Abstract
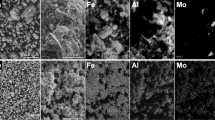
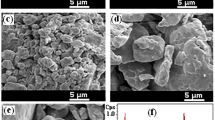
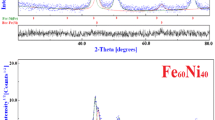
Iron and molybdenum powder mixture exposed to stepwise mechanical alloying in air and in nitrogen is studied by X-ray diffraction, Mössbauer spectrometry, electron microscopy, magnetic measurements, and differential thermal analysis. The Mössbauer spectra are interpreted in terms of various contributions. The main contribution is associated with the FeMo nanograin core, which is similar to the bcc-FeMo bulk alloy of the same composition, i.e., a ferromagnetic solid solution of Mo in Fe. The increasing milling time contributes to a decrease in grain size. It results in a decrease of the volume fraction of the grain cores and simultaneously to an increase in a volume fraction of other contributions of highly defected surface zones and very close surface layers influenced by the milling atmosphere. The Rietveld interpretation of diffraction patterns, the scanning, and transmission electron microscopy completed by the EDX analysis and magnetic measurements are in good agreement with the Mössbauer spectra interpretation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suryanarayana, C.: Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 1–184 (2001)
Otmane, F., et al.: Structural, mechanical and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed Fe40Co60 powders. Defect Diffus. Forum 312–315, 743–747 (2011)
Jartych, E.: Local Atomic Order in nanocrystalline Fe-based alloys obtained by mechanical alloying. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 265, 176–188 (2003)
Jartych, E., et al.: Structure and hyperfine interactions in mechanosynthesized iron-molybdenum alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 337, 69–75 (2002)
Moumeni, H., et al.: Formation of ball-milled Fe-Mo nanostructured powders. J. Alloys Compd. 419, 140–144 (2006)
Jirásková, Y., et al.: Microstructure and physical properties of mechanically alloyed Fe-Mo powder. J. Alloys Compd. 477, 55–61 (2009)
D’Incau, M., et al.: High-energy grinding of FeMo powder. J. Mater. Res. 22, 1744–1753 (2007)
Young, R.A. (ed.): The Rietveld Metod. International Union of Crystallography, Oxford University Press, Oxford (1993)
Žák, T., Jirásková, Y.: CONFIT: Mössbauer spectra fitting program. Surf. Interface Anal. 38, 710–714 (2006)
Fuchs, A., Ilschner, B.: Gitterkonstanten von Fe-Mo-Legierungen mit Mo-Gehalt bis 20 Gew. -Prozent. Acta Crystallogr. 19, 488–491 (1965)
Turek, I., et al.: Electronic structure of disordered alloys, surfaces and interfaces. Kluwer Academic, Boston (1997)
Chien, C.L., et al.: Structural and magnetic behavior of vapor quenched Fe-Mo alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 54–57, 291–292 (1986)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank M. Hapla and Dr. A. Kroupa for magnetic and DTA measurements and the Czech Science Foundation (P108/11/1350) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jirásková, Y., Buršík, J. & Turek, I. Nanostructure, Composition, and Magnetic Behavior of Mechanically Alloyed Fe–Mo. J Supercond Nov Magn 26, 1717–1721 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-012-2049-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-012-2049-4