Abstract
Methodologies are presented that enable the construction of provably linearly stable and conservative high-order discretizations of partial differential equations in curvilinear coordinates based on generalized summation-by-parts operators, including operators with dense-norm matrices. Specifically, three approaches are presented for the construction of stable and conservative schemes in curvilinear coordinates using summation-by-parts (SBP) operators that have a diagonal norm but may or may not include boundary nodes: (1) the mortar-element approach, (2) the global SBP-operator approach, and (3) the staggered-grid approach. Moreover, the staggered-grid approach is extended to enable the development of stable dense-norm operators in curvilinear coordinates. In addition, collocated upwind simultaneous approximation terms for the weak imposition of boundary conditions or inter-element coupling are extended to curvilinear coordinates with the new approaches. While the emphasis in the paper is on tensor-product SBP operators, the approaches that are covered are directly applicable to multidimensional SBP operators.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boom, P.D., Zingg, D.W.: High-order implicit time-marching methods based on generalized summation-by-parts operators. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 6(37), A2682–A2709 (2015)
Carpenter, M.H., Del Rey Fernández, D.C.: On entropy stable dicretizations using generalized summation-by-parts operators on curvilinear coordiantes. NASA Technical Report (2018)
Carpenter, M.H., Fisher, T.C., Nielsen, E.J., Frankel, S.H.: Entropy stable spectral collocation schemes for the Navier–Stokes equations: discontinuous interfaces. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 36(5), B835–B867 (2014)
Carpenter, M.H., Fisher, T.C., Nielsen, E.J., Parsani, M., Svärd, M., Yamaleev, N.: Entropy stable summation-by-parts formulations for computational fluid dynamics. Handb. Numer. Anal. 17, 495–524 (2016)
Carpenter, M.H., Gottlieb, D., Abarbanel, S.: Time-stable boundary conditions for finite-difference schemes solving hyperbolic systems: methodology and application to high-order compact schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 111(2), 220–236 (1994)
Carpenter, M.H., Nordström, J., Gottlieb, D.: A stable and conservative interface treatment of arbitrary spatial accuracy. J. Comput. Phys. 148(2), 341–365 (1999)
Carpenter, M.H., Nordström, J., Gottlieb, D.: Revisiting and extending interface penalties for multi-domain summation-by-parts operators. J. Sci. Comput. 45(1–3), 118–150 (2010)
Carpenter, M.H., Parsani, M., Fisher, T.C., Nielsen, E.J.: Towards an entropy stable spectral element framework for computational fluid dynamics. In: 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA 2016-1058. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) (2016)
Chan, J.: Weight-adjusted discontinuous Galerkin methods: matrix-valued weights and elastic wave propagation in heterogeneous media. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 113(12), 1779–1809 (2017)
Chan, J.: On discretely entropy conservative and entropy stable discontinuous Galerkin methods. J. Comput. Phys. 362, 346–374 (2018)
Chan, J., Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Carpenter, M.H.: Efficient entropy stable Gauss collocation methods. Submitted to SIAM J. Sci. Comput. (2018)
Chan, J., Hewett, R.J., Warburton, T.: Weight-adjusted discontinuous Galerkin methods: wave propogation in hetrogeneous media. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 39(6), A2935–A2961 (2017)
Chan, J., Hewett, R.J., Warburton, T.: Weight-adjusted discontinuous Galerkin methods: curvilinear meshes (2018). arXiv:1608.03836v1 [math.NA]
Chen, T., Shu, C.W.: Entropy stable high order discontinuous Galerkin methods with suitable quadrature rules for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 345, 427–461 (2017)
Cheng, Y., Chou, C.S., Li, F., Xing, Y.: L2 stable discontinuous Galerkin methods for one-dimensional two-way wave equations. Math. Comput. 86, 121–155 (2017)
Crean, J., Hicken, J.E., Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Zingg, D.W., Carpenter, M.H.: Entropy-stable summation-by-parts discretization of the Euler equations on general curved elements. J. Comput. Phys. 356, 410–438 (2018)
Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Boom, P.D., Zingg, D.W.: A generalized framework for nodal first derivative summation-by-parts operators. J. Comput. Phys. 266(1), 214–239 (2014)
Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Carpenter, M.H., Friedrich, L., Winters, A.R., Gassner, G.J., Dalcin, L., Parsani, M.: Entropy stable non-conforming discretizations with the summation-by-parts property for curvilinear coordinates. NASA Technical Report (2018)
Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Crean, J., Carpenter, M.H., Hicken, J.E.: Staggered-grid entropy-stable multidimensional summation-by-parts discretizations on curvilinear coordinates. J. Comput. Phys. 392, 161–186 (2019)
Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Hicken, J.E., Zingg, D.W.: Review of summation-by-parts operators with simultaneous approximation terms for the numerical solution of partial differential equations. Comput. Fluids 95(22), 171–196 (2014)
Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Hicken, J.E., Zingg, D.W.: Simultaneous approximation terms for multidimensional summation-by-parts operators. J. Sci. Comput. 1(75), 83–110 (2018)
Deng, X., Mao, M., Tu, G., Liu, H., Zhang, H.: Geometric conservation law and applications to high-order finite difference schemes with stationary grids. J. Comput. Phys. 230(4), 1100–1115 (2011)
Deng, X., Min, Y., Mao, M., Liu, H., Tu, G., Zhang, H.: Further studies on geometric conservation law and applications to high-order finite difference schemes with stationary grids. J. Comput. Phys. 239, 90–111 (2013)
Derigs, D., Winters, A.R., Gassner, J.G., Walch, S.: A novel averaging technique for discrete entropy-stable dissipation operators for ideal mhd. J. Comput. Phys. 330(1), 624–632 (2017)
Fisher, T.C.: High-order \(l^{2}\) stable multi-domain finite difference method for compressible flows. Ph.D. thesis, Purdue University (2012)
Fisher, T.C., Carpenter, M.H.: High-order entropy stable finite difference schemes for nonlinear conservation laws: finite domains. J. Comput. Phys. 252(1), 518–557 (2013)
Fisher, T.C., Carpenter, M.H.: High-order entropy stable finite difference schemes for nonlinear conservation laws: finite domains. J. Comput. Phys. 252, 518–557 (2013)
Fisher, T.C., Carpenter, M.H., Nordström, J., Yamaleev, N.K.: Discretely conservative finite-difference formulations for nonlinear conservation laws in split form: theory and boundary conditions. J. Comput. Phys. 234(1), 353–375 (2013)
Friedrich, L., Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Winters, A.R., Gassner, G.J., Zingg, D.W., Hicken, J.E.: Conservative and stable degree preserving SBP operators for non-conforming meshes. J. Sci. Comput. 75(2), 657–686 (2018)
Friedrich, L., Winters, A.R., Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Gassner, G.J., Parsani, M., Carpenter, M.H.: An entropy stable \(h/p\) non-conforming discontinuous Galerkin method with the summation-by-parts property. J. Sci. Comput. 77, 1–37 (2018)
Gassner, G.J.: A skew-symmetric discontinuous Galerkin spectral element discretization and its relation to SBP-SAT finite difference methods. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 35(3), A1233–A1253 (2013)
Gassner, G.J., Winters, A.R., Kopriva, D.A.: A well balanced and entropy conservative discontinuous Galerkin spectral element method for the shallow water equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 272(2), 291–308 (2016)
Hicken, J.E., Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Zingg, D.W.: Multidimensional summation-by-part operators: general theory and application to simplex elements. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 38(4), A1935–A1958 (2016)
Hicken, J.E., Zingg, D.W.: Aerodynamic optimization algorithm with integrated geometry parameterization and mesh movement. AIAA J. 48(2), 400–413 (2010)
Lax, P.D., Wendroff, B.: Systems of conservation laws. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 13, 217–237 (1960)
Nordström, J., Carpenter, M.H.: Boundary and interface conditions for high-order finite-difference methods applied to the Euler and Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 148(2), 621–645 (1999)
Nordström, J., Carpenter, M.H.: High-order finite-difference methods, multidimensional linear problems, and curvilinear coordinates. J. Comput. Phys. 173(1), 149–174 (2001)
Osusky, L.M.: A numerical methodology for aerodynamic shape optimization in turbulent flow enabling large geometric variation. Ph.D. thesis, University of Toronto (2014)
Parsani, M., Carpenter, M.H., Fisher, T.C., Nielsen, E.J.: Entropy stable staggered grid discontinuous spectral collocation methods of any order for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 38(5), A3129–A3162 (2016)
Parsani, M., Carpenter, M.H., Nielsen, E.J.: Entropy stable wall boundary conditions for the three-dimensional compressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 292(1), 88–113 (2015)
Ranocha, H., Glaubitz, J., Öffner, P., Sonar, T.: Stability of artificial dissipation and modal filtering for flux reconstruction schemes using summation-by-parts operators. Appl. Numer.l Math. 128, 1–23 (2018)
Ranocha, H., Öffner, P., Sonar, T.: Summation-by-parts operators for correction procedure via reconstruction. J. Comput. Phys. 311(15), 299–328 (2016)
Ranocha, H., Öffner, P., Sonar, T.: Extended skew-symmetric form for summation-by-parts operators and varying jacobians. J. Comput. Phys. 342(C), 13–28 (2017)
Shi, C., Shu, C.W.: On local conservation of numerical methods for conservation laws. Comput. Fluids 169(4), 3–9 (2018)
Svärd, M.: On coordinate transformations for summation-by-parts operators. J. Sci. Comput. 20(1), 29–42 (2004)
Svärd, M., Nordström, J.: Review of summation-by-parts schemes for initial-boundary-value-problems. J. Comput. Phys. 268(1), 17–38 (2014)
Thomas, D., Lombard, C.K.: Geometric conservation law and its application to flow computations on moving grids. AIAA J. 17(10), 1030–1037 (1979)
Vinokur, M., Yee, H.C.: Extension of efficient low dissipation high order schemes for \(3\)-D curvilinear moving grids. In: Caughey, D.A., Hafez, M. (eds.) Frontiers of Computational Fluid Dynamics, pp. 129–164. World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore (2002)
Wintermeyer, N., Winters, A.R., Gassner, G.J., Kopriva, D.A.: An entropy stable nodal discontinuous Galerkin method for the two dimensional shallow water equations on unstructured curvilinear meshes with discontinuous bathymetry. J. Comput. Phys. 340(1), 200–242 (2017)
Winters, A.R., Derigs, D., Gassner, G.J., Walch, S.: Uniquely defined entropy stable matrix dissipation operator for high mach number ideal MHD and compressible Euler simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 332(1), 274–289 (2017)
Winters, A.R., Gassner, G.J.: Affordable, entropy conserving and entropy stable flux functions for the ideal mhd equations. J. Comput. Phys. 304(1), 72–108 (2016)
Winters, A.R., Gassner, J.G.: A comparison of two entropy stable discontinuous Galerking spectral element approximations to the shallow water equations with non-constant topography. J. Comput. Phys. 301(1), 357–376 (2015)
Yamaleev, N.K., Carpenter, M.H.: A family of fourth-order entropy stable non-oscillatory spectral collocation schemes for the 1-d Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 331, 90–107 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Portions of this paper were previously published in “Numerical Investigation of Tensor-Product Summation-by-Parts Discretization Strategies and Operators” AIAA paper 2017-0530.
Periodic Boundary Conditions for the Global SBP-Operator Approach
Periodic Boundary Conditions for the Global SBP-Operator Approach
The computation of the metrics and Jacobian involve derivatives of the physical nodal locations. The global SBP-operator approach includes the use of interface SATs to couple the derivative values in adjacent elements. Unfortunately, for problems with periodic boundary conditions, the nodal locations are not necessarily periodic, even if the solution is periodic. As a result, naively applying the SBP operator approach will not give the correct solution. In order to use the global SBP-operator approach, the interface SATs for periodic boundary conditions used in the computation of the metrics and Jacobian must be modified. This requires knowledge of the domain’s geometry.
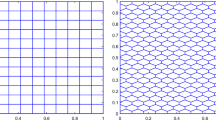
For the test case used in Sect. 12, the size of the domain relative to any point is unity in each direction. In other words, traveling one unit along any of the coordinate directions in physical space will bring you back to the same point, even though the domain is not a unit cube. Therefore, the interface SATs involving nodal locations used at periodic faces only require the addition or subtraction of a unit value. A one-dimensional example is shown in Fig. 4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Del Rey Fernández, D.C., Boom, P.D., Carpenter, M.H. et al. Extension of Tensor-Product Generalized and Dense-Norm Summation-by-Parts Operators to Curvilinear Coordinates. J Sci Comput 80, 1957–1996 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-019-01011-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-019-01011-3