Abstract
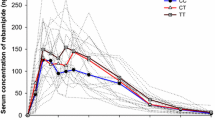
The objective of this study was to perform population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of gabapentin in healthy Korean subjects and to investigate the possible effect of genetic polymorphisms (1236C > T, 2677G > T/A, and 3435C > T) of ABCB1 gene on PK parameters of gabapentin. Data were collected from bioequivalence studies, in which 173 subjects orally received three different doses of gabapentin (300, 400, and 800 mg). Only data from reference formulation were used. Population pharmacokinetics (PKs) of gabapentin was estimated using a nonlinear mixed-effects model (NONMEM). Gabapentin showed considerable inter-individual variability (from 5.2- to 8.7-fold) in PK parameters. Serum concentration of gabapentin was well fitted by a one-compartment model with first-order absorption and lag time. An inhibitory Emax model was applied to describe the effect of dose on bioavailability. The oral clearance was estimated to be 11.1 L/h. The volume of distribution was characterized as 81.0 L. The absorption rate constant was estimated at 0.860 h−1, and the lag time was predicted at 0.311 h. Oral bioavailability was estimated to be 68.8% at dose of 300 mg, 62.7% at dose of 400 mg, and 47.1% at dose of 800 mg. The creatinine clearance significantly influenced on the oral clearance (P < 0.005) and ABCB1 2677G > T/A genotypes significantly influenced on the absorption rate constant (P < 0.05) of gabapentin. However, ABCB1 1236C > T and 3435C > T genotypes showed no significant effect on gabapentin PK parameters. The results of the present study indicate that the oral bioavailability of gabapentin is decreased when its dosage is increased. In addition, ABCB1 2677G > T/A polymorphism can explain the substantial inter-individual variability in the absorption of gabapentin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mao J, Chen LL (2000) Gabapentin in pain management. Anesth Analg 91:680–687. doi:10.1213/00000539-200009000-00034
Mellegers MA, Furlan AD, Mailis A (2001) Gabapentin for neuropathic pain: systematic review of controlled and uncontrolled literature. Clin J Pain 17:284–295. doi:10.1097/00002508-200112000-00002
McLean MJ, Gidal BE (2003) Gabapentin dosing in the treatment of epilepsy. Clin Ther 25:1382–1406. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(03)80127-3
Pandya KJ, Morrow GR, Roscoe JA, Zhao H, Hickok JT, Pajon E, Sweeney TJ, Banerjee TK, Flynn PJ (2005) Gabapentin for hot flashes in 420 women with breast cancer: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 366:818–824. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67215-7
Cheikh Hassan HI, Brennan F, Collett G, Josland EA, Brown MA (2015) Efficacy and safety of gabapentin for uremic pruritus and restless legs syndrome in conservatively managed patients with chronic kidney disease. J Pain Symptom Manag 49:782–789. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2014.08.010
Kleinman NL, Sadosky A, Seid J, Martin RC, Labiner DM (2012) Costs, work absence, and adherence in patients with partial onset seizures prescribed gabapentin or pregabalin. Epilepsy Res 102:13–22. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2012.04.019
Nonoda Y, Iwasaki T, Ishii M (2014) The efficacy of gabapentin in children of partial seizures and the blood levels. Brain Dev 36:194–202. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2013.04.006
Tallian KB, Nahata MC, Lo W, Tsao C-Y (2004) Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in paediatric patients with uncontrolled seizures. J Clin Pharm Ther 29:511–515. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2004.00596.x
Yamauchi T, Kaneko S, Yagi K, Sase S (2006) Treatment of partial seizures with gabapentin: double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 60:507–515. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2006.01553.x
Dickens D, Webb SD, Antonyuk S, Giannoudis A, Owen A, Rädisch S, Hasnain SS, Pirmohamed M (2013) Transport of gabapentin by LAT1 (SLC7A5). Biochem Pharmacol 85:1672–1683. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2013.03.022
McLean MJ (1995) Gabapentin. Epilepsia 36(Suppl 2):S73–S86
Gidal BE, DeCerce J, Bockbrader HN, Gonzalez J, Kruger S, Pitterle ME, Rutecki P, Ramsay RE (1998) Gabapentin bioavailability: effect of dose and frequency of administration in adult patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 31:91–99. doi:10.1016/S0920-1211(98)00020-5
Bockbrader HN, Wesche D, Miller R, Chapel S, Janiczek N, Burger P (2010) A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. Clin Pharmacokinet 49:661–669. doi:10.2165/11536200-000000000-00000
Stewart BH, Kugler AR, Thompson PR, Bockbrader HN (1993) A saturable transport mechanism in the intestinal absorption of gabapentin is the underlying cause of the lack of proportionality between increasing dose and drug levels in plasma. Pharm Res 10:276–281
Berry DJ, Beran RG, Plunkeft MJ, Clarke LA, Hung WT (2003) The absorption of gabapentin following high dose escalation. Seizure 12:28–36
Gabapentin - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses. https://www.drugs.com/pro/gabapentin.html. Accessed 3 Aug 2017
Vollmer KO, von Hodenberg A, Kölle EU (1986) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of gabapentin in rat, dog and man. Arzneimittelforschung 36:830–839
Ouellet D, Bockbrader HN, Wesche DL, Shapiro DY, Garofalo E (2001) Population pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in infants and children. Epilepsy Res 47:229–241. doi:10.1016/S0920-1211(01)00311-4
Lal R, Sukbuntherng J, Luo W, Tovera J, Lassauzet ML, Cundy KC (2013) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of gabapentin after administration of gabapentin enacarbil. J Clin Pharmacol 53:29–40. doi:10.1177/0091270012439209
Gidal BE, Radulovic LL, Kruger S, Rutecki P, Pitterle M, Bockbrader HN (2000) Inter- and intra-subject variability in gabapentin absorption and absolute bioavailability. Epilepsy Res 40:123–127. doi:10.1016/S0920-1211(00)00117-0
Browne TR, Holmes GL (2001) Epilepsy. N Engl J Med 344:1145–1151. doi:10.1056/NEJM200104123441507
Kwan P, Brodie MJ (2000) Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N Engl J Med 342:314–319. doi:10.1056/NEJM200002033420503
Regesta G, Tanganelli P (1999) Clinical aspects and biological bases of drug-resistant epilepsies. Epilepsy Res 34:109–122
Sills GJ, Kwan P, Butler E, de Lange ECM, van den Berg D-J, Brodie MJ (2002) P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of antiepileptic drugs: preliminary studies in mdr1a knockout mice. Epilepsy Behav 3:427–432. doi:10.1016/S1525-5050(02)00511-5
Meng H, Guo G, Ren J, Zhou H, Ge Y, Guo Y (2011) Effects of ABCB1 polymorphisms on plasma carbamazepine concentrations and pharmacoresistance in Chinese patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 21:27–30. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2011.02.015
Bellamy WT (1996) P-glycoproteins and multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36:161–183. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.36.040196.001113
Germann UA, Pastan I, Gottesman MM (1993) P-glycoproteins: mediators of multidrug resistance. Semin Cell Biol 4:63–76
Chen CJ, Chin JE, Ueda K, Clark DP, Pastan I, Gottesman MM, Roninson IB (1986) Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell 47:381–389
Allikmets R, Gerrard B, Hutchinson A, Dean M (1996) Characterization of the human ABC superfamily: isolation and mapping of 21 new genes using the expressed sequence tags database. Hum Mol Genet 5:1649–1655
Cordon-Cardo C, O’Brien JP, Boccia J, Casals D, Bertino JR, Melamed MR (1990) Expression of the multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human normal and tumor tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 38:1277–1287. doi:10.1177/38.9.1974900
Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC (1987) Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7735–7738
Sparreboom A, van Asperen J, Mayer U, Schinkel AH, Smit JW, Meijer DK, Borst P, Nooijen WJ, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O (1997) Limited oral bioavailability and active epithelial excretion of paclitaxel (Taxol) caused by P-glycoprotein in the intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2031–2035
Chowbay B, Cumaraswamy S, Cheung YB, Zhou Q, Lee EJD (2003) Genetic polymorphisms in MDR1 and CYP3A4 genes in Asians and the influence of MDR1 haplotypes on cyclosporin disposition in heart transplant recipients. Pharmacogenetics 13:89–95
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmöller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U (2000) Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3473–3478. doi:10.1073/pnas.050585397
Wolf SJ, Bachtiar M, Wang J, Sim TS, Chong SS, Lee CGL (2011) An update on ABCB1 pharmacogenetics: insights from a 3D model into the location and evolutionary conservation of residues corresponding to SNPs associated with drug pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenomics J 11:315–325. doi:10.1038/tpj.2011.16
Kim RB, Leake BF, Choo EF, Dresser GK, Kubba SV, Schwarz UI, Taylor A, Xie HG, McKinsey J, Zhou S, Bin Lan L, Schuetz JD, Schuetz EG, Wilkinson GR (2001) Identification of functionally variant MDR1 alleles among European Americans and African Americans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 70:189–199. doi:10.1067/mcp.2001.117412
Anglicheau D, Verstuyft C, Laurent-Puig P, Becquemont L, Schlageter M-H, Cassinat B, Beaune P, Legendre C, Thervet E (2003) Association of the multidrug resistance-1 gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms with the tacrolimus dose requirements in renal transplant recipients. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1889–1896
Zheng H, Webber S, Zeevi A, Schuetz E, Zhang J, Lamba J, Bowman P, Burckart GJ (2002) The MDR1 polymorphisms at exons 21 and 26 predict steroid weaning in pediatric heart transplant patients. Hum Immunol 63:765–770
Kurata Y, Ieiri I, Kimura M, Morita T, Irie S, Urae A, Ohdo S, Ohtani H, Sawada Y, Higuchi S, Otsubo K (2002) Role of human MDR1 gene polymorphism in bioavailability and interaction of digoxin, a substrate of P-glycoprotein*. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:209–219. doi:10.1067/mcp.2002.126177
Siegmund W, Ludwig K, Giessmann T, Dazert P, Schroeder E, Sperker B, Warzok R, Kroemer HK, Cascorbi I (2002) The effects of the human MDR1 genotype on the expression of duodenal P-glycoprotein and disposition of the probe drug talinolol. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:572–583. doi:10.1067/mcp.2002.127739
Sakaeda T, Nakamura T, Horinouchi M, Kakumoto M, Ohmoto N, Sakai T, Morita Y, Tamura T, Aoyama N, Hirai M, Kasuga M, Okumura K (2001) MDR1 genotype-related pharmacokinetics of digoxin after single oral administration in healthy Japanese subjects. Pharm Res 18:1400–1404
Verstuyft C, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Kerb R, Brinkmann U, Jaillon P, Funck-Brentano C, Becquemont L (2003) Digoxin pharmacokinetics and MDR1 genetic polymorphisms. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 58:809–812. doi:10.1007/s00228-003-0567-5
Drescher S, Schaeffeler E, Hitzl M, Hofmann U, Schwab M, Brinkmann U, Eichelbaum M, Fromm MF (2002) MDR1 gene polymorphisms and disposition of the P-glycoprotein substrate fexofenadine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 53:526–534. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01591.x
Kang H-A, Chol H-Y, Lee Y-B (2007) The effect of MDR1 G2677T/A polymorphism on pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in healthy Korean subjects. Arch Pharm Res 30:96–101. doi:10.1007/BF02977784
Carlsson KC, van de Schootbrugge M, Eriksen HO, Moberg ER, Karlsson MO, Hoem NO (2009) A population pharmacokinetic model of gabapentin developed in nonparametric adaptive grid and nonlinear mixed effects modeling. Ther Drug Monit 31:86–94. doi:10.1097/FTD.0b013e318194767d
Papathanasiou T, Juul RV, Gabel-Jensen C, Kreilgaard M, Lund TM (2016) Population pharmacokinetic modelling of morphine, gabapentin and their combination in the rat. Pharm Res 33:2630–2643. doi:10.1007/s11095-016-1988-z
Cho HY, Kang HA, Lee YB (2006) Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence evaluation of two gabapentin preparations after a single oral dose in healthy Korean volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 44:386–392
Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I (2001) Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69:169–174. doi:10.1067/mcp.2001.114164
Mosteller RD (1987) Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N Engl J Med 317:1098. doi:10.1056/NEJM198710223171717
Buchman BP, Sallis JF, Criqui MH, Dimsdale JE, Kaplan RM (1991) Physical activity, physical fitness, and psychological characteristics of medical students. J Psychosom Res 35:197–208
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31–41
Avdeef A (2001) Physicochemical profiling (solubility, permeability and charge state). Curr Top Med Chem 1:277–351
Camenisch G, Folkers G, van de Waterbeemd H (1996) Review of theoretical passive drug absorption models: historical background, recent developments and limitations. Pharm Acta Helv 71:309–327. doi:10.1016/S0031-6865(96)00031-3
Ueda CT, Lemaire M, Gsell G, Misslin P, Nussbaumer K (1984) Apparent dose-dependent oral absorption of cyclosporin a in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 5:141–151. doi:10.1002/bdd.2510050207
Wetterich U, Spahn-Langguth H, Mutschler E, Terhaag B, Rösch W, Langguth P (1996) Evidence for intestinal secretion as an additional clearance pathway of talinolol enantiomers: concentration- and dose-dependent absorption in vitro and in vivo. Pharm Res 13:514–522. doi:10.1023/A:1016029601311
Blum RA, Comstock TJ, Sica DA, Schultz RW, Keller E, Reetze P, Bockbrader H, Tuerck D, Busch JA, Reece PA (1994) Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in subjects with various degrees of renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther 56:154–159
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education (2017RIDIAB04035667).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Appendix
Appendix
Extraction of the codes used in modeling drug absorption | ||
|---|---|---|
$PK | ||
; ABCB1-DEFINITION START | ||
IF(EX21.EQ. 1) COEX21 = 1 | ; Subjects of GG group | |
IF(EX21.EQ. 2) COEX21 = 1 | ; Subjects of GT, GA group | |
IF(EX21.EQ. 3) COEX21 = 1 + THETA(8) | ; Subject of TT, AT group | |
; ABCB1-DEFINITION END | ||
TVCL | = THETA(1)* (CRCL/106.3)**THETA(7) | ; Clearance |
CL | = TVCL * EXP(ETA(1)) | |
TVV | = THETA(2) | ; Volume of distribution |
V | = TVV * EXP(ETA(2)) | |
TVKA | = THETA(3)* COEX21 | ; Absorption rate constant |
KA | = TVKA * EXP(ETA(3)) | |
TVLG | = THETA(4) | ; Lag time |
ALAG1 | = TVLG * EXP(ETA(4)) | |
IMAX | = THETA(5) | ; Maximum inhibition of dose on bioavailability |
ID50 | = THETA(6) * EXP(ETA(5)) | ; Dose which produces 50% of maximum inhibition effect |
F1 | = 1 – IMAX * DOSE/(ID50 + DOSE) | ; Bioavailability |
S2 | = V | ; Scaling factor |
$ERROR | ||
FLAG = 0 | ||
IF (F. Equation 0) FLAG = 1 | ||
IPRED = LOG(F + FLAG) | ||
Y = (1 − FLAG)*IPRED + EPS(1) | ||
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, P., Yoo, HD., Ngo, L. et al. Population pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in healthy Korean subjects with influence of genetic polymorphisms of ABCB1 . J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 44, 567–579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-017-9549-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-017-9549-6