Abstract
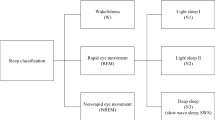
Analysis and classification of sleep stages is essential in sleep research. In this particular study, an alternative system which estimates sleep stages of human being through a multi-layer neural network (NN) that simultaneously employs EEG, EMG and EOG. The data were recorded through polisomnography device for 7 h for each subject. These collective variant data were first grouped by an expert physician and the software of polisomnography, and then used for training and testing the proposed Artificial Neural Network (ANN). A good scoring was attained through the trained ANN, so it may be put into use in clinics where lacks of specialist physicians.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Penzel, T., and Conradt, R., Computer based sleep recording and analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 4:131–148, 2000. doi:10.1053/smrv.1999.0087.
Carskadon, M. A., and Rechtschaffen, A., Monitoring and staging human sleep. In: Kryger, M. H., Roth, T., and Dement, W. C. (Eds.), Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine, 4th edition. Saunders, Philadelphia, 2005.
Jones, B. E., Basic mechanisms of sleep–wake states. In: Kyger, M. H., Roth, T., and Dement, W. C. (Eds.), Principles and Practice of Sleep MedicineSaunders, Philadelphia, pp. 145–162, 1984.
Principe, J. C., Gala, S. K., and Chang, T. G., Sleep staging automation based on the theory of evidence. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 36 (5)503–509, 1989. doi:10.1109/10.24251.
Hellyar, M. T., Ifeachor, E. C., Mapps, D. J., Allen, E. M., and Hudson, N. R., Expert system approach to electroencephalogram signal processing. Knowl.-Based. Syst. 8 (4)164–173, 1995. doi:10.1016/0950-7051(95)96213-B.
Shimada, T. and Shiina, T., Detection of characteristic waves of sleep EEG by neural network analysis. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Biomed. Eng., 1995, 823–824.
Shimada, T., Shiina, T., and Saito, Y., Sleep stage diagnosis system with neural network analysis. Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vol. 20, No. 4, 1998.
Guler, I., and Ubeyli, E. D., Multiclass support vector machines for EEG signals classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 11 (2)117–126, 2007. doi:10.1109/TITB.2006.879600.
Guler, I., and Ubeyli, E. D., Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for classification of EEG signals using wavelet coefficients. J. Neurosci. Methods. 148:113–121, 2005. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.04.013.
Akin, M., Kurt, M. B., Sezgin, N., and Bayram, M., Estimating vigilance level by using EEG and EMG signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 17 (3)227–236, 2008. doi:10.1007/s00521-007-0117-7.
Halici, U., Lecture notes on Neural Networks. The dynamic of brain multidisipliner, Diyarbakir, 1999.
Kiymik, M. K., Akin, M., and Subasi, A., Automatic recognition of alertness level by using wavelet transform and artificial neural network. J. Neurosci. Methods. 139 (2)231–240, 2004. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.04.027.
Akin, M., Bayram, M., Eroglu, O., and Sezgin, N., Determining of dose level analysing EEG signals by using wavelet transform and neural networks. Int. J. Comput. Intell. IJCI Proceedings of International XII Turkish Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Neural Networks, TAINN 2003, ISSN 1304–2386, Volume:1, Number:1, pages:302–305, July 2003.
Gelir, E. and Ardiç, S., Insan uyku evrelerinin standart terminoloji. Yontem ve Skorlama El Kitabi, 2000.
Horner R., PSL 472/1472 sleep physiology. Last updated 20.12.2001.
Hazarika N., Classification of EEG signals using the wavelet transform. Signal Processing [H. W. Wilson—AST], Vol. 59, ISS: 1, pg: 61., May 1997.
Yazgan, E. and Korurek, M., Tıp Elektroniği. Istanbul Technical University, publication no:1574, ISBN 975- 561-073-1, 1996.
Khahill, M., and Duchene, J., Detection and classification of multiple events in piecewise stationary signals. J. Signal Process. S0165-684 (98)00236–00239, 1999.
Jung, T. P., Makeig, S., Stensmo, M., and Sejnowski, T. J., Estimating alertness from the EEG power spectrum. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 44:60–69, 1997. doi:10.1109/10.553713.
Peters, B. O., Pfurtscheller, G., and Flyvbjerg, H., Automatic differentiation of multichannel EEG signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 48:111–116, 2001. doi:10.1109/10.900270.
Gevins, A., and Smith, M. E., Detecting transient cognitive impairment with EEG pattern recognition methods. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 70 (10)1018–1024, 1999.
Basheer, I. A., and Hajmeer, M., Artificial neural networks: fundamentals, computing, design, and application. J. Microbiol. Methods. 43:3–31, 2000. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00201-3.
Haykin, S., Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation. Macmillan, New York, 1994.
Guler, N. F., and Ubeyli, E. D., Wavelet-based neural network analysis of ophthalmic artery Doppler signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 34 (7)601–613, 2004. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2003.09.001.
Eyfe, C., Artificial Neural Network. The University of Paisley, Edition 1.1, 1996.
Fausett, L., Fundamentals of Neural Networks architectures, algorithms, and applications. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1994.
Rechtschaffen, A., and Kales, A., A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stage of human subjects. Public Health Service U. S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1968.
Watanabe, T., and Watanabe, K., Noncontact method for sleep stage estimation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51 (10)1735–1748, 2004. doi:10.1109/TBME.2004.828037.
Himanen, S. L., and Hasan, J., Limitations of Rechtschaffen and Kales. Sleep Med. Rev. 4 (2)149–167, 2000. doi:10.1053/smrv.1999.0086.
Shimohira, M., et al., Video analysis of gross movements during sleep. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 52 (2)176–177, 1998. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.1998.tb01015.x.
Salmi, T., and Leinonen, L., Automatic analysis of sleep records with static charge sensitive bed. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 64:84–87, 1986. doi:10.1016/0013-4694(86)90047-7.
Doi, S., Nagai, I., and Sakuma, T., A decision method for sleeping-states from body movement using neural network. Trans. Inst. Elect. Eng. Jpn. 114-C (11)1160–1165, 1994.
Hanaoka, M., Kobayashi, M., and Yamazaki, H., Automated sleep stage scoring by decision tree learning, 23rd Annual EMBS International Conference, 1751–1754, 2001.
Kurt, M. B., Sezgin, N., Akin, M., Kirbas, G., and Bayram, M., The ANN-based computing of drowsy level. Expert Syst. Appl. 36 (2)2534–2542, 2009. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2008.01.085.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tagluk, M.E., Sezgin, N. & Akin, M. Estimation of Sleep Stages by an Artificial Neural Network Employing EEG, EMG and EOG. J Med Syst 34, 717–725 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9286-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9286-5