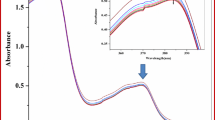
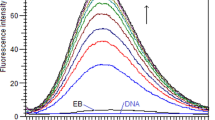
Abstract
Ethidium bromide displacement assay by fluorescence is frequently used as a diagnostic tool to identify the intercalation ability of DNA binding small molecules. Here we have demonstrated that the method has pitfalls. We have employed fluorescence, absorbance and label free technique such as isothermal titration calorimetry to probe the limitations. Ethidium bromide, a non-specific intercalator, netropsin, a (A-T) specific minor groove binder, and sanguinarine, a (G-C) specific intercalator, have been used in our experiments to study the association of a ligand with DNA in presence of a competing ligand. Here we have shown that netropsin quenches the fluorescence intensity of an equilibrium mixture of ethidium bromide - calf thymus DNA via displacement of ethidium bromide. Isothermal titration calorimetry results question the accepted interpretation of the observed decrease in fluorescence of bound ethidium bromide in terms of competitive binding of two ligands to DNA. Furthermore, isothermal titration calorimetry experiments and absorbance measurements indicate that the fluorescence change might be due to formation of ternary complex and not displacement of one ligand by another.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EtBr:
-
Ethidium bromide
- ITC:
-
Isothermal titration calorimetry
- Net:
-
Netropsin
- ct DNA:
-
Calf thymus DNA
- SGR:
-
Sanguinarine
References
Das BB, Sen N, Roy A, Dasgupta SB, Ganguly A, Mohanta BC, Dinda B, Majumder HK (2006) Differential induction of Leishmania donovani bi-subunit topoisomerase I-DNA cleavage complex by selected flavones and camptothecin: activity of flavones against camptothecin-resistant topoisomerase I. Nucleic Acids Res 34(4):1121–1132
Ting CY, Hsu CT, Hsu HT, Su JS, Chen TY, Tarn WY, Kuo YH, Whang-Peng J, Liu LF, Hwang J (2003) Isodiospyrin as a novel human DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor. Biochem Pharmacol 66(10):1981–1991
Marverti G, Cusumano M, Ligabue A, Di Pietro ML, Vainiglia PA, Ferrari A, Bergomi M, Moruzzi MS, Frassineti C (2008) Studies on the anti-proliferative effects of novel DNA-intercalating bipyridyl-thiourea-Pt(II) complexes against cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant human ovarian cancer cells. J Inorg Biochem 102(4):699–712
Chowdhury AR, Sharma S, Mandal S, Goswami A, Mukhopadhyay S, Majumder HK (2002) Luteolin, an emerging anti-cancer flavonoid, poisons eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I. Biochem J 366(Pt 2):653–661
Prescott TA, Sadler IH, Kiapranis R, Maciver SK (2007) Lunacridine from Lunasia amara is a DNA intercalating topoisomerase II inhibitor. J Ethnopharmacol 109(2):289–294
Ahmed MS, Ramesh V, Nagaraja V, Parish JH, Hadi SM (1994) Mode of binding of quercetin to DNA. Mutagenesis 9(3):193–197
Solimani R (1996) Quercetin and DNA in solution: analysis of the dynamics of their interaction with a linear dichroism study. Int J Biol Macromol 18(4):287–295
Yan H, Mizutani TC, Nomura N, Takakura T, Kitamura Y, Miura H, Nishizawa M, Tatsumi M, Yamamoto N, Sugiura W (2005) A novel small molecular weight compound with a carbazole structure that demonstrates potent human immunodeficiency virus type-1 integrase inhibitory activity. Antivir Chem Chemother 16(6):363–373
Brotz-Oesterhelt H, Knezevic I, Bartel S, Lampe T, Warnecke-Eberz U, Ziegelbauer K, Habich D, Labischinski H (2003) Specific and potent inhibition of NAD + -dependent DNA ligase by pyridochromanones. J Biol Chem 278(41):39435–39442
Marshall KM, Andjelic CD, Tasdemir D, Concepcion GP, Ireland CM, Barrows LR (2009) Deoxyamphimedine, a pyridoacridine alkaloid, damages DNA via the production of reactive oxygen species. Mar Drugs 7(2):196–209
Jamalian A, Shafiee A, Hemmateenejad B, Khoshneviszadeh M, Madadkar-Sobhani A, Zahra Bathaie S, Akbar Moosavi-Movahedi A (2011) Novel imidazolyl derivatives of 1, 8-acridinedione as potential DNA-intercalating agents. J Iran Chem Soc 8(4):1098–1112
Ahmadi F, Bakhshandeh F (2009) In vitro study of damaging effects of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on DNA structure by spectroscopic and voltammetric techniques. DNA Cell Biol 28(10):527–533
Bera R, Sahoo BK, Ghosh KS, Dasgupta S (2008) Studies on the interaction of isoxazolcurcumin with calf thymus DNA. Int J Biol Macromol 42(1):14–21
Fortune JM, Osheroff N (1998) Merbarone inhibits the catalytic activity of human topoisomerase IIalpha by blocking DNA cleavage. J Biol Chem 273(28):17643–17650
Rao KE, Dasgupta D, Sasisekharan V (1988) Interaction of synthetic analogues of distamycin and netropsin with nucleic acids. Does curvature of ligand play a role in distamycin-DNA interactions? Biochemistry 27(8):3018–3024
Baguley BC (1982) Nonintercalative DNA-binding antitumour compounds. Mol Cell Biochem 43(3):167–181
Lah J, Vesnaver G (2000) Binding of distamycin A and netropsin to the 12mer DNA duplexes containing mixed AT.GC sequences with at most five or three successive AT base pairs. Biochemistry 39(31):9317–9326
Luck G, Triebel H, Waring M, Zimmer C (1974) Conformation dependent binding of netropsin and distamycin to DNA and DNA model polymers. Nucleic Acids Res 1(3):503–530
Wartell RM, Larson JE, Wells RD (1974) Netropsin. A specific probe for A-T regions of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 249(21):6719–6731
Cosa G, Focsaneanu KS, McLean J, McNamee J, Scaiano J (2001) Photophysical properties of fluorescent DNA-dyes bound to single- and double-stranded DNA in aqueous buffered solution. Photochem Photobiol 73(6):585–599
Scaria PV, Shafer RH (1991) Binding of ethidium bromide to a DNA triple helix. Evidence for intercalation. J Biol Chem 266(9):5417–5423
Liang D, Zhang J, Chu B (2003) Study of ethidium bromide effect on dsDNA separation by capillary zone electrophoresis and laser light scattering. Electrophoresis 24(19–20):3348–3355
Motulsky HJ, Neubig RR (2010) Analyzing binding data. Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter 7:Unit 7 5. doi:10.1002/0471142301
Taquet A, Labarbe R, Houssier C (1998) Calorimetric investigation of ethidium and netropsin binding to chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Biochemistry 37(25):9119–9126
Adhikari A, Hossain M, Maiti M, Suresh Kumar G (2008) Energetics of the binding of phototoxic and cytotoxic plant alkaloid sanguinarine to DNA: isothermal titration calorimetric studies. J Mol Struct 889(1):54–63
Baguley BC, Falkenhaug EM (1978) The interaction of ethidium with synthetic double-stranded polynucleotides at low ionic strength. Nucleic Acids Res 5(1):161–171
Reichmann M, Rice S, Thomas C, Doty P (1954) A further examination of the molecular weight and size of desoxypentose nucleic acid. J Am Chem Soc 76(11):3047–3053
Waring MJ (1965) Complex formation between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. J Mol Biol 13(1):269–282
Selvi BR, Pradhan SK, Shandilya J, Das C, Sailaja BS, Shankar GN, Gadad SS, Reddy A, Dasgupta D, Kundu TK (2009) Sanguinarine interacts with chromatin, modulates epigenetic modifications, and transcription in the context of chromatin. Chem Biol 16(2):203–216
Matthews J, Zacharewski T (2000) Differential binding affinities of PCBs, HO-PCBs, and aroclors with recombinant human, rainbow trout (Onchorhynkiss mykiss), and green anole (Anolis carolinensis) estrogen receptors, using a semi-high throughput competitive binding assay. Toxicol Sci 53(2):326–339
Matthews J, Celius T, Halgren R, Zacharewski T (2000) Differential estrogen receptor binding of estrogenic substances: a species comparison. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 74(4):223–234
Weiss JM, Andersson PL, Lamoree MH, Leonards PE, van Leeuwen SP, Hamers T (2009) Competitive binding of poly- and perfluorinated compounds to the thyroid hormone transport protein transthyretin. Toxicol Sci 109(2):206–216
Sigurskjold BW (2000) Exact analysis of competition ligand binding by displacement isothermal titration calorimetry. Anal Biochem 277(2):260–266
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by CBAUNP project of Intramural Funding from Department of Atomic Energy, Govt. of India. Jasdeep Singh did this work as a part of his project work in the M.S.(Pharm.), Pharmacoinformatics program of NIPER-Kolkata, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, A., Singh, J. & Dasgupta, D. Fluorescence Spectroscopic and Calorimetry Based Approaches to Characterize the Mode of Interaction of Small Molecules with DNA. J Fluoresc 23, 745–752 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-013-1211-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-013-1211-0