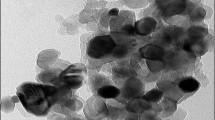
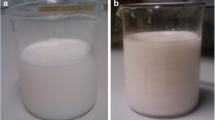
Nanofluids have been prepared by dispersing TiO2 nanoparticles in 70:30% (by weight) water–propylene glycol mixture. The thermal conductivity and viscosity were found experimentally at various temperatures with the volume concentrations 0.1–0.8%. The results indicate that the thermal conductivity of the nanofluids increases with the volume concentration and temperature. Similarly, the viscosity of the nanofluids increases with the volume concentration but decreases with increase in the temperature. Correlations have been proposed for estimating the thermal conductivity and viscosity of the nanofluids. The potential heat transfer benefits of their use in laminar and turbulent flow conditions has been explained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. S. Choi, Y. I. Cho, and K. E. Kasza, Degradation effects of dilute polymer solutions on turbulent friction and heat transfer behavior, J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech., 41, 289–307 (1992).
U. S. Choi, D. M. France, and B. D. Knodel, Impact of advanced fluids on costs of district cooling systems, in: Proc. 83rd Ann. Int. District Heating and Cooling Association Conf., Danvers, Washington, D. C. (1992), pp. 343–359.
V. Bianco, O. Manca, and S. Nardini, Numerical simulation of water/nanofluid turbulent convection, Adv. Mech. Eng., 2, 1–10 (2010).
Y. Touloukian, Thermal Conductivity: Nonmetallic Liquids and Gases (Thermophysical Properties of Matter), Springer, New York (1970).
S. U. S. Choi and J. A. Eastman, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, in: Proc. ASME Int. Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Francisco (1995), pp. 99–105.
X. Q. Wang and A. S. Mujumdar, Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: A review, Therm. Sci., 46, 1–19 (2007).
J. A. Eastman, S. U. S. Choi, S. Li, W. Yu, and L. J. Thompson, Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 78, 718–720 (2001).
K. S. Hong, T. K. Hong, and H. S. Yang, Thermal conductivity of Fe nanofluids depending on the cluster size of nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 88, 031901–031903 (2006).
D. Hemanth Kumar, H. E. Patel, V. R. R. Kumar, T. Pradeep, and S. K. Das, Model for heat conduction in nanofluids, Phys. Rev. Lett., 93, 144301–144304 (2004).
S. Lee, S. U. S. Choi, S. Li, and J. A. Eastman, Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles, Heat Transf., 121, 280–289 (1999).
Y. Xuan and Q. Li, Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids, Heat Fluid Flow, 21, 58–64 (2000).
J. Jeong, C. Li, Y. Kwon, J. Lee, S. H. Kim, and R. Yun, Particle shape effect on the viscosity and thermal conductivity of ZnO nanofluids, Int. J. Refrig., 36, 2233–2241 (2013).
A. Ghadimi and I. H. Metselaar, The influence of surfactant and ultrasonic processing on improvement of stability, thermal conductivity and viscosity of titania nanofluid, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci., 51, 1–9 (2013).
W. Duangthongsuk and S. Wongwises, Measurement of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and viscosity of TiO2-water nanofluids, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci., 33, 706–714 (2009).
W. J. Tseng and C. H. Wu, Aggregation, rheology and electrophoretic packing structure of aqueous Al2O3 nanoparticle suspensions, Acta Mater., 50, 3757–3766 (2002).
Y. He, Y. Jin, H. Chen, Y. Ding, D. Cang, and H. Lu, Heat transfer and flow behaviour of aqueous suspensions of TiO2 nanoparticles (nanofluids) flowing upward through a vertical pipe, Heat Mass Transf., 50, 2272–2281 (2007).
S. H. Kim, S. R. Choi, and D. Kim, Thermal conductivity of metal-oxide nanofluids: particle size dependence and effect of laser irradiation, Heat Transf., 129, 298–307 (2006).
D. H. Yoo, K. S. Hong, and H. S. Yang, Study of thermal conductivity of nanofluids for the application of heat transfer fluids, Thermochim. Acta, 455, 66–69 (2007).
S. A. Ibrahim and S. Sreekantan, Effect of pH on TiO2 nanoparticles via sol-gel method, in: Proc. ICXRI, 9–10 June, 2010, Aseania Resort Langkawi, Malaysia (2010), pp. 84–87.
K. D. Kihm, Fundamendals of energy transport in nanofluids, Annual Report, 1–42 (2003).
Y. Zhao, C. Li, X. Liu, F. Gu, H. Jiang, W. Shao, L. Zhang, and Y. Ge, Synthesis and optical properties of TiO2 nanoparticles, Mater. Lett., 61, 79–83 (2007).
K. M. Reddy, S. V. Manorama, and A. Ramachandra Reddy, Bandgap studies on anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles, Mater. Chem. Phys., 78, 239–245 (2002).
B. C. Pak and Y. I. Cho, Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles, Exp. Heat Transf., 11, 151–170 (1999).
Z. Haddad, C. Abid, O. Rahil, O. Margeat, W. Dachraoui, and A. Mataoui, Is it important to measure the volumetric mass density of nanofluids? Math. Phys. Electrical Comput. Eng., 8, 310–313 (2014).
D. A. Drew and S. L. Passman, Theory of Multicomponent Fluids, Springer, Berlin (1999).
A. Einstein, Eine neue Bestimmung der Moleküldimensionen, Ann. Phys., 19, 289–306 (1906).
H. C. Brinkman, The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions, Chem. Phys., 20, 571–580 (1952).
G. K. Batchelor, The effect of Brownian motion on the bulk stress in a suspension of spherical particles, Fluid Mech., 83, 97–117 (1977).
N. Jamshidi, M. Farhadi, D. D. Ganji, and K. Sedighi, Experimental investigation on the viscosity of nanofluids, Eng. Transact. B, 25, 201–209 (2012).
S. M. S. Murshed, K. C. Leong, and C. Yang, Enhanced thermal conductivity of TiO2-water based nanofluids, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 44, 367–373 (2005).
M. Jalal, H. Meisami, and M. Pouyagohar, Experimental study of CuO/water nanofluid effect on convective heat transfer of a heat sink, Sci. Res., 13, 606–611 (2013).
R. Prasher, D. Song, J. Wang, and P. Phelan, Measurements of nanofluid viscosity and its implications for thermal applications, Appl. Phys. Lett., 89, 133108–1331083 (2006).
R. E. Simons, Comparing heat transfer rates of liquid coolants using the Mouromtseff number, Electron. Cool., 12, No. 2 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Inzhenerno-Fizicheskii Zhurnal, Vol. 91, No. 2, pp. 525–533, March–April, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leena, М., Srinivasan, S. Experimental Investigation of the Thermophysical Properties of TiO2/Propylene Glycol–Water Nanofluids for Heat-Transfer Applications. J Eng Phys Thermophy 91, 498–506 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-018-1770-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-018-1770-7