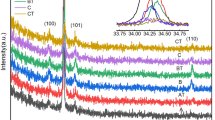
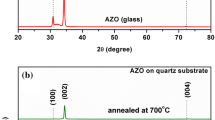
Abstract
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Raman spectroscopy and spectrophotometry were used to study the effect of RF power on the properties of gallium and aluminium co-doped zinc oxide (GAZO) thin films for optoelectronic device fabrication. Two peaks appeared in the XPS spectra of the Zn 2p core-level at 1045 and 1022 eV, and these were assigned to \({\text{Zn}}~2{{\text{p}}_{1/2}}\) and \({\text{Zn}}~2{{\text{p}}_{3/2}}\), respectively. The O 1s core-level revealed peaks at 530 and 531 eV which indicated the presence of two different forms of oxygen. Raman spectroscopy confirmed the films’ hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure and revealed the presence of few defects and negligible residual tensile stress. Spectral dependence of the refractive index was analyzed on the basis of the Cauchy’s dispersion model and the Wemple and DiDomenico (WDD) single oscillator model. Low refractive indices (1.6–2.0) and nearly zero extinction coefficients were obtained in the visible region (400–700 nm), indicating the high transparency nature of the GAZO thin films. The optical band gap decreased with increasing RF power, in accordance with the Burstein–Moss effect. Low Urbach energy values were obtained at low RF power, indicating less structural disorder. The free carrier concentration to effective mass ratio \(({N_c}{\text{/}}{m^*})\), plasma frequency \(({\omega _P})\) and zero frequency dielectric constant \(({\varepsilon _\infty })\) were determined. Films deposited at 150 W exhibited the optimum optical properties, desirable for optoelectronic application.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.P. Singh, Synthesis and growth of ZnO nanowires. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2, 245–272 (2010)
I. Udom, M.K. Ram, E.K. Stefanakos, A.F. Hepp, One dimensional-ZnO nanostructures: synthesis, properties and environmental applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 2070–2083 (2013)
C. Chevalier-César, M. Capochichi-Gnambodoe, F. Lin, D. Yu, Y. Leprince-Wang, Effect of growth time and annealing on the structural defect concentration of hydrothermally grown ZnO nanowires. AIMS Mater. Sci. 3, 562–572 (2016)
E. Muchuweni, T.S. Sathiaraj, H. Nyakotyo, Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide thin films for optoelectronic applications. Heliyon 3, e00285 (2017)
S.K. Das, F. Güell, C. Gray, P.K. Das, R. Grunwald, E. McGlynn, ZnO nanorods for efficient third harmonic UV generation: erratum. Opt. Mater. Express 4, 1243–1243 (2014)
H.J. Zhou, S.S. Wong, A facile and mild synthesis of 1-D ZnO, CuO, and α-Fe2O3 nanostructures and nanostructured arrays. ACS Nano 2, 944–958 (2008)
H. Morkoç, Ü Özgür, Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology (Wiley-WCH, Weinheim, 2009), pp. 246–247
C.M. Muiva, T.S. Sathiaraj, K. Maabong, Effect of doping concentration on the properties of aluminium doped zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis for transparent electrode applications. Ceram. Int. 37, 555–560 (2011)
E. Muchuweni, T.S. Sathiaraj, H. Nyakotyo, Effect of gallium doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 42, 10066–10070 (2016)
E. Muchuweni, T.S. Sathiaraj, H. Nyakotyo, Physical properties of gallium and aluminium co-doped zinc oxide thin films deposited at different radio frequency magnetron sputtering power. Ceram. Int. 42, 17706–17710 (2016)
E. Reza, G.M. Reza, A. Hossein, Sol-gel derived Al and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films: an optoelectronic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 290, 252–259 (2014)
J. Liu, W. Zhang, D. Song, Q. Ma, L. Zhang, H. Zhang, L. Zhang, R. Wu, Investigation of aluminium-gallium co-doped zinc oxide targets for sputtering thin film and photovoltaic application. J. Alloys Compd. 575, 174–182 (2013)
E. Muchuweni, T.S. Sathiaraj, H. Nyakotyo, Low temperature synthesis of radio frequency magnetron sputtered gallium and aluminium co-doped zinc oxide thin films for transparent electrode fabrication. Appl. Surf. Sci. 390, 570–577 (2016)
W. Lee, S. Shin, D.-R. Jung, J. Kim, C. Nahm, T. Moon, B. Park, Investigation of the electronic and optical properties in Al–Ga codoped ZnO thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 628–631 (2012)
E. Muchuweni, T.S. Sathiaraj, H. Nyakotyo, Effect of O2/Ar flow ratio on Ga and Al co-doped ZnO thin films by RF sputtering for optoelectronic device fabrication. Mater. Res. Bull. 95, 123–128 (2017)
R. Al-Gaashani, S. Radiman, A.R. Daud, N. Tabet, Y. A-Douri, XPS and optical studies of different morphologies of ZnO nanostructures prepared by microwave methods. Ceram. Int. 39, 2283–2292 (2013)
Z.-W. Wu, S.-L. Tyan, H.-H. Chen, J.-C.-A. Huang, Y.-C. Huang, C.-R. Lee, T.-S. Mao, Temperature-dependent photoluminescence and XPS study of ZnO nanowires grown on flexible Zn foil via thermal oxidation. Superlatt. Microstuct. 107, 38–43 (2017)
F. Decremps, J. Pellicer-Porres, A. Marco Saitta, J.C. Chervin, A. Polian, High-pressure Raman spectroscopy study of wurtzite ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 65, 092101–092105 (2002)
K.A. Alim, V.A. Fonoberov, A.A. Balandin, Origin of the phonon frequency shifts in ZnO quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 053103 (2005)
L. Wang, Y. Pu, Y.F. Chen, C.L. Mo, W.Q. Fang, C.B. Xiong, J.N. Dai, F.Y. Jiang, MOCVD growth of ZnO films on Si(111) substrate using a thin AIN buffer layer. J. Cryst. Growth 284, 459–463 (2005)
A. Ismail, M.J. Abdullah, The structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared at different RF sputtering power. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 25, 209–215 (2013)
R.G. Waykar, A.S. Pawbake, R.R. Kulkarni, A.A. Jadhavar, A.M. Funde, V.S. Waman, H.M. Pathan, S.R. Jadkar, Influence of RF power on structural, morphology, electrical, composition and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 1134–1143 (2016)
M. Caglar, S. Ilican, Y. Caglar, Influence of dopant concentration on the optical properties of ZnO: in films by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 517, 5023–5028 (2009)
G.C. Xie, L. Fang, L.P. Peng, G.B. Liu, H.B. Ruan, F. Wu, C.Y. Kong, Effect of In-doping on the optical constants of ZnO thin films. Phys. Procedia 32, 651–657 (2012)
M.H. Mamat, M.F. Malek, N.N. Hafizah, M.N. Asiah, A.B. Suriani, A. Mohamed, N. Nafarizal, M.K. Ahmad, M. Rusop, Effect of oxygen flow rate on the ultraviolet sensing properties of zinc oxide nanocolumn arrays grown by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 42, 4107–4119 (2016)
S.W. Xue, X.T. Zu, W.L. Zhou, H.X. Deng, X. Xiang, L. Zhang, H. Deng, Effects of post-thermal annealing on the optical constants of ZnO thin film. J. Alloys Compd. 448, 21–26 (2008)
D.-Y. Zhang, P.-P. Wang, R.-I. Murakami, X.-P. Song, First-principles simulation and experimental evidence for improvement of transmittance in ZnO films. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. 21, 40–45 (2011)
A. Bedia, F.Z. Bedia, M. Aillerie, N. Maloufi, B. Benyoucef, Influence of the thickness on optical properties of sprayed ZnO hole-blocking layers dedicated to inverted organic solar cells. Energy Procedia 50, 603–609 (2014)
N. Hamzaoui, A. Boukhachem, M. Ghamnia, C. Fauquet, Investigation of some physical properties of ZnO nanofilms synthesized by micro-droplet technique. Results Phys. 7, 1950–1958 (2017)
T.S. Sathiaraj, Effect of annealing on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ITO films by RF sputtering under low vacuum level. Microelectron. J. 39, 1444–1451 (2008)
S.K. Ahmmad, M.A. Samee, A. Edukondalu, S. Rahman, Physical and optical properties of zinc arsenic tellurite glasses. Results Phys. 2, 175–181 (2012)
R.A. Smith, Semiconductors (Academic Publishers, Calcutta, 1989), pp. 461–463
P.O. Edward, Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids (Academic Press, New York, 1985)
D.C. Look, D.C. Reynolds, J.R. Sizelove, R.L. Jones, C.W. Litton, G. Cantwell, W.C. Harsch, Electrical properties of bulk ZnO. Solid State Commun. 105, 399–401 (1998)
A.-S. Gadallah, M.M. El-Nahass, Structural, optical constants and photoluminescence of ZnO thin films grown by sol-gel spin coating, Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2013, 234546 (2013)
S.H. Wemple, M. DiDomenico, Behavior of the electronic dielectric constant in covalent and ionic materials. Phys. Rev. B 3, 1338–1351 (1971)
S.H. Wemple, M. DiDomenico, Theory of the elasto-optic effect in non-metallic crystals. Phys. Rev. B 1, 193–202 (1970)
D. Komaraiah, E. Radha, Y. Vijayakumar, J. Sivakumar, M.V.R. Reddy, R. Sayanna, Optical, structural and morphological properties of photocatalytic ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. Mod. Res. Catal. 5, 130–146 (2016)
R.H.A. Orainy, Single oscillator model and refractive index dispersion properties of ternary ZnO films by sol gel method. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 70, 47–52 (2014)
F. Yakuphanoglu, S. Ilican, M. Caglar, Y. Caglar, The determination of the optical band gap and optical constants of non-crystalline and crystalline ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 9, 2180–2185 (2007)
G. Malik, J. Jaiswal, S. Mourya, R. Chandra, Optical and other physical properties of hydrophobic ZnO thin films prepared by dc magnetron sputtering at room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 122, 143105 (2017)
F. Urbach, The long-wavelength edge of photographic sensitivity and of the electronic absorption of solids. Phys. Rev. 92, 1324 (1953)
Acknowledgements
This work was performed using Botswana International University of Science and Technology’s research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muchuweni, E., Sathiaraj, T.S., Masanganise, J. et al. The Effect of RF Power on the Properties of Gallium and Aluminium Co-doped Zinc Oxide (GAZO) Thin Films. J Inorg Organomet Polym 29, 49–58 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0963-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0963-z