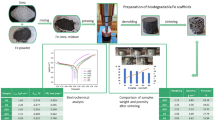
Abstract
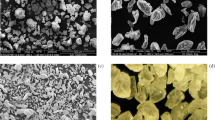
The iron open cell foams were synthesized by the replication method based on powder metallurgical technologies as biodegradable bone replacement material. Open cell metal foams provide extraordinary combinations of the properties. Samples containing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and Mg were produced with the aim to affect degradation rate and enhance the biocompatibility. The microstructure, corrosion behaviour and in vitro biocompatibilities were investigated by scanning electron microscopy, immersion tests in Hank’s solution during the time of 8 weeks, cytotoxicity and haemolysis tests. The addition of CNTs and Mg induced the higher surface inhomogeneity and roughness, which was more pronounced for Fe–Mg sample. The homogenous degradation on the whole surface was registered for bare iron sample, while progressive local corrosion sites were found on the surface of samples with CNTs and Mg. Highest corrosion rate was determined for Fe–Mg sample which came to be disintegrated after 3 weeks of immersion. The slowest degradation rate was detected for Fe–CNTs sample. The fast dieback of fibroblast cells was registered under static conditions in monolayer cell culture. However, all the experimental samples were found to be highly haemocompatible. Additionally, the haemolysis percentage value of about 2 % determined for Fe–Mg sample proved its good performance for blood vessel related cellular application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Purnama, H. Hermawan, J. Couet, D. Mantovani, Assessing the biocompatibility of degradable metallic materials: state-of-the-art and focus on the potential of genetic regulation. Acta Biomater. 6, 1800 (2010)
B. Wegener, B. Sievers, S. Utzschneider, P. Müller, V. Jansson, S. Rößler, B. Nies, G. Stephani, B. Kieback, P. Quadbeck, Microstructure, cytotoxicity and corrosion of powder-metallurgical iron alloys for biodegradable bone replacement materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 1789 (2011)
H. Hermawan, D. Mantovani, Degradable metallic biomaterials: the concept, current developments and future directions. Minerva Biotechnol. 21, 207 (2009)
A.H. Yusop, A.A. Bakir, N.A. Shaharom, M.R. Abdul Kadir, H. Hermawan, Porous biodegradable metals for hard tissue scaffolds: a review. Int. J. Biomater. Article ID 641430, p 10 (2012)
P. Quadbeck, G. Stephani, K. Kümmel, J. Adler, G. Standke, Synthesis and properties of open-celled metal foams. Mat. Sci. Forum. 534/536, 1005 (2007)
G. Song, Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 49/4, 1696 (2007)
M. Schinhammer, A.C. Hanzi, J.F. Loffler, P.J. Uggowitzer, Design strategy for biodegradable Fe-based alloys for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 6, 1705 (2010)
H. Hermawan, H. Alamdari, D. Mantovani, D. Dube, Iron-manganese: new class of degradable metallic biomaterials prepared by powder metallurgy. Powder Metall. 51, 38 (2008)
Y. Xin, C. Liu, X. Zhang, G. Tang, X. Tian, P.K. Chu, Corrosion behaviour of biomedical AZ91 magnesium alloy in simulated body fluids. J. Mater. Res. 22, 2004 (2007)
J. Levesque, H. Hermawan, D. Dube, D. Mantovani, Design of a pseudophysiological test bench specific to the development of biodegradable metallic biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 4, 284 (2008)
F. Witte, V. Kaese, H. Haferkamp, E. Switzer, A.M. Linderberg, C.J. Wirth, H. Windhagen, In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials 26, 3557 (2005)
M. Peuster, P. Wohlsein, M. Brügmann, M. Ehlerding, K. Seidler, C. Fink, H. Brauer, A. Fischer, G. Hausdorf, A novel approach to temporary stenting: degradable cardiovascular stents produced from corrodible metal-results 6–18 months after implantation into New Zealand white rabbits. Heart 86, 563 (2001)
J. Farack, C. Wolf-Brandstetter, S. Glorius, B. Nies, G. Standke, P. Quadbeck, H. Worch, D. Scharnweber, The effect of perfusion culture on proliferation and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on biocorrodible bone replacement material. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 1767 (2011)
T.L. Nguyen, M.P. Staiger, G.J. Dia, T.B.F. Woodfield, A novel manufacturing route for fabrication of topologically-ordered porous magnesium scaffolds. Adv. Eng. Mater. 13, 872 (2011)
L. Tan, M. Gong, F. Zheng, B. Zhang, K. Yang, Study on compression behavior of porous magnesium used as bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomed. Mater. 4, Article ID 015016 (2009)
S.C. Keal, K. Vince, M.A. Hodgson, Biodegradable surgical implants based on magnesium alloys—a review of current research. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 4, 012011 (2009)
M.P. Staiger, A.M. Pietak, J. Huadmai, G. Dias, Magnesium and its alloys as orthopaedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials 27, 1728 (2006)
L. Li, J. Gao, Y. Wang, Evaluation of cytotoxicity and corrosion behavior of alkaliheat-treated magnesium in simulated body fluid. Surf. Coat. Technol. 185, 92 (2004)
G.B. Stroganov, E. Savitsky, T. Mikhailovich, M. Nina, V. Terekhova, V. Fedorovna, Magnesium-base alloys for use in bone surgery. US Patent no. 3, 687, 135 (1972)
Y. Yamasaki, Y. Yoshida, M. Okazaki, A. Shimazu, T. Uchida, T. Kubo, Y. Akagawa, Y. Hamada, J. Takahashi, N. Matsuura, Synthesis of functionally graded MgCO3 apatite accelerating osteoblast adhesion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 62, 99 (2002)
H. Zreiqat, C.R. Howlett, A. Zannettino, P. Evans, G. Schulze-Tanzil, C. Knabe, M. Shakibaei, Mechanisms of magnesium-stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 62, 175 (2002)
P.A. Tran, L. Zhang, T.J. Webster, Carbon nanofibers and carbon nanotubes in regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 61, 1097 (2009)
K. Sahithi, M. Swetha, K. Ramasamy, N. Srinivasan, N. Selvamurugan, Polymeric composites containing carbon nanotubes for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 46, 281 (2010)
T. Shokuhfar, A. Makradi, E. Titus, G. Cabral, S. Ahzi, A.C. Sousa, S. Belouettar, J. Gracio, Prediction of the mechanical properties of HA/PNMA/CNTs nano-composite. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 4279 (2008)
L.P. Zanello, B. Zhao, H. Hu, R.C. Haddon, Bone cell proliferation on carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 6, 562 (2006)
W. Tutak, K.H. Park, A. Vasilov, V. Starovoytov, G. Fanchini, S.Q. Cai, N.C. Partridge, F. Sesti, M. Chhowalla, Toxicity induced enhanced extracellular matrix production in osteoblastic cells cultured on single-walled carbon nanotube networks. Nanotechnology 20, 255101 (2009)
B. Sitharaman, X. Shi, L.A. Tran, P.P. Spicer, I. Rusakova, L.J. Wilson, A.G. Mikos, Injectable in situ cross-linkable nanocomposites of biodegradable polymers and carbon nanostructures for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 18, 655 (2007)
J.J. Jacobs, J.L. Gilbert, R.M. Urban, Current concepts review—corrosion of metal orthopaedic implants. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 80, 268 (1998)
G. Ryan, A. Pandit, D.P. Apatsidis, Fabrication methods of porous metals for use in orthopaedic applications. Biomaterials 27, 2651 (2006)
P. Quadbeck, R. Hauser, K. Kümmel, G. Standke, G. Stephani, B. Nies, S. Rößler, B. Wegener, Iron based cellular metals for degradable synthetic bone replacement. Proceedings of the Powder Metallurgy World Congress (PM’10), Florence, Italy (2010)
C.S.Y. Jee, Z.X. Guo, J.R.G. Evans, N. Özgüven, Preparation of high porosity metal foams. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 31, 1345 (2000)
T. Murakami, K. Ohara, T. Narushima, C. Ouchi, Development of a new method for manufacturing iron foam using gases generated by reduction of iron oxide. Mater. Trans. 48, 2937 (2007)
J. Banhart, Manufacture, characterisation and application of cellular metals and metallic foams. Prog. Mater Sci. 46, 559 (2001)
X.N. Gu, W.R. Zhou, Y.F. Zheng, Y. Liu, Y.X. Li, Degradation and cytotoxicity of lotus-type porous pure magnesium as potential tissue engineering scaffold material. Mater. Lett. 64, 1871 (2010)
F. Witte, H. Ulrich, M. Rudert, E. Willbold, Biodegradable magnesium scaffolds: part I: appropriate inflammatory response. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 81, 748 (2007)
W. Khan, M. Kapoor, N. Kumar, Covalent attachment of proteins to functionalized polypyrrole-coated metallic surfaces for improved biocompatibility. Acta Biomater. 3, 541 (2007)
W.G. Brodbeck, M.S. Shive, E. Colton, Y. Nakayama, T. Matsuda, J.M. Anderson, Influence of biomaterial surface chemistry on the apoptosis of adherent cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 55, 661 (2001)
Y. Li, K.G. Neoh, E.T. Kang, Plasma protein adsorption and thrombus formation on surface functionalized polypyrrole with and without electrical stimulation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 275, 488 (2004)
S. Torgerson, N.R. Gjerdet, Retrieval study of stainless steel and titanium miniplates and screws used in maxillofacial surgery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 5, 256 (1994)
M. Schinhammer, J. Hofstetter, C. Wegmann, F. Moszner, J. Löffler, P.J. Uggowitzer, On the immersion testing of degradable implant materials in simulated body fluid: active pH regulation using CO2. Adv. Eng. Mater. 15, 434 (2013)
B. Liu, Y.F. Zheng, Effects of alloying elements (Mn Co., Al, W, Sn, B, C and S) on biodegradability and in vitro biocompatibility of pure iron. Acta Biomater. 7, 1407 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Projects APVV-0677-11 and APVV-0280-11 of the Slovak Research and Development Agency and Project VEGA 1/0211/12 of the Slovak Scientific Grant Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oriňák, A., Oriňáková, R., Králová, Z.O. et al. Sintered metallic foams for biodegradable bone replacement materials. J Porous Mater 21, 131–140 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-013-9757-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-013-9757-4