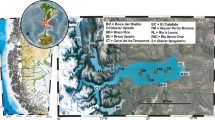
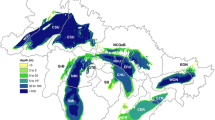
Abstract
Reconstructing climate from lake sediments can be challenging, because the response of lakes and various components of lake systems are mediated by non-climatic factors, such as geomorphic and hydrologic stetting. As a result, the magnitude of lake response to climatic forcing may be non-linear. In addition, changes in the lake system associated with the aging process or non-climatic influences may alter the response to a given climate perturbation. These non-linear and non-stationary characteristics can produce spatial heterogeneity in the pattern and timing of inferred change. One approach for generating regionally robust climatic interpretations from lakes is to increase coordinated efforts to generate and synthesize large data sets, so that localized influences can be more clearly distinguished from broad-scale regional patterns. This approach will be most successful for evaluating climate variation at multi-decadal or longer temporal scales; the climatic interpretation of higher frequency limnological variation can be more complicated, because of dating uncertainties and differential response times of individual proxies and systems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebly F, Fritz SC (2007) Paleohydrology of Kangerlussuaq (Sondre Stromfjord), west Greenland during the last ∼8000 years. Holocene (accepted)
Almendinger JE (1993) A groundwater model to explain past lake levels at Parkers Prairie, Minnesota, USA. Holocene 3:105–115
Bigler C, Larocque I, Peglar SM, Birks HJB, Hall RI (2002) Quantitative multiproxy assessment of long-term patterns of Holocene environmental change from a small lake near Abisko, northern Sweden. Holocene 12:481–496
Binford MW, Deevey ES (1983) Paleolimnology: an historical perspective on lacustrine ecosystems. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 14:255–286
Brown KJ, Clark JS, Grimm EC, Donovan JJ, Mueller PG, Hansen B, Stefanova I (2005) Fire cycles in North American interior grasslands and their relation to prairie drought. Proc Nat Acad Sci 102:8865–8870
Cohen AS (2003) Paleolimnology: the history and evolution of lake systems. Oxford University Press, New York
Dean WE (1999) The carbon cycle and biogeochemical dynamics in lake sediments. J Paleolimnol 21:375–393
Digerfeldt G, Almendinger JE, Bjorck S (1993) Reconstruction of past lake levels and their relation to groundwater hydrology in the Parkers Prairie sandplain, west-central Minnesota. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 94:99–118
Donovan JJ, Smith AJ, Panek VA, Engstrom DR, Ito E (2002) Climate-driven hydrologic transients in lake sediment records: calibration of groundwater conditions using 20th century drought. Quat Sci Rev 21:605–624
Ekdahl E, Fritz SC, Baker PA, Rigsby CA, Coley K (2007) Holocene multi-decadal to millennial-scale hydrologic variability on the South American Altiplano. Holocene (accepted)
Engstrom DR, Fritz SC, Almendinger JE, Juggins S (2000) Chemical and biological trends during lake evolution in recently deglaciated terrain. Nature 408:161–166
Eugster HP, Hardie LA (1978) Saline lakes. In: Lerman A (ed) Lakes, chemistry geology physics. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 237–293
Fritz SC, Ito E, Yu Z, Laird KR, Engstrom DR (2000) Hydrologic variation in the northern Great Plains during the last two millennia. Quat Res 53:175–184
Fritz SC, Metcalfe SE, Dean W (2001) Holocene climate patterns in the Americas inferred from paleolimnological records. In: Markgraf V (ed) Interhemispheric climate linkages. Academic Press, New York, pp 241–263
Gorham E, Dean WE, Sanger JE (1983) The chemical composition of lakes in the north-central United States. Limnol Oceanogr 28:287–301
Hodell DA, Brenner M, Curtis JH, Guilderson T (2001) Solar forcing of drought frequency in the Maya lowlands. Science 292:1367–1370
Laird KR, Fritz SC, Maasch KA, Cumming BF (1996) Greater drought intensity and frequency before AD 1200 in the Northern Great Plains, USA. Nature 384:552–555
McGowan S, Ryves DB, Anderson NJ (2003) Holocene records of effective precipitation in West Greenland. Holocene 13:239–250
Reed JM, Roberts N, Leng MJ (1999) An evaluation of the diatom response to Late Quaternary environmental change in two lakes in the Konya Basin, Turkey, by comparison with stable isotope data. Quat Sci Rev 18:631–646
Renberg I (1990) A 12,600 year perspective on the acidification of Lilla Oresjon, southwest Sweden. Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond B 327:357–361
Russell JM, Johnson TC (2007) Little Ice Age drought in equatorial Africa: ITCZ migrations and ENSO variability. Geology 35:21–24
Saros JE, Interlandi SJ, Wolfe AP, Engstrom DR (2003) Recent changes in the diatom community structure of lakes in the Beartooth Mountain Range (USA). Arctic Ant Alpine Res 35:18–23
Saros JE, Michel TJ, Interlandi SJ, Wolfe AP (2005) Resource requirements of Asterionella formosa and Fragilaria crotonensis in oligotropic alpine lakes: implications for recent phytoplankton community reoroganizations. Can J Fish Aq Sci 62:1681–1689
Shuman B, Bartlein P, Logar N, Newby P, Webb TW (2002) Parallel climate and vegetation responses to the early Holocene collapse of the Laurentide Ice Sheet. Quat Sci Rev 21:1793–1805
Smith AJ, Donovan JJ, Ito E, Engstrom DR, Panek VA (2002) Climate-driven hydrologic transients in lake sediment records: multiproxy record of mid-Holocene drought. Quat Sci Rev 21:625–646
Smol JP, Wolfe AP, John H, Birks B, Douglas MSV, Jones VJ, Korhola A, Pienitz R, Ruhland K, Sorvari S, Antoniades D, Brooks SJ, Fallu M, Hughes M, Keatley BE, Laing TE, Michelutti N, Nazarova L, Nyman M, Paterson AM, Perren B, Quinlan R, Rautio M, Saulnier-Talbot E, Siitonen S, Solovieva N, Weckstrom J (2005) Climate-driven regime shifts in the biological communities of Arctic lakes. Proc Nat Acad Sci 102:4397–4402
Stevens LR, Stone JR, Campbell J, Fritz SC (2006) A 2200-yr record of hydrologic variability from Foy Lake, Montana, USA, inferred from diatom and geochemical data. Quat Res 65:264–274
Stone JR, Fritz SC (2004) Three-dimensional modeling of lacustrine diatom habitat areas: improving paleolimnological interpretation of planktic:benthic ratios. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1540–1548
Stone JR, Fritz SC (2006) Multidecadal drought and Holocene climate instability in the Rocky Mountains. Geology 34:409–412
Telford RJ, Lamb HF, Mohammed MU (1999) Diatom-derived palaeoconductivity estimates for Lake Awassa, Ethiopia: evidence for pulsed inflows of saline groundwater? J Paleolimnol 21:409–421
Verschuren D, Laird KR, Cumming BF (2000) Rainfall and drought in equatorial east Africa during the past 1,100 years. Nature 403:410–414
Westover KS (2006) Diatom-inferred records of paleolimnlogical and Holocene paleoclimate variability from the Altai Mountains (Siberia) and Columbia Mountains (British Columbia). Ph. D. Thesis, Department of Geosciences, University of Nebraska, Lincoln
Wolfe AP, Baron JS, Cornett RJ (2001) Anthropogenic nitrogen deposition induces rapid ecological changes in alpine lakes of the Colorado Front Range (USA). J Paleolimnol 25:1–7
Zlotnik VA, Burbach M, Swinehart J, Bennett D, Fritz SC, Loope DB, Olaguera F (2007) A case study of direct push methods for aquifer characterization in dune-lake environments of the Nebraska Sand Hills. Environ Eng Geol 13, in press
Acknowledgments
I thank John Smol and Bill Last for encouraging me to submit this manuscript and Frank Aeby, Erik Ekdahl, Jeffery Stone, and Karlyn Westover for assistance with figures. A Bullard Fellowship at Harvard Forest (Harvard University) and NSF Grant EAR-0602154 provided partial support during the writing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is based on a plenary talk at the 10th International Paleolimnology Conference in Duluth, Minnesota in July 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fritz, S.C. Deciphering climatic history from lake sediments. J Paleolimnol 39, 5–16 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-007-9134-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-007-9134-x