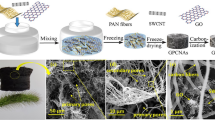
Abstract
“Red oil” explosion is an important safety issue in spent fuel reprocessing and the most fundamental measure to prevent “red oil” explosion is the capture of organic solvents in water phase requiring further treatment. In this paper, superhydrophobic graphene/polyvinylidene fluoride composite aerogel (GA–PVDF) was synthesized by using HI as reductant under mild condition. The characterizations of SEM, FTIR, XRD, contact angle, mechanical property and oil/water absorption ability were performed to optimize the preparation conditions of GA–PVDF. It is found under optimal condition, the composite shows excellent water resistance, oil–water separation and mechanical properties. Furthermore, the recyclability and possible operation model of obtained GA–PVDF were also investigated. The result demonstrates that the composite material can be simply and efficiently used to capture the organic solvents without water uptake, which is attractive in the application of spent fuel reprocessing. Moreover, the recyclability of material also ensures the reduction of secondary waste. All of these indicate that GA–PVDF has great application potential for oil–water separation and “red oil” explosion prevention in spent fuel reprocessing.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.A. El-Nadi, Solvent extraction and its applications on ore processing and recovery of metals: classical approach. Sep. Purif. Rev. 46(3), 195–215 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/15422119.2016.1240085
K. Chandran, B. Sreenivasulu, N. Ramanathan, P.C. Clinsha, A. Suresh, N. Sivaraman, Thermal decomposition behaviour of irradiated tri n-butyl phosphate and mixture of di and mono n-butyl phosphate-nitric acid systems. Thermochim. Acta 657, 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2017.09.018
R. Li, C. Liu, H. Zhao, S. He, Z. Li, Q. Li, L. Zhang, Di-1-methyl heptyl methylphosphonate (DMHMP): a promising extractant in Th-based fuel reprocessing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 173, 105–112 (2017)
T.G. Srinivasan, P.R. Vasudeva Rao, Red oil excursions: a review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 49(15), 2315–2329 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.928321
S. Manohar, K. Narayan Kutty, B.V. Shah, P.K. Wattal, S.L. Bajoria, N.S. Kolhe, V.K. Rathod, Removal of dissolved Trin-butyl phosphate from aqueous streams of reprocessing origin: engineering scale studies. Desalin Water Treat 38(1–3), 146–150 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.664316
V.G. Lade, P.C. Wankhede, V.K. Rathod, Removal of tributyl phosphate from aqueous stream in a pilot scale combined air-lift mixer-settler unit: process intensification studies. Chem. Eng. Process. 95, 72–79 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2015.05.004
R. Natarajan, Reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel in India: present challenges and future programme. Prog. Nucl. Energy 101, 118–132 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2017.03.001
T. Liu, G. Zhao, W. Zhang, H. Chi, C. Hou, Y. Sun, The preparation of superhydrophobic graphene/melamine composite sponge applied in treatment of oil pollution. J. Porous Mater. 22(6), 1573–1580 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-0040-8
M.H. Sorour, H.A. Hani, G.A. Al-Bazedi, A.M. El-Rafei, Hydrophobic silica aerogels for oil spills clean-up, synthesis, characterization and preliminary performance evaluation. J. Porous Mater. 23(5), 1401–1409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0200-5
B. Doshi, M. Sillanpaa, S. Kalliola, A review of bio-based materials for oil spill treatment. Water Res. 135, 262–277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.034
X. Yue, J. Li, T. Zhang, F. Qiu, D. Yang, M. Xue, In situ one-step fabrication of durable superhydrophobic-superoleophilic cellulose/LDH membrane with hierarchical structure for efficiency oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 328, 117–123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.026
F. Guo, Q. Wen, Z. Guo, Low cost and non-fluoride flowerlike superhydrophobic particles fabricated for both emulsions separation and dyes adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 507, 421–428 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.021
N. Cao, Q. Lyu, J. Li, Y. Wang, B. Yang, S. Szunerits, R. Boukherroub, Facile synthesis of fluorinated polydopamine/chitosan/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 326, 17–28 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.05.117
P. Saha, L. Dashairya, Reduced graphene oxide modified melamine formaldehyde (rGO@MF) superhydrophobic sponge for efficient oil–water separation. J. Porous Mater. 25(5), 1475–1488 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-018-0560-0
S. Song, H. Yang, C. Su, Z. Jiang, Z. Lu, Ultrasonic-microwave assisted synthesis of stable reduced graphene oxide modified melamine foam with superhydrophobicity and high oil adsorption capacities. Chem. Eng. J. 306, 504–511 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.086
S. Yang, L. Chen, C. Wang, M. Rana, P.C. Ma, Surface roughness induced superhydrophobicity of graphene foam for oil-water separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 508, 254–262 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.061
C. Li, D. Jiang, H. Liang, B. Huo, C. Liu, W. Yang, J. Liu, Superelastic and arbitrary-shaped graphene aerogels with sacrificial skeleton of melamine foam for varied applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(8), 1704674 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201704674
S. Moradi, P. Englezos, S.G. Hatzikiriakos, Contact angle hysteresis: surface morphology effects. Colloid Polym. Sci. 291(2), 317–328 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2746-3
M.A. Riaz, P. Hadi, I.H. Abidi, A. Tyagi, X. Ou, Z. Luo, Recyclable 3D graphene aerogel with bimodal pore structure for ultrafast and selective oil sorption from water. RSC Adv. 7(47), 29722–29731 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02886e
J. Li, J. Li, H. Meng, S. Xie, B. Zhang, L. Li, H. Ma, J. Zhang, M. Yu, Ultra-light, compressible and fire-resistant graphene aerogel as a highly efficient and recyclable absorbent for organic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(9), 2934 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta14725h
Y. Lin, G.J. Ehlert, C. Bukowsky, H.A. Sodano, Superhydrophobic functionalized graphene aerogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 3(7), 2200–2203 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/am200527j
H. Chang, J. Qin, P. Xiao, Y. Yang, T. Zhang, Y. Ma, Y. Huang, Y. Chen, Highly reversible and recyclable absorption under both hydrophobic and hydrophilic conditions using a reduced bulk graphene oxide material. Adv. Mater. 28(18), 3504–3509 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201505420
S. Pei, J. Zhao, J. Du, W. Ren, H.-M. Cheng, Direct reduction of graphene oxide films into highly conductive and flexible graphene films by hydrohalic acids. Carbon 48(15), 4466–4474 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.08.006
W. Chen, L. Yan, In situ self-assembly of mild chemical reduction graphene for three-dimensional architectures. Nanoscale 3(8), 3132–3137 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1nr10355e
W. Li, A. Amirfazli, A thermodynamic approach for determining the contact angle hysteresis for superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 292(1), 195–201 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.05.062
R. Rioboo, B. Delattre, D. Duvivier, A. Vaillant, J. De Coninck, Superhydrophobicity and liquid repellency of solutions on polypropylene. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 175, 1–10 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2012.03.003
A. Marmur, Solid-surface characterization by wetting. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 39(1), 473–489 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.matsci.38.060407.132425
L. Peng, W. Lei, P. Yu, Y. Luo, Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)/hydrophobic nano-silica (H-SiO2) coated superhydrophobic porous materials for water/oil separation. RSC Adv. 6(13), 10365–10371 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra17728f
W. Wu, R. Huang, W. Qi, R. Su, Z. He, Bioinspired peptide-coated superhydrophilic poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane for oil/water emulsion separation. Langmuir 34(22), 6621–6627 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01017
C. Wei, F. Dai, L. Lin, Z. An, Y. He, X. Chen, L. Chen, Y. Zhao, Simplified and robust adhesive-free superhydrophobic SiO2-decorated PVDF membranes for efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 555, 220–228 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.03.058
G.J. Ross, J.F. Watts, M.P. Hill, P. Morrissey, Surface modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) by alkaline treatment 1. The degradation mechanism. Polymer 41(5), 1685–1696 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(99)00343-2
B. Zhao, C. Zhao, C. Wang, C.B. Park, Poly(vinylidene fluoride) foams: a promising low-k dielectric and heat-insulating material. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(12), 3065–3073 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tc00547h
A. Lund, C. Gustafsson, H. Bertilsson, R.W. Rychwalski, Enhancement of β phase crystals formation with the use of nanofillers in PVDF films and fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71(2), 222–229 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.11.014
Z. Peng, C. Xiong, W. Wang, F. Tan, X. Wang, X. Qiao, P.K. Wong, Hydrophobic modification of nanoscale zero-valent iron with excellent stability and floatability for efficient removal of floating oil on water. Chemosphere 201, 110–118 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.149
H. Sun, Z. Xu, C. Gao, Multifunctional, ultra-flyweight, synergistically assembled carbon aerogels. Adv. Mater. 25(18), 2554–2560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204576
Y. Wu, N. Yi, L. Huang, T. Zhang, S. Fang, H. Chang, N. Li, J. Oh, J.A. Lee, M. Kozlov, A.C. Chipara, H. Terrones, P. Xiao, G. Long, Y. Huang, F. Zhang, L. Zhang, X. Lepro, C. Haines, M.D. Lima, N.P. Lopez, L.P. Rajukumar, A.L. Elias, S. Feng, S.J. Kim, N.T. Narayanan, P.M. Ajayan, M. Terrones, A. Aliev, P. Chu, Z. Zhang, R.H. Baughman, Y. Chen, Three-dimensionally bonded spongy graphene material with super compressive elasticity and near-zero Poisson’s ratio. Nat. Commun. 6, 6141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7141
A.B.D. Cassie, S. Baxter, Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 40(4), 546–551 (1944). https://doi.org/10.1039/tf9444000546
M. Chen, Z. Li, Y. Geng, H. Zhao, S. He, A. Chen, Q. Li, L. Zhang, A modular process for the treatment of high level liquid waste (HLLW) using solvent-impregnated graphene aerogel. Hydrometallurgy 179, 167–174 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.06.005
W. Wan, Y. Lin, A. Prakash, Y. Zhou, Three-dimensional carbon-based architectures for oil remediation: from synthesis and modification to functionalization. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(48), 18687–18705 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta07211a
F. Chen, Y. Lu, X. Liu, J. Song, G. He, M.K. Tiwari, C.J. Carmalt, I.P. Parkin, Table salt as a template to prepare reusable porous PVDF-MWCNT foam for separation of immiscible oils/organic solvents and corrosive aqueous solutions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27(41), 1702926 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201702926
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11305244; 11505270) and “Strategic Priority Research Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA02030000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10934_2019_760_MOESM1_ESM.mpg
Supplementary material 1 (MPG 11524 kb) Movie S1 Squeezing recovery process of GA-PVDF impregnated with 30% TBP-n-dodecane.
10934_2019_760_MOESM2_ESM.mpg
Supplementary material 2 (MPG 10924 kb) Movie S2 The static oil-water separation experiment for removing 30% TBP-n-dodecane from a system.
10934_2019_760_MOESM3_ESM.mpg
Supplementary material 3 (MPG 21744 kb) Movie S3 The continuous oil-water separation experiment for removing 30% TBP-n-dodecane from a system.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, Y., Li, J., Li, Z. et al. Facile preparation of 3D graphene-based/polyvinylidene fluoride composite for organic solvents capture in spent fuel reprocessing. J Porous Mater 26, 1619–1629 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-019-00760-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-019-00760-8