential anticancer prodrugs. J. Med. Chem. 57, 6751–6764 (2014)
Wang, M.J., Liu, Y.Q., Chang, L.C., Wang, C.Y., Zhao, Y.L., Zhao, X.B., Qian, K., Nan, X., Yang, L., Yang, X.M, Hung, H.Y., Yang, J.S., Kuo, D.H., Goto, M., Morris-Natschke, S.L., Pan, S.L., Teng, C.M., Kuo, S.C., Wu, T.S., Wu, Y.C., Lee, K.H.: Design, synthesis, mechanisms of action, and toxicity of novel 20(s)-sulfonylamidine derivatives of camptothecin as potent antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 57, 6008–6018 (2014)
Wang, C., Ravi, S., Garapati, U.S., Das, M., Howell, M., Mallela, J., Alwarappan, S., Mohapatra, S.S., Mohapatra, S.: Multifunctional chitosan magnetic-graphene(CMG) nanoparticles: a theranostic platform for tumor-targeted co-delivery of drugs, genes and MRI contrast agents. J. Mater. Chem. B 1, 4396–4405 (2013)
Mandal, A., Sekar, S., Kanagavel, M., Chandrasekaran, N., Mukherjee, A., Sastry, T.P.: Collagen based magnetic nanobiocomposite as MRI contrast agent andfor targeted delivery in cancer therapy, Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 1830, 4628–4633 (2013)
Majewski, A.P., Schallon, A., Jérôme, V., Freitag, R., Müller, A.H.E., Schmalz, H.: Dual-responsive magnetic core–shell nanoparticles for nonviral gene deliveryand cell separation. Biomacromolecules 13, 857–866 (2012)
Liu, H., Li, S., Liu, L., Tian, L., He, N.: An integrated and sensitive detectionplatform for biosensing application based on Fe@Au magnetic nanoparticlesas bead array carries. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 1442–1448 (2010)
Chandra, S., Barola, N., Bahadur, D.: Impedimetric biosensor for early detectionof cervical cancer. Chem. Commun. 47, 11258–11260 (2011)
Yalcı̧n, S., Erkan, M., Ünsoy, G., Parsian, M., Kleeff, J., Gündüz, U.: Effect of gemcitabine and retinoic acid loaded PAMAM dendrimer-coated magneticnanoparticles on pancreatic cancer and stellate cell lines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 68, 737–743 (2014)
Majewski, A.P., Schallon, A., Jérôme, V., Freitag, R., Müller, A.H.E., Schmalz, H.: Dual-responsive magnetic core–shell nanoparticles for nonviral gene delivery and cell separation. Biomacromolecules 13, 857–866 (2012)
Shan, Z., Jiang, Y., Guo, M., Bennett, J.C., Li, X., Tian, H., Oakes, K., Zhang, X., Zhou, Y., Huang, Q., Chen, H., Promoting, D N A: loading on magnetic nanoparticles using aDNA condensation strategy. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 125, 247–254 (2015)
Zhang, L., Dong, W.-F., Sun, H.-B.: Multifunctional superparamagnetic ironoxide nanoparticles: design, synthesis and biomedical photonic applications. Nanoscale 5, 7664–7684 (2013)
Roy, E., Patra, S., Madhuri, R., Sharma, P.K.: Stimuli-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-tyrosine@gadolinium: iron oxide nanoparticle-basednanotheranostic for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 142, 248–258 (2016)
Mahmoudi, M., Sant, S., Wang, B., Laurent, S., Sen, T.: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63, 24–46 (2011)
Ling, D., Hackett, M.J., Hyeon, T.: Surface ligands in synthesis modification,assembly and biomedical applications of nanoparticles. Nano Today 9, 457–477 (2014)
Liu, X.L., Choo, E.S.G., Ahmed, A.S., Zhao, L.Y., Yang, Y., Ramanujan, R.V., Xue, J.M., Fan, D.D., Fan, H.M., Ding, J.: Magnetic nanoparticle-loaded polymernanospheres as magnetic hyperthermia agents. J. Mater. Chem. B 2, 120–128 (2014)
Sun, L., Wu, Q., Peng, F., Liu, L., Gong, C.: Strategies of polymeric nanoparticles forenhanced internalization in cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 135, 56–72 (2015)
Lu, X., Jiang, R., Yang, M., Fan, Q., Hu, W., Zhang, L., Yang, Z., Deng, W., Shen, Q., Huang, Y., Liu, X., Huang, W.: Monodispersed grafted conjugated polyelectrolyte-stabilized magnetic nanoparticles as multifunctional platform for cellular imaging and drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2, 376–386 (2014)
Rouhollah, K., Pelin, M., Serap, Y., Gozde, U., Ufuk, G.: Doxorubicin loading, release, and stability of polyamidoamine dendrimer-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 102, 1825–1835 (2013)
Cocchietto, M., Skert, N., Nimis, P.L., Sava, G.: Naturwissenschaften 89(4), 137–146 (2002)
Grumezescu, A.M., Saviuc, C., Chifiriuc, M.C., Hristu, R., Mihaiescu, D.E., Balaure, P., Stanciu, G., Lazar, V.: IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 10(4), 269–274 (2011)
Chifiriuc, M.C., Ditu̧, L.M., Oprea, E., Litȩscu, S., Bucur, M., Marut escu, L., Enache, G., Saviuc, C., Burlibasa̧, M., Traistaru, T., Tanase, G., Lazar, V.: Roum Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 68(4), 215–222 (2009)
Mitrovic, T., Stamenkovic, S., Cvetkovic, V., Tosic, S., Stankovic, M., Radojevic, I., Stefanovic, O., Comic, L., Dacic, D., Curcic, M., Markovic, S.: Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12(8), 5428–5448 (2011)
Cocchietto, M., Skert, N., Nimis, P., Sava, G.: A review on usnic acid: an interesting natural compound. Naturwissenschaften 89, 137–146 (2002)
Francolini, I., Taresco, V., Crisante, F., Martinelli, A., D’Ilario, L., Piozzi, A.: Water soluble usnic acid-polyacrylamide complexes with enhanced antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Int. J. Mol. Sci 14, 7356–7369 (2013)
da Silva Santos, N.P., Nascimento, S.C., Wanderley, M.S., Pontes-Filho, N.T., da Silva, J.F., de Castro, C.M., Pereira, E.C., da Silva, N.H., Honda, N.K., Santos-Magalhaes, N.S.: Nanoencapsulation of usnic acid: an attempt to improve antitumour activity and reduce hepatotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 64, 154–160 (2006)
Lira, M.C., Siqueira-Moura, M.P., Rolim-Santos, H.M., Galetti, F.C., Simioni, A.R., Santos, N.P., Tabosa Do Egito, E.S., Silva, C.L., Tedesco, A.C., Santos-Magalhaes, N.S.: In vitro uptake and antimycobacterial activity of liposomal usnic acid formulation. J. Liposome Res. 19, 49–58 (2009)
Martinelli, A., Bakry, A., D’Ilario, L., Francolini, I., Piozzi, A., Taresco, V.: Release behavior and antibiofilm activity of usnic acid-loaded carboxylated poly(l-lactide) microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 88, 415–423 (2014)
Grumezescu, A.M., Saviuc, C., Chifiriuc, M.C., Hristu, R., Mihaiescu, D.E., Balaure, P., Stanciu, G., Lazar, V.: Inhibitory activity of Fe3 O 4/oleic acid/usnic acid-core/shell/extrashell nanofluid on S. aureus biofilm development. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 10, 269–274 (2011)
Grumezescu, A.M., Cotar, A.I., Andronescu, E., Ficai, A., Ghitulica, C.D., Grumezescu, V., Vasile, B.S., Chifiriuc, M.C.: In vitro activity of the new water-dispersible Fe3 O 4@ usnic acid nanostructure against planktonic and sessile bacterial cells. J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1766–1776 (2013)
Baykal, A., Amir, Md., Güner, S., Sözeri, H.: Preparation and characterization of SPION functionalized via caffeic acid. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 395, 199–204 (2015)
Manikandan, A., Vijaya, J.J., Mary, J. Arul., Kennedy, L.J., Dinesh, A.: Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe3 O 4 nanoparticles prepared by a facile microwave combustion method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 2077–2085 (2014)
Akal, Z.U., Alpsoy, L., Baykal, A.: Superparamagnetic iron oxide conjugated with folic acid and carboxylated quercetin for chemotherapy applications. Ceram. Int. 42, 9065–9072 (2016)
Marıawıllıam, S.M., Francıs, A.P., Devasena, T.: In situ isolation and characterizatıon of nano-usnic acid for medical applications. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6(6), 222–226 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J.: Surface modification of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles for improved intracellular uptake to breast cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 283, 352–357 (2005)
Dousseau, F., Pezolet, M.: Determination of the secondary structure content of proteins in aqueous solutions from their amide I and amide II infrared bands. Comparison between classical and partial least-squares methods. Biochemistry 29, 8771–8779 (1990)
Barth, A., Zscherp, C.: What vibrations tell about proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 35, 369–430 (2002)
Kurtan, U., Onuş, E., Amir, Md., Baykal, A.: Fe3 O 4@Hpipe-4@Cu Nanocatalyst for hydrogenation of nitro-aromatics and azo dyes. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 25, 1120–1128 (2015)
Manikandan, A., Vijaya, J.J., Joh, J.K.: Structural, optical and magnetic properties of porous α-Fe2 O 3 nanostructures prepared by rapid combustion method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13, 2986–2992 (2013)
Zhang, L., Wu, Z., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Li, X., Xu, H., Wang, H., Zhu, G.: Preparation of magnetic Fe3 O 4/TiO2/Ag composite microspheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Solid State Sci. 52, 42–48 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alpsoy, L., Baykal, A., Amir, M. et al. SPION@APTES@FA-PEG@Usnic Acid Bionanodrug for Cancer Therapy. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 1395–1401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4333-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4333-9