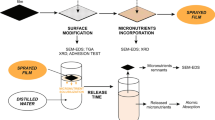
Abstract
Iron is an essential micronutrient for higher plants. Although abundant in most soils, Fe3+ is not available for plant uptake, because of its poor solubility. Ferrous sulfate is a fertilizer used for crops but, Fe2+ is readily oxidized to the plant-unavailable ferric form. It is therefore important to provide Fe2+ to plants, minimizing the loss of this nutrient by oxidation in Fe3+. This paper reports the development of a composite material consisting of a matrix (PLARAM), obtained by the chemical modification of poly(lactic acid), capable of retaining ferrous carbonate (siderite) within PLARAM (PLARAMFe). From the matrix, Fe2+ is released into the soil, enhancing its bioavailability. PLARAM and PLARAMFe films were obtained and their water wettability was studied. One side of the films was more hydrophilic than the other, turning this material attractive as a protective film when it is necessary to avoid loss of humidity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castro-Aguirre E, Iñiguez-Franco F, Samsudin H, Fang X, Auras R (2016) Poly(lactic acid)—mass production, processing, industrial applications, and end of life. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 107:333–366
Jamshidian M, Tehrany EA, Imran M, Jacquot M, Desobry S (2010) Poly-lactic acid: production, applications, nanocomposites, and release studies. Compr Rev Food Sci F 9(5):552–571
Sin LT, Rahmat AR, Rahman WAWA (2013) 1—overview of poly(lactic acid). In: Polylactic acid. William Andrew Publishing, Oxford, pp 1–70
Sinha Ray S, Okamoto M (2003) Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: a review from preparation to processing. Progr Polym Sci 28(11):1539–1641
Pluta M, Galeski A, Alexandre M, Paul MA, Dubois P (2002) Polylactide/montmorillonite nanocomposites and microcomposites prepared by melt blending: structure and some physical properties. J Appl Polym Sci 86(6):1497–1506
Sabliov C, Chen H, Yada R (2015) Nanotechnology and functional foods: effective delivery of bioactive ingredients. Wiley, Chichester
Helfferich FG (1962) Ion exchange. McGraw-Hill, New York
Del Campilllo Garcia MC, Sanchez Alcala I, Barron de la Torre V, Torrent Castelet J, Delgado Garcia A, Method for preventing and correcting iron chlorosis in plants. Patent WO2010076353: 2010
Garcia N, Lamanna M, D’Accorso N, Dufresne A, Aranguren M, Goyanes S (2012) Biodegradable materials from grafting of modified PLA onto starch nanocrystals. Polym Degrad Stab 97:2021–2026
Liu X, Wang H, Su C, Zhang P, Bai J (2010)) Controlled fabrication and characterization of microspherical FeCO3 and α-Fe2O3. J Colloid Interface Sci 351(2):427–432
Qu X-F Y, Qi-Zhi Zhou, Gen-Tao (2011) Synthesis of siderite microspheres and their transformation to magnetite microspheres. Eur J Mineral 11(23):759–770
Guan J, Yan G, Wang W, Liu J (2012) External field-assisted solution synthesis and selectively catalytic properties of amorphous iron nanoplatelets. J Mater Chem 22(9):3909–3915
Kopinke FD, Remmler M, Mackenzie K, Möder M, Wachsen O (1996) Thermal decomposition of biodegradable polyesters—II. Poly(lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 53(3):329–342
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2013) Kinetics of hydrolytic degradation of PLA. J Polym Environ 21(2):313–318
García NL, Ribba L, Dufresne A, Aranguren MI, Goyanes S (2009) Physico-mechanical properties of biodegradable starch nanocomposites. Macromol Mater Eng294(3):169–177
Lamanna M, Morales NJ, García NL, Goyanes S (2013) Development and characterization of starch nanoparticles by gamma radiation: potential application as starch matrix filler. Carbohydr Polym 97(1):90–97
Zilli D, Chiliotte C, Escobar MM, Bekeris V, Rubiolo GR, Cukierman AL, Goyanes S (2005) Magnetic properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube–epoxy composites. Polym 46(16):6090–6095
Flannery RL, Busscher WJ (1982) Use of a synthetic polymer in potting soils to improve water holding capacity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 13(2):103–111
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial support of UBACyT (No. 20020130100495BA and 20020130100021BA), ANPCyT (PICT- 2012-0717 and PICT-2012-1093), and CONICET (PIP 2013–2015, 11220120100508CO and 11220110100370CO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, N.L., Fascio, M., Errea, M.I. et al. Absorption of Siderite Within a Chemically Modified Poly(lactic acid) Based Composite Material for Agricultural Applications. J Polym Environ 26, 2173–2181 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1119-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1119-x