Abstract
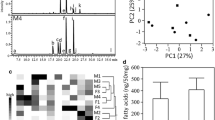
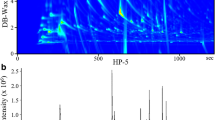
Scents emitted from excretions provide important information about the owner. Volatile compounds with higher levels in a species and/or sex, or that vary among individuals could be odor cues for species and/or sex, or individual recognition. However, such compounds have been identified in only a few vertebrate species. In domestic cats (Felis silvestris catus), it is known that unburied cat feces are territorial markers asserting the border of their home range, but little was known which fecal compounds are scent cues for species, sex, and individual recognition in cats. In the present study, we demonstrated the chemical basis for species, sex, and individual recognition using feces of cats. For males, major contents were fatty acids and 3-mercapto-3-methyl-1-butanol (MMB), a derivative of the unusual amino acid, felinine. MMB emission levels from feces had sex-based differences (male > female) and dynamic temporal changes during aging. Cats distinguished fecal odors with and without MMB, and different fatty acid compositions among individuals. No cat-specific compound, such as MMB, was detectable from their anal odor emitting fatty acids. We concluded that fecal MMB is a male sex recognition pheromone in cats and also provides a temporal trace of the owner. After sensing MMB, they may distinguish individual differences of conspecific feces with variable subsets of fatty acids. In contrast to scent marks, since cats can obtain species information from visual cues before sniffing conspecific anal odors, they may use their efforts to distinguish individual differences of anal odors during sniffing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apfelbach R, Blanchard CD, Blanchard RJ, Hayes RA, McGregor IS (2005) The effects of predator odors in mammalian prey species: a review of field and laboratory studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1123–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.05.005
Apps P, Mmualefe L, Jordan NR, Golabek KA, McNutt JW (2014) The “tomcat compound” 3-mercapto-3-methylbutanol occurs in the urine of free-ranging leopards but not in African lions or cheetahs. Biochem Syst Ecol 53:17–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2013.12.013
Apps P, Claase M, Yexley B, McNutt JW (2017) Interspecific responses of wild African carnivores to odour of 3- mercapto-3-methylbutanol, a component of wildcat and leopard urine. J Ethol 10:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10164-016-0503-7
Arbuckle EP, Smith GD, Gomez MC, Lugo JN (2015) Testing for odor discrimination and habituation in mice J Vis Exp e52615 doi:https://doi.org/10.3791/52615
Arnould C, Malosse C, Signoret J-P, Descoins C (1998) Which chemical constituents from dog feces are involved in its food repellent effect in sheep? J Chem Ecol 24:559–576. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022321104758
Buesching CD, Waterhouse JS, Macdonald DW (2002a) Gas-chromatographic analyses of the subcaudal gland secretion of the European badger (Meles meles) part I: chemical differences related to individual parameters. J Chem Ecol 28:41–56. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013558718057
Buesching CD, Waterhouse JS, Macdonald DW (2002b) Gas-chromatographic analyses of the subcaudal gland secretion of the European badger (Meles meles) Part II: time-related variation in the individual-specific composition. J Chem Ecol. 28:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013510802127
Crowell-Davis SL, Curtis TM, Knowles RJ (2004) Social organization in the cat: a modern understanding. J Feline Med Surg 6:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfms.2003.09.013
Dehasse J (1997) Feline urine spraying. Appl Anim Behav Sci 52:365–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1591(96)01135-5
Feldman H (1994) Methods of scent marking in the domestic cat. Can J Zool 72:1093–1099. https://doi.org/10.1139/z94-147
Futsuta A, Hojo W, Miyazaki T, Yamashita T, Miyazaki M (2018) LC-MS/MS quantification of felinine metabolites in tissues, fluids, and excretions from the domestic cat (Felis cutus). J Chromatogr B 1072:99–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.11.006
Goodrich B, Hesterman E, Shaw K, Mykytowycz R (1981) Identification of some volatile compounds in the odor of fecal pellets of the rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus. J Chem Ecol 7:817–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00992380
Goodrich B, Gambale S, Pennycuik PR, Redhead T (1990) Volatiles from feces of wild male house mice. J Chem Ecol 16:2091–2106. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01026922
Gorman ML (1976) A mechanism for individual recognition by odour in Herpestes auropunctatus (Carnivora: Viverridae). Anim Behav 24:141–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-3472(76)80107-8
Hegab IM, Jin Y, Ye M, Wang A, Yin B, Yang S, Wei W (2014) Defensive responses of Brandt's voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii) to stored cat feces. Physiol Behav 123:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.10.030
Hendriks WH, Moughan PJ, Tarttelin MF, Woolhouse AD (1995a) Felinine: a urinary amino acid of Felidae. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 112:581–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(95)00130-1
Hendriks WH, Tarttelin MF, Moughan PJ (1995b) Twenty-four hour felinine excretion patterns in entire and castrated cats. Physiol Behav 58:467–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(95)00084-V
Hendriks WH, Rutherfurd-Markwick KJ, Weidgraaf K, Ugarte C, Rogers QR (2008) Testosterone increases urinary free felinine, N-acetylfelinine and methylbutanolglutathione excretion in cats (Felis catus). J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 92:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2007.00710.x
Hurst JL, Beynon RJ (2004) Scent wars: the chemobiology of competitive signalling in mice BioEssays: news and reviews in molecular, cellular and. Dev Biol 26:1288–1298. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20147
Kotani A, Miyaguchi Y, Kohama M, Ohtsuka T, Shiratori T, Kusu F (2009) Determination of short-chain fatty acids in rat and human feces by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Anal Sci 25:1007–1011. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.25.1007
Lin DY, Zhang SZ, Block E, Katz LC (2005) Encoding social signals in the mouse main olfactory bulb. Nature 434:470–477. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03414
MacDonald ML, Rogers QR, Morris JG (1984) Nutrition of the domestic cat, a mammalian carnivore. Annu Rev Nutr 4:521–562. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nu.04.070184.002513
Mattina MJ, Pignatello JJ, Swihart RK (1991) Identification of volatile components of bobcat (Lynx rufus) urine. J Chem Ecol 17:451–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994344
Miyazaki M, Yamashita T, Suzuki Y, Saito Y, Soeta S, Taira H, Suzuki A (2006a) A major urinary protein of the domestic cat regulates the production of felinine, a putative pheromone precursor. Chem Biol 13:1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.08.013
Miyazaki M, Yamashita T, Taira H, Suzuki A (2006b) The biological function of cauxin, a major urinary protein of the domestic cat (Felis catus). In: Hurst J, Beynon R, Roberts S, Wyatt T (eds) Chemical Signals in Vertebrates 11, vol 11. Springer, New York, pp 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-73945-8_4
Miyazaki M, Nishimura T, Hojo W, Miyazaki T, Laine R, Yamashita T (2017) Potential use of domestic cat (Felis catus) urinary extracts for manipulating the behavior of free-roaming cats and wild small felids. Appl Anim Behav Sci 196:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2017.07.003
Miyazaki T, Nakata K, Nishimura T, Abe S, Yamashita T, Miyazaki M (2018a) Identification of 2-phenylethanol with a rose-like odor from anal sac secretions of the small Indian mongoose (Herpestes auropunctatus). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2017.1419854
Miyazaki T, Nishimura T, Yamashita T, Miyazaki M (2018b) Olfactory discrimination of anal sac secretions in the domestic cat and the chemical profiles of the volatile compounds. J Ethol 36:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10164-017-0532-x
Nakabayashi M, Yamaoka R, Nakashima Y (2012) Do faecal odours enable domestic cats (Felis catus) to distinguish familiarity of the donors? J Ethol 30:325–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10164-011-0321-x
Natoli E (1985) Behavioural responses of urban feral cats to different types of urine marks. Behaviour 94:234–243. https://doi.org/10.1163/156853985X00208
Vaughn S, Berhow M, Winkler-Moser J, Lee E (2011) Formulation of a biodegradable, odor-reducing cat litter from solvent-extracted corn dried distillers grains. Ind Crops Prod 34:999–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.03.005
Vernet-Maury E, Constant B, Chanel J (1992) Repellent effect of trimethyl thiazoline in the wild rat Rattus norvegicus Berkenhout. Chemical signals in vertebrates VI. Plenum Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9655-1_49
Vogt K, Boos S, Breitenmoser U, Kölliker M (2016) Chemical composition of Eurasian lynx urine conveys information on reproductive state, individual identity, and urine age. Chemoecology 26:205–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-016-0220-2
Voznessenskaya VV (2014) Influence of cat odor on reproductive behavior and physiology in the house mouse (Mus Musculus). In: Mucignat-Caretta C (ed) Neurobiology of chemical communication, vol Chapter 14. Frontiers in Neuroscience. CRC press, Boca Raton, p Chapter 14
Westall RG (1953) The amino acids and other ampholytes of urine. 2. The isolation of a new Sulphur-containing amino acid from cat urine. Biochem J 55:244–248. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0550244
Wyatt TD (2010) Pheromones and signature mixtures: defining species-wide signals and variable cues for identity in both invertebrates and vertebrates. J Comp Physiol A 196:685–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-010-0564-y
Wyatt TD (2014) Pheromones and animal behavior vol Second Edition, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139030748
Yamane A, Ono Y, Doi T (1994) Home range size and spacing pattern of a feral cat population on a small island. J Mammal Soc Japan 19:9–20. https://doi.org/10.11238/jmammsocjapan.19.9
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. T. Wyatt for invaluable discussion. This research was funded by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 17H03937 and 17 K19215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 228 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazaki, M., Miyazaki, T., Nishimura, T. et al. The Chemical Basis of Species, Sex, and Individual Recognition Using Feces in the Domestic Cat. J Chem Ecol 44, 364–373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-018-0951-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-018-0951-3