Abstract
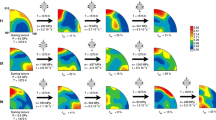
The high-temperature rheology of heterogeneous anorthite — diopside aggregates has been investigated numerically, in support to experimental data obtained by triaxial torsion tests, performed at high pressure (400 MPa) and temperature (1150° C). The mechanical data exhibited linear viscous flow. Accordingly, scanning electron microscopy revealed grain sliding mechanisms, but also crystal slip plasticity, recrystallization and micro-fracturing. Finite element computations at the aggregate scale aimed at the understanding of the sequence of active mechanisms and their link to the macroscopic behavior. For instance, we show that the presence of coarser and stronger diopside inclusions in weaker and fine grained anorthite matrix results in very heterogeneous local stress fields, allowing for the activation of multiple deformation mechanisms. Our study indicates that shear zones in the lower crust should be dominated by Newtonian rheology in relation with grain sliding mechanisms, even though complementary accommodation mechanisms such as crystal plasticity and damage may be necessary at the local scale, due to the heterogeneous microstructures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Bürgmann and G. Dresen, “Rheology of the lower crust and upper mantle: evidences from rock mechanics, geodesy, and field observations,” Annual Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 36 (2008).
Tullis and Yund, “Dynamic recrystallization of feldspar: a mechanism for ductile shear zone formation,” Geology, 13, No. 4 (1985).
A. M. Boullier and Y. Guéguen, “SP mylonites: origin of some mylonites by superplastic flow,” Contr. Mineral. Petrol., 50 (1975).
J. H. Behrmann and D. Mainprice, “Deformation mechanisms in a high temperature quartz-feldspar mylonite: evidence for superplastic flow in the lower crust,” Tectonophysics, 140 (1987).
T. Kenkmann and G. Dresen, “Stress gradients around porphyroclasts: paleopiezometric estimates and numerical modeling,” J. Struct. Geol., 20, Nos. 2 and 3 (1998).
T. Kenkmann and G. Dresen, “Dislocation microstructure and phase distribution in a lower crustal shear zone — an example from the Ivrea-Zone, Italy,” Int. J. Earth Sci., 91, No. 3 (2002).
R. Kruse and H. Stunitz, “Deformation mechanisms and phase distribution in mafic high-temperature mylonites from the Jotun Nappe, southern Norway,” Tectonophys., 303 (1999).
A. Dimanov and G. Dresen, “Rheology of synthetic anorthite-diopside aggregates: implications for ductile shear zones,” J. Geophys. Res., 110, B7, B07203 (2005).
R. L. Rudnick and S. R. Taylor, “The composition and petrogenesis of the lower continental crust: a xenolith study,” J. Geophys. Res., 92 (1987).
M. S. Paterson and D. L. Olgaard, “Deformation tests to large shear strains in torsion,” Journal of Structural Geology, 22 (2000).
E. Rybacki and G. Dresen, “Dislocation and diffusion creep of synthetic anorthite aggregates,” J. Geophys. Res., 105 (2000).
A. Dimanov, M. P. Lavie, G. Dresen, et al., “Creep of polycrystalline anorthite and diopside,” J. Geophys. Res., 108, B1 (2003).
E. Rybacki, M. Gottschalk, and G. Dresen, “Influence of water fugacity and activation volume on the flow properties of fine-grained anorthite aggregates,” J. Geophys. Res., 111 (2006).
A. Dimanov, E. Rybacki, R. Wirth, and G. Dresen, “Creep and strain-dependent microstructures of synthetic anorthite — diopside aggregates,” J. Struct. Geol., 29 (2007).
F. Gueydan, Y. M. Leroy, L. Jolivet, and P. Agard, “Analysis of continental midcrustal strain localization induced by reaction-softening and microfracturing,” Journal of Geophysical Research, 108, B2 (2003).
J. L. Raphanel, G. Ravichandran, and Y. M. Leroy, “Three-dimensional rate-dependent crystal plasticity based on Runge — Kutta algorithms for update and consistent linearization,” IJSS, 41 (2004).
L. A. Nazarova and L. A. Nazarov, “Dilatation and the formation and evolution of disintegration zones in the vicinity of heterogeneities in a rock mass,” Journal of Mining Science, No. 5 (2009).
L. A. Nazarov, L. A. Nazarova, and A. I. Artemova, “Statistic approach to the equivalent modeling of rock masses,” Journal of Mining Science, No. 6 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raphanel, J., Dimanov, A., Nazarova, L.A. et al. High temperature rheology of synthetic two-phase gabbroic aggregates: microstructural heterogeneities and local deformation mechanism. J Min Sci 46, 495–502 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10913-010-0062-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10913-010-0062-1