Abstract
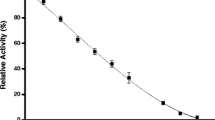
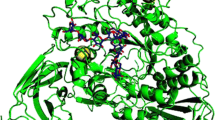
α-Glucosidase is a critical metabolic enzyme that produces glucose molecules by catalyzing carbohydrates. The aim of this study is to elucidate biological toxicity of Cd2+ based on α-glucosidase activity and conformational changes. We studied Cd2+-mediated inactivation as well as conformational modulation of α-glucosidase by using kinetics coupled with simulation of molecular dynamics. The enzyme was significantly inactivated by Cd2+ in a reversibly binding behavior, and Cd2+ binding induced a non-competitive type of inhibition reaction (the K i was calculated as 0.3863 ± 0.033 mM). Cd2+ also modulated regional denaturation of the active site pocket as well as overall partial tertiary structural change. In computational simulations using molecular dynamics, simulated introduction of Cd2+ induced in a depletion of secondary structure by docking Cd2+ near the saccharides degradation at the active site, suggesting that Cd2+ modulating enzyme denaturation. The present study elucidated that the binding of Cd2+ triggers conformational changes of α-glucosidase as well as inactivates catalytic function, and thus suggests an explanation of the deleterious effects of Cd2+ on α-glucosidase.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- pNPG:
-
p-Nitrophenyl α-d-glucopyranoside
- pNP:
-
4-Nitrophenol
- ANS:
-
1-Anilino-8-naphthalenesulfonate
- MD:
-
Molecular dynamics
References
Chiba S (1997) Molecular mechanism in alpha-glucosidase and glucoamylase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:1233–1239
Dasouki M, Jawdat O, Almadhoun O, Pasnoor M, McVey AL, Abuzinadah A, Herbelin L, Barohn RJ, Dimachkie MM (2014) Pompe disease: literature review and case series. Neurol Clin 32:751–776
Schoser B, Hill V, Raben N (2008) Therapeutic approaches in glycogen storage disease type II/Pompe disease. Neurotherapeutics 5:569–578
Vissing J, Lukacs Z, Straub V (2013) Diagnosis of Pompe disease: muscle biopsy vs blood-based assays. JAMA Neurol 70:923–927
Zeng YF, Lü ZR, Yan L, Oh S, Yang JM, Lee J, Ye ZM (2012) Towards alpha-glucosidase folding induced by trifluoroethanol: kinetics and computational prediction. Process Biochem 47:2284–2290
Wu XQ, Xu H, Yue H, Liu KQ, Wang XY (2009) Inhibition kinetics and the aggregation of alpha-glucosidase by different denaturants. Protein J 28:448–456
Wu XQ, Wang J, Lü ZR, Tang HM, Park D, Oh SH, Bhak J, Shi L, Park YD, Zou F (2010) Alpha-glucosidase folding during urea denaturation: enzyme kinetics and computational prediction. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:1341–1355
Zeng YF, Lee J, Si YX, Yan L, Kim TR, Qian GY, Lü ZR, Ye ZM, Yin SJ (2012) Inhibitory effect of Zn2+ on α-glucosidase: Inhibition kinetics and molecular dynamics simulation. Process Biochem 47:2510–2517
Zhang X, Shi L, Li X, Sheng Q, Yao L, Shen D, Lü ZR, Zhou HM, Park YD, Lee J, Zhang Q (2014) Effect of Ca2+ on the activity and structure of α-glucosidase: inhibition kinetics and molecular dynamics simulations. J Biosci Bioeng 117:696–705
Li X, Lü ZR, Shen D, Zhan Y, Yang JM, Park YD, Zhou HM, Sheng Q, Lee J (2014) The inhibitory role of Co2+ on α-glucosidase: inhibition kinetics and molecular dynamics simulation integration study. Process Biochem 49:1913–1919
Li X, Lü ZR, Wang W, Han XP, Yang JM, Park YD, Zhou HM, Sheng Q, Lee J (2015) Effect of Ba2+ on the activity and structure of α-glucosidase: inhibition kinetics and molecular dynamics simulation. Process Biochem 50:582–588
Arita A, Costa M (2009) Epigenetics in metal carcinogenesis: nickel, arsenic, chromium and cadmium. Metallomics 1:222–228
Satoh M, Koyama H, Kaji T, Kito H, Tohyama C (2002) Perspectives on cadmium toxicity research. Tohoku J Exp Med 196:23–32
Takebayashi S, Jimi S, Segawa M, Takaki A (2003) Mitochondrial DNA deletion of proximal tubules is the result of itai–itai disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 7:18–26
Feki-Tounsi M, Hamza-Chaffai A (2014) Cadmium as a possible cause of bladder cancer: a review of accumulated evidence. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:10561–11073
Matovic V, Buha A, Dukic-Cosic D, Bulat Z (2015) Insight into the oxidative stress induced by lead and/or cadmium in blood, liver and kidneys. Food Chem Toxicol 78:130–140
Alterio V, Langella E, De Simone G, Monti SM (2015) Cadmium-containing carbonic anhydrase CDCA1 in marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. Mar Drugs 13:1688–1697
Xu Y, Morel FM (2013) Cadmium in marine phytoplankton. Met Ions Life Sci 11:509–528
Kim TR, Oh S, Yang JS, Lee S, Shin S, Lee J (2012) A simplified homology-model builder toward highly protein-like structures: an inspection of restraining potentials. J Comput Chem 33:1927–1935
Brooks BR, Brooks CL 3rd, Mackerell AD Jr, Nilsson L, Petrella RJ, Roux B, Won Y, Archontis G, Bartels C, Boresch S et al (2009) CHARMM: the biomolecular simulation program. J Comput Chem 30:1545–1614
Acknowledgments
Dr. Hang Mu was supported by a grant from the Science and Technology Planning Project of Jiaxing (No. 2013AY21032). Dr. Jinhyuk Lee was supported through grants from the KOBIC Research Support Program, KRIBB Research Initiative Program, and the Pioneer Research Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded through the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2013M3C1A3064780). Dr. Yong-Doo Park was supported through a grant from the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, “Towards studying the function of C3dg protein and elucidating its role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis” (Grant No. LY14H110001) and a fund from the Science and Technology Planning Project of Jiaxing (No. 2014AY21026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tao Luo and Jinhyuk Lee authors have equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, T., Lee, J., Lü, ZR. et al. Effect of Cadmium Ion on alpha-Glucosidase: An Inhibition Kinetics and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Integration Study. Protein J 35, 218–224 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-016-9664-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-016-9664-z