Abstract
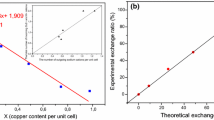
Phase pure sample of the microporous copper silicate CuSH–1Na has been obtained by simplified hydrothermal method without using additives (H2O2 and Na2HPO4). Ion exchange of Na+ by Cs+, Ca2+ and Sr2+ ions showed that the structure can suffer partial replacement of the charge compensating cations. Ion exchange with Cs+ resulted in distinct dehydration while the ion exchange with Sr2+ increased the total amount of water. Water content in the Ca-exchanged sample is comparable to the as-synthesized sodium phase. Raman spectroscopy revealed that the divalent cations as Ca2+ and Sr2+ induce stronger local structural deformations than the monovalent Cs+. These structural changes have been also followed by the refined lattice distortions. Magnetic analyses showed that CuSH–1Na presents a very weak ferromagnetic interaction along the Cu2+ chains with a nearly vanishing Curie–Weiss temperature. This magnetic coupling is associated with super-super-exchange interactions through Cu–Na–O–Na–Cu paths. Antiferromagnetic coupling, attributed to inter-chains super-super-exchange interactions, competes with the ferromagnetic one and prevails at the lowest temperature.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Rocha, M.W. Anderson, Microporous titanosilicates and other novel mixed octahedral-tetrahedral framework oxides. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 5, 801–818 (2000)
K. Popa, C.C. Pavel, Radioactive wastewaters purification using titanosilicates materials: state of the art and perspectives. Desalination 293, 78–86 (2012)
C.C. Pavel, K. Popa, Investigations on the ion exchange process of Cs+ and Sr2+ cations by ETS materials. Chem. Eng. J. 245, 288–294 (2014)
O. Oleksiienko, C. Wolkersdorfer, M. Sillanpaa, Titanosilicates in cation adsorption and cation exchange—a review. Chem. Eng. J. 317, 570–585 (2017)
M.W. Anderson, O. Terasaki, T. Ohsuna, A. Philippou, S.P. Mackay, A. Ferreira, J. Rocha, S. Lidin, Structure of the microporous titanosilicate Ets-10. Nature 367(6461), 347–351 (1994)
D.M. Chapman, A.L. Roe, Synthesis, characterization and crystal-chemistry of microporous titanium-silicate materials. Zeolites 10(8), 730–737 (1990)
M.S. Dadachov, J. Rocha, A. Ferreira, Z. Lin, M.W. Anderson, Ab initio structure determination of layered sodium titanium silicate containing edge-sharing titanate chains (AM-4) Na-3(Na,H)Ti2O2[Si2O6]·2.2H2O. Chem. Commun. 24, 2371–2372 (1997)
S. Ferdov, U. Kolitsch, O. Petrov, V. Kostov-Kytin, C. Lengauer, E. Tillmanns, Synthesis and crystal structure of a new microporous zircono silicate, MCV-2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 81(1–3), 79–86 (2005)
S.R. Jale, A. Ojo, F.R. Fitch, Synthesis of microporous zirconosilicates containing ZrO6 octahedra and SiO4 tetrahedra. Chem. Commun. 5, 411–412 (1999)
S.M. Kuznicki, D.T. Hayhurst, Synthesis of Ets-10, a new wide-pore titanium silicate molecular-sieve. Abs. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 202, 78-Petr (1991)
Z. Lin, J. Rocha, Small-pore framework zirconium and hafnium silicates with the structure of mineral tumchaite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 76(1–3), 99–104 (2004)
Z. Lin, J. Rocha, Hydrothermal synthesis of the tin analogue of penkvilksite-2O. Eur. J. Mineral. 17(6), 869–873 (2005)
Z. Lin, J. Rocha, P. Brandao, A. Ferreira, A.P. Esculcas, J.D.P. deJesus, A. Philippou, M.W. Anderson, Synthesis and structural characterization of microporous umbite, penkvilksite, and other titanosilicates. J. Phys. Chem. B 101(36), 7114–7120 (1997)
Z. Lin, J. Rocha, J.D.P. de Jesus, A. Ferreira, Synthesis and structure of a novel microporous framework stannosilicate. J. Mater. Chem. 10(6), 1353–1356 (2000)
R.P. Nikolova, K. Fujiwara, N. Nakayama, V. Kostov-Kytin, Crystal structure of a new small-pore zirconosilicate Na2ZrSi2O7·H2O and its relation to stoichiometrically and topologically similar compounds. Solid State Sci. 11(2), 382–388 (2009)
J. Rocha, P. Brandao, Z. Lin, M.W. Anderson, V. Alfredsson, O. Terasaki, The first large-pore vanadosilicate framework containing hexacoordinated vanadium. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 36(1–2), 100–102 (1997)
X.Q. Wang, L.M. Liu, A.J. Jacobson, Open-framework and microporous vanadium silicates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(26), 7812–7820 (2002)
X.Q. Wang, L.M. Liu, A.J. Jacobson, The novel open-framework vanadium silicates K-2(VO)(Si4O10)·H2O (VSH-1) and Cs-2(VO)(Si6O14)·3H2O (VSH-2). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40(11), 2174–2176 (2001)
D.M. Poojary, R.A. Cahill, A. Clearfield, Synthesis, crystal-structures, and ion-exchange properties of a novel porous titanosilicate. Chem. Mater. 6(12), 2364–2368 (1994)
Z. Lin, J. Rocha, A. Valente, Synthesis and characterisation of a framework microporous stannosilicate. Chem. Commun. 24, 2489–2490 (1999)
R. Millini, A. Carati, G. Bellussi, G. Cruciani, W.O. Parker, C. Rizzo, S. Zanardi, Synthesis, characterization and crystal structure of EMS-2—a novel microporous stannosilicate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 101(1–2), 43–49 (2007)
M.A.R. Peixoto, S. Ferdov, Crystal structure, thermal flexibility and structural transformations of tin umbite and copper exchanged tin umbite prepared from clear solution. J. Porous Mater. 20(5), 1171–1178 (2013)
L. Zhang, D.L. He, Y.C. Zou, S.J. Ma, F.S. Xiao, Synthesis and characterization of a novel microporous framework stannosilicate. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 31(4), 635–637 (2010)
S. Zanardi, A. Carati, G. Cruciani, G. Bellussi, R. Millini, C. Rizzo, Synthesis, characterization and crystal structure of new microporous bismuth silicates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 97(1–3), 34–41 (2006)
D. Ananias, S. Ferdov, F.A.A. Paz, R.A.S. Ferreira, A. Ferreira, C.F.G.C. Geraldes, L.D. Carlos, Z. Lin, J. Rocha, Photoluminescent layered lanthanide silicate nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 20(1), 205–212 (2008)
D. Ananias, A. Ferreira, J. Rocha, P. Ferreira, J.P. Rainho, C. Morais, L.D. Carlos, Novel microporous europium and terbium silicates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(24), 5735–5742 (2001)
D. Ananias, M. Kostova, F.A.A. Paz, A. Ferreira, L.D. Carlos, J. Klinowski, J. Rocha, Photoluminescent layered lanthanide silicates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(33), 10410–10417 (2004)
A. Ferreira, D. Ananias, L.D. Carlos, C.M. Morais, J. Rocha, Novel microporous lanthanide silicates with tobermorite-like structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(47), 14573–14579 (2003)
S.M. Kuznicki, V.A. Bell, S. Nair, H.W. Hillhouse, R.M. Jacubinas, C.M. Braunbarth, B.H. Toby, M. Tsapatsis, A titanosilicate molecular sieve with adjustable pores for size-selective adsorption of molecules (vol 412, pg 720, 2001). Nature 413(6856), 652–652 (2001)
F.X.L.I. Xamena, P. Calza, C. Lamberti, C. Prestipino, A. Damin, S. Bordiga, E. Pelizzetti, A. Zecchina, Enhancement of the ETS-10 titanosilicate activity in the shape-selective photocatalytic degradation of large aromatic molecules by controlled defect production. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(8), 2264–2271 (2003)
K. Popa, C.C. Pavel, N. Bilba, A. Cecal, Purification of waste waters containing Co-60(2+), Cd-115m(2+) and Hg-203(2+) radioactive ions by ETS-4 titanosilicate. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 269(1), 155–160 (2006)
M.L. Pinto, J. Rocha, J.R.B. Gomes, J. Pires, Slow release of NO by microporous titanosilicate ETS-4. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(16), 6396–6402 (2011)
S. Ferdov, E. Shikova, Z. Ivanova, L.T. Dimowa, R.P. Nikolova, Z. Lin, B.L. Shivachev, A microporous titanosilicate for selective killing of HeLa cancer cells. RSC Adv. 3(23), 8843–8848 (2013)
S. Ferdov, Low-density macroporous foams obtained from a molecular sieve by temperature-induced amorphization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52(46), 12135–12138 (2013)
X.Q. Wang, L.M. Liu, A.J. Jacobson, Nanoporous copper silicates with one-dimensional 12-ring channel systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42(18), 2044–2047 (2003)
X.Q. Wang, L.M. Liu, L.B. Wang, A.J. Jacobson, Hydrothermal synthesis and structures of the open-framework copper silicates Na-2[Cu2Si4O11](H2O)(2) (CuSH-2Na), Na-2[CuSi3O8] (CuSH-3Na), Cs2Na4[Cu2Si12O7(OH)(2)](OH)(2) (CuSH-4NaCs), and Na-2[Cu2Si5O13](H2O)(3) (CuSH-6Na). Solid State Sci. 7(11), 1415–1422 (2005)
S.J. Datta, C. Khumnoon, Z.H. Lee, W.K. Moon, S. Docao, T.H. Nguyen, I.C. Hwang, D. Moon, P. Oleynikov, O. Terasaki, K.B. Yoon, CO2 capture from humid flue gases and humid atmosphere using a microporous coppersilicate. Science 350(6258), 302–306 (2015)
A. Le Bail, Whole powder pattern decomposition methods and applications: a retrospection. Powder Diffr. 20(4), 316–326 (2005)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic-radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 32(Sep1), 751–767 (1976)
G.J. Kramer, N.P. Farragher, B.W.H. Vanbeest, R.A. Vansanten, Interatomic force-fields for silicas, aluminophosphates, and zeolites—derivation based on abinitio calculations. Phys. Rev. B 43(6), 5068–5080 (1991)
A.J.M. Deman, R.A. Vansanten, The relation between zeolite framework structure and vibrational-spectra. Zeolites 12(3), 269–279 (1992)
R.L. Frost, Y.F. Xi, Raman spectroscopic study of the mineral shattuckite Cu-5(SiO3)(4)(OH)(2). Spectrochim. Acta Part A 87 (2012) 241–244
M. Tribaudino, L. Mantovani, D. Bersani, P.P. Lottici, Raman spectroscopy of (Ca,Mg)MgSi2O6 clinopyroxenes. Am. Mineral. 97(8–9), 1339–1347 (2012)
P.K. Dutta, B. Delbarco, Raman-spectroscopic studies of zeolite framework—hydrated zeolite a and the influence of cations. J. Phys. Chem. 89(10), 1861–1865 (1985)
S. Nair, M. Tsapatsis, B.H. Toby, S.M. Kuznicki, A study of heat-treatment induced framework contraction in strontium-ETS-4 by powder neutron diffraction and vibrational spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(51), 12781–12790 (2001)
J.C. Bonner, M.E. Fisher, Linear magnetic chains with anisotropic coupling. Phys. Rev. 135(3A), A640 (1964)
B. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Z.M. Wang, D.W. Wang, P.J. Baker, F.L. Pratt, D.B. Zhu, Candidate quantum spin liquid due to dimensional reduction of a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice. Sci. Rep. 4 (2014)
S. Bala, S. Bhattacharya, A. Goswami, A. Adhikary, S. Konar, R. Mondal, Designing functional metal-organic frameworks by imparting a hexanuclear copper-based secondary building unit specific properties: structural correlation with magnetic and photocatalytic activity. Cryst. Growth Des. 14(12), 6391–6398 (2014)
P. Brandao, M.S. Reis, Z. Gai, A.M. dos Santos, Novel alkaline earth copper germanates with ferro and antiferromagnetic S = 1/2 chains. J. Solid State Chem. 198, 39–44 (2013)
S. Blundell, Magnetism in Condensed Matter. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2001)
J.B. Goodenough, An interpretation of the magnetic properties of the perovskite-type mixed crystals La1-Xsrxcoo3-λ. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 6(2–3), 287–297 (1958)
H.J. Koo, D. Dai, M.H. Whangbo, Importance of supersuperexchange interactions in determining the dimensionality of magnetic properties. Determination of strongly interacting spin exchange paths in A(2)CU(PO4)(2) (A = Ba, Sr), ACuP(2)O(7) (Ba, Ca, Sr, Pb), CaCuGe2O6, and Cu2UO2(PO4)(2) on the basis of qualitative spin dimer analysis. Inorg. Chem. 44(12), 4359–4365 (2005).
M.H. Whangbo, H.J. Koo, D. Dai, D. Jung, Interpretation of the magnetic structures of Cu2Te2O5 × 2 (X = Cl, Br) and Ca3.1Cu0.9RuO6 on the basis of electronic structure considerations: cases for strong super-superexchange interactions involving Cu2+ ions. Inorg. Chem. 42(12), 3898–3906 (2003)
J. Deisenhofer, R.M. Eremina, A. Pimenov, T. Gavrilova, H. Berger, M. Johnsson, P. Lemmens, H.A.K. von Nidda, A. Loidl, K.S. Lee, M.H. Whangbo, Structural and magnetic dimers in the spin-gapped system CuTe2O5. Phys. Rev. B 74(17) (2006)
H.J. Koo, K.S. Lee, M.H. Whangbo, Spin dimer analysis of the magnetic structures of Ba3Cr2O8, Ba3Mn2O8, Na4FeO4, and Ba2CoO4 with a three-dimensional network of isolated MO4 (M = Cr, Mn, Fe, Co) tetrahedra. Inorg. Chem. 45(26), 10743–10749 (2006)
R. Nath, K.M. Ranjith, J. Sichelschmidt, M. Baenitz, Y. Skourski, F. Alet, I. Rousochatzakis, A.A. Tsirlin, Hindered magnetic order from mixed dimensionalities in CuP2O6. Phys. Rev. B 89(1) (2014)
R. Nath, A.A. Tsirlin, E.E. Kaul, M. Baenitz, N. Buttgen, C. Geibel, H. Rosner, Strong frustration due to competing ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic interactions: Magnetic properties of M(VO)(2)(PO(4))(2) (M = Ca and Sr). Phys. Rev. B 78(2) (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (IF/01516/2013 and IF/00686/2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, A.M.L., Lin, Z. & Ferdov, S. Rapid and phase pure synthesis of microporous copper silicate (CuSH–1Na) with 12-ring channel system. J Porous Mater 25, 1309–1316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0541-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0541-8