Abstract
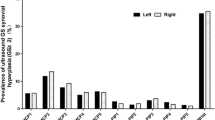
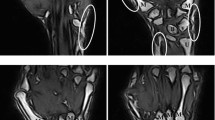
The present study focuses on automatically to segment the blood flow pattern of color Doppler ultrasound in hand region of rheumatoid arthritis patients and to correlate the extracted the statistical features and color Doppler parameters with standard parameters. Thirty patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and their total of 300 joints of both the hands, i.e., 240 MCP and 60 wrists were examined in this study. Ultrasound color Doppler of both the hands of all the patients was obtained. Automated segmentation of color Doppler image was performed using color enhancement scaling based segmentation algorithm. The region of interest is fixed in the MCP joints and wrist of the hand. Features were extracted from the defined ROI of the segmented output image. The color fraction was measured using Mimics software. The standard parameters such as HAQ score, DAS 28 score, and ESR was obtained for all the patients. The color fraction tends to be increased in wrist and MCP3 joints which indicate the increased blood flow pattern and color Doppler activity as part of inflammation in hand joints of RA. The ESR correlated significantly with the feature extracted parameters such as mean, standard deviation and entropy in MCP3, MCP4 joint and the wrist region. The developed automated color image segmentation algorithm provides a quantitative analysis for diagnosis and assessment of RA. The correlation study between the color Doppler parameters with the standard parameters provides moral significance in quantitative analysis of RA in MCP3 joint and the wrist region





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carol A, Hitchon and Hani S, Gabalawy EI (2011). The synovium in Rheumatoid arthritis. The open Rheumatology Journal 5:107–114
Vander Heijde, D.M.F.M., Vant Hof, M.A., Van Riel, P.L.C.M., and de putte LBA, v., Development of a disease activity score based on judgement in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J Rheumatol. 20:579–581, 1993.
Felson, D.T., Anderson, J.J., Boers, M., Bombardier, C., Chernoff, M., Fried, B., et al., The American college of rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 36:729–740, 1993.
Brown, A.K., Connor, P.J., Roberts, T.J., Wakefield, R.J., Karim, Z., and Emery, P., Recommendations for musculoskeletal ultrasonography by rheumatologists: setting global standards for best practice by expert consencus. Arthritis Rheum. 53:83–92, 2005.
Bresnihan, B., and Kane, D., Sonography and subclinical synovitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:333–334, 2004.
Grassi, W., Filippucci, E., Carotti, M., and Salaffi, F., Imaging modalities for identifying the origin of regional musculoskeletal pain. Best pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 17:17–32, 2003.
Wakefield, R.J., Green, M.J., Marzo-Ortega, H., et al., Should oligoarthritis be reclassified? Ultrasound reveals a high prevalence of subclinical disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:382–385, 2004.
Grassi, W., and Filippucci, Ultrasonography and the rheumatologist. Current opinion in Rheumatology. 19:55–60, 2007.
Albrecht, K., Muller-Ladner, U., and Strunk, J., Quantification of the synovial perfusion in rheumatoid arthritis using Doppler ultrasonography. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 25:630–638, 2007.
Qvistgaard, E., Rogind, H., Torp-Pedersen, S., Terslev, L., Danneskiold-samsoe, B., and Bliddal, H., Quantitative ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: Evaluation of inflammation by Doppler technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 60:690–693, 2001.
Scheel, A.K., Hermann, K.G., Ohmdorf, S., et al., Prospective 7 year follow up imaging study comparing radiography, ulrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis finger joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:595–600, 2006.
Wakefield, R.J., Gibbon, W.W., Conaghan, P.G., et al., The value of sonography in the detection of bone erosions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with conventional radiography. Arthritis rheum. 43:2762–2770, 2000.
Tersley, L., Torp-Pedersen, S., Qyistgaard, E., Danneskiold-Samsoe, B., and Bliddal, H., Estimation of inflammation by Doppler ultrasound: Quantitative changes after intra-articular treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 62:1049–1053, 2003.
McNally, E.G., Ultrasound of the small joints of the hands and feet: current status. Skeletal Radiol. 37:99–113, 2008.
Liu, Y., Cheng, H.D., Huang, J.H., Zhang, Y.T., Tang, X.L., Tian, J.W., and Wang, Y., Computer aided diagnosis system for breast cancer based on color Doppler flow imaging. J Med Syst. 36:3975–3982, 2012.
Diao, X.F., Zhang, X.Y., Wang, T.F., Chen, S.P., Yang, Y., and Zhong, L., Highly sensitive computer aided diagnosis system for breast tumor based on color Doppler flow images. J Med Syst. 35:801–809, 2011.
Branas, C.C., Weingarten, M.S., Czeredarczuk, M., and Schafer, P.F., Examination of carotid arteries with quantitative color Doppler flow imaging. J Ultrasound Med. 13:121–127, 1994.
Tokmakc, M., and Erdogan, N., Investigation of the arterial stiffness on renal artery Doppler sonograms. J Med Syst. 33(2):101–106, 2009.
Saadeh, C., Gaylor, P., Lee, D., Malacara, J., and Gaylor, M., Color Doppler ultrasound of the hand : observations on clinical utility in rheumatoid arthritis. J clin Rheumatol. 10(1):1–5, 2004.
Terslev, Recke, P.V., Torp-pedersen, S., Koenig, M.J., and Bliddal, H., Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of Doppler ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 35:49–53.
Naredo, E., Collado, P., Cruz, A., et al., Longitudinal power Doppler ultrasonographic assessment of joint inflammatory activity in early rheumatoid arthritis: predictive value in disease activity and radiologic progression. Arthritis Rheum. 57:116–124, 2007.
Naredo E, Bonilla G, Gamero F, Uson J. Carmano L, Laffon A (2005). Assessment of inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis: A comparative study of clinical evaluation with grey scale and power Doppler ultrasonography. Ann Rheum Dis 64:375–381.
Filippucci, E., Iagnocco, A., Salaffi, F., Cerioni, A., Valesini, G., and Grassi, W., Power Doppler sonography monitoring of synovial perfusion at wrist joint in rheumatoid patients treated with adlimumab. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:1433–1437, 2006.
Newman JS, Laing TJ, McCarthy CJ, Adler RS (1996). Power Doppler sonography of synovitis: assessment of therapeutic response. preliminary observations. Radiology 198:582–584.
Hau, M., Schultz, H., Tony, H.P., Keberle, M., Jahns, R., Harten, R., et al., Evaluation of pannus and vascularization of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis by high-resolution ultrasound (multidimensional linear array). Arthritis Rheum. 42:2303–2308, 1999.
Mills DM, Cao K, Thiele R, Patwardhan KA (2012). Volumetric ultrasound and computer –assisted analysis at the point of care: A musculoskeletal exemplar. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012: 2318–2322. doi:10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346427.
Segen, J., Kulbacki, M., and Wereszczynski, Registration of ultrasound images for automated assessment of synovitis activity. Intelligent information and database systems, Lecture notes in computer science. 9012:307–316, 2015. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-15705-4_30.
Aletaha, D., Neogi, T., Silman, A.J., Funovitis, J., Felson, D.T., et al., 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 62(9):2569–2581, 2010.
Fransen, J., and van Riel, P.L.C.M., “the disease activity score and EULAR response criteria. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 23:93–99, 2005.
Kumar, A., Malaviya, A.N., Pandhi, A., and Singh, R., Validation of an Indian version of the health Assessment questionnaire in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 41(12):1457–1145, 2002.
Ellegaard K, Torp-Pedersen S, Lund H, Pedersen K, Henriksen M, Danneskiold-samsoe B,, Bliddal H (2013). The effect of isometric exercise of the hand on the synovial blood flow in patients with rheumatoid arthritis measured by color Doppler ultrasound. Rheumatol Int 33:65–70
Lin, G.S., Veena, S., and Naval, M.A., Pattern of Doppler flow indices at the carotid bifurcation: Evaluation by hemodynamic color Doppler imaging. J Ultrasound Med. 20:1329–1339, 2001.
Ivanac, G., Vergles, J.M., and Brkljacic, B., Gray scale and color duplex Doppler ultrasound of hand joints in the evaluation of disease activity and treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Croat Med J. 56:280–289, 2015.
Mukhopadhyay J, Image and video processing in the compressed domain CRC press pp 157–159.
Salvatore D, Reagle D (2012), Theory and problem of statistics and econometric, 2nd edition schaum outline series-Mcgraw-hill.
Terslev, L., Torp-Pedersen, S., Savnik, A., der recke P, V., Qvistgaard, E., Danneskiold-samsoe, B., and Bliddal, H., Doppler ultrasound and Magnetic resonance imaging of synovial inflammation of the hand in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A comparative study. Arthritis Rheum. 48(9):2434–2441, 2003.
Ellegaard, K., Torp-Pedersen, S., Terslev, L., Danneskiold-samsoe, B., Henriksen, M., and Bliddal, H., Ultrasound colour Doppler measurements in a single joint as measure of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis–assessment of concurrent validity. Rheumatology. 48(3):254–257, 2009. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken459.
Weidekamm, C., Koller, M., Weber, M., and Kainberger, F., Diagnostic value of high-resolution B-mode and Doppler sonography for imaging of hand and finger joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 48:325–333, 2003.
Szkudlarek, M., Court-Payen, M., Jacobsen, S., Klarlund, M., Thomsen, H.S., and Ostergaard, M., Interobserver agreement in Ultrasonography of the finger and toe joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 48:955–962, 2003.
Naredo, E., Gamero, T., Bonilla, G., Uson, J., Carmona, L., and Laffon, A., Ultrasonogrpahic assessment of inflammatory activity in RA: Comparison of extended vs reduced joint evaluation. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 23:881–884, 2005.
Hammed, B., Pilcker, J., Heron, C., and Kiley, P.D.W., The relation between composite ultrasound measures and the DAS 28 score, Its components and acute phase markers in adult RA. Rheumatology. 47:476–480, 2008.
Midiri, M., Iovane, A., Finazzo, M., Brancatelli, G., Gallo, C., and Lagalla, R., Color Doppler-echo in rheumatoid arthritis with extra-articular location: preliminary experience. Radiol Med (Torino). 98:123–126, 1999.
Troltzsch, M., Color Doppler study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma. Z Rheumatol. 53:2–6, 1994.
Grisan E, Rizzo G, Coran A, Raffeiner B, Stramare R (2015). Quantitative ultrasound for diagnosis and assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. Proc SPIE 2015. doi:10.1117/2.1201506.006000
Grisan, E., Raffeiner, B., Coran, A., Rizzo, G., Liprian, L., et al., A comparison of region based and pixel based CEUS kinetics parameters in the assessment of arthritis. Proc SPIE 9040, Medical imaging 2014. Ultrasonic imaging and Tomography:90400F, 2014. doi:10.1117/12.2042801.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure Statement
All the authors of this article have no conflict of interest
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Patient Facing Systems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snekhalatha, U., Muthubhairavi, V., Anburajan, M. et al. Ultrasound Color Doppler Image Segmentation and Feature Extraction in MCP and Wrist Region in Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Med Syst 40, 197 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0552-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0552-z