Abstract
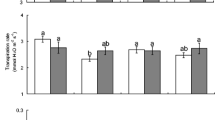
Root herbivores can indirectly affect aboveground herbivores by altering the food quality of the plant. However, it is largely unknown whether plant genotypes differ in their response to root herbivores, leading to variable defensive phenotypes. In this study, we investigated whether root-feeding insect larvae (Agriotes sp. larvae, wireworms) induce different responses in Plantago lanceolata plants from lines selected for low and high levels of iridoid glycosides (IG). In the absence of wireworms, plants of the “high-IG line” contained approximately twofold higher levels of total IG and threefold higher levels of catalpol (one of the IG) in leaves than plants from the “low-IG line,” whereas both lines had similar levels of IG in roots. In response to wireworms, roots of plants from both lines showed increased concentrations of catalpol. Leaves of “low-IG line” plants increased catalpol concentrations in response to wireworms, whereas catalpol concentrations of leaves of “high-IG line” plants decreased. In contrast, glucose concentrations in roots of “low-IG” plants decreased, while they increased in “high-IG” plants after feeding by wireworms. The leaf volatile profile differed between the lines, but was not affected by root herbivores. In the field, leaf damage by herbivores was higher in wireworm-induced compared to noninduced “low-IG” plants and lower in wireworm-induced compared to noninduced “high-IG” plants, despite induction of catalpol in leaves of the “low-IG” plants and reduction in “high-IG” plants. This pattern might arise if damage is caused mainly by specialist herbivores for which catalpol may act as feeding stimulant rather than as deterrent. The present study documents for the first time that intraspecific variation in plant defense affects the outcome of plant-mediated interactions between root and shoot herbivores.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, L. S., Schmitt, J., and Bowers, M. D. 1995. Genetic variation in defensive chemistry in Plantago lanceolata (Plantaginaceae) and its effect on the specialist herbivore Junonia coenia (Nymphalidae). Oecologia 101:75–85.
Agrawal, A. A., and Karban, R. 1999. Why induced defenses may be favored over constitutive strategies in plants, in R. Tollrian, and C. D. Harvell (eds.). The Ecology and Evolution of Inducible DefensesPrinceton University Press, Princeton.
Bezemer, T. M., and Van Dam, N. M. 2005. Linking aboveground and belowground interactions via induced plant defenses. TREE 20:617–624.
Bezemer, T. M., Wagenaar, R., Van Dam, N. M., and Wäckers, F. L. 2003. Interactions between above- and belowground insect herbivores as mediated by the plant defense system. Oikos 101:555–562.
Bezemer, T. M., Wagenaar, R., Van Dam, N. M., Van der Putten, W. H., and Wäckers, F. L. 2004. Above- and below-ground terpenoid aldehyde induction in cotton, Gossypium herbaceum, following root and leaf injury. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:53–67.
Biere, A., Marak, H. B., and Van Damme, J. M. M. 2004. Plant chemical defense against herbivores and pathogens: generalized defense or trade-offs? Oecologia 140:3430–441.
Birch, A. N. E., Griffiths, D. W., Hopkins, R. J., Smith, W. H. M., and Mckinlay, R. G. 1992. Glucosinolate responses of swede, kale, forage and oilseed rape to root damage by turnip root fly (Delia floralis) larvae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 60:1–9.
Borowicz, V. A., Albrecht, U., and Mayer, R. T. 2003. Effects of nutrient supply on citrus resistance to root herbivory by Diaprepes abbreviatus L. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ. Entomol. 32:1242–1250.
Bowers, M. D. 1983. The role of iridoid glycosides in host-plant specificity of checkerspot butterflies. J. Chem. Ecol. 9:475–493.
Bowers, M. D., and Puttick, G. M. 1988. Response of generalist and specialist insects to qualitative allelochemical variation. J. Chem. Ecol. 14:319–334.
Bowers, M. D., and Stamp, N. E. 1992. Chemical variation within and between individuals of Plantago lanceolata (Plantaginaceae). J. Chem. Ecol. 18:985–995.
Darrow, K., and Bowers, M. D. 1999. Effects of herbivore damage and nutrient level on induction of iridoid glycosides in Plantago lanceolata. J. Chem. Ecol. 25:61427–1440.
Dicke, M. 1999. Evolution of induced indirect defense of plants, in R. Tollrian, and C. D. Harvell (eds.). The Ecology and Evolution of Inducible DefensesPrinceton University Press, Princeton.
Gange, A. C. 2001. Specie-specific responses of a root- and shoot-feeding insect to arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of its host plant. New Phytol. 150:611–618.
Gange, A. C., and West, H. M. 1994. Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and foliar-feeding insects in Plantago lanceolata L. New Phytol. 128:79–87.
Gange, A. C., Brown, V. K., and Sinclair, G. S. 1994. Reduction of black vine weevil larval growth by vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal infection. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 70:115–119.
Karban, R., and Baldwin, I. T. 1997. Induced Responses to Herbivory. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Lepš, J., and Šmilauer, P. 2003. Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Marak, H. B., Biere, A., and Van Damme, J. M. M. 2000. Direct and correlated responses to selection on iridoid glycosides in Plantago lanceolata L. J. Evol. Biol. 13:985–996.
Marak, H. B., Biere, A., and Van Damme, J. M. M. 2002a. Two herbivore-deterrent iridoid glycosides reduce the in-vitro growth of a specialist but not of a generalist pathogenic fungus of Plantago lanceolata L. Chemoecology 12:185–192.
Marak, H. B., Biere, A., and Van Damme, J. M. M. 2002b. Systemic, genotype-specific induction of two herbivore-deterrent iridoid glycosides in Plantago lanceolata L. in response to fungal infection by Diaporthe adunca (Rob.) Niessel. J. Chem. Ecol. 28:2429–2448.
Marak, H. B., Biere, A., and Van Damme, J. M. M. 2003. Fitness costs of chemical defense in Plantago lanceolata L.: effects of nutrient and competition stress. Evolution 57:2519–2530.
Masters, G. J., Brown, V. K., and Gange, A. C. 1993. Plant mediated interactions between above- and below-ground insect herbivores. Oikos 66:148–151.
Moran, N. A., and Whitham, T. G. 1990. Interspecific competition between root-feeding and leaf-galling aphids mediated by host-plant resistance. Ecology 71:1050–1058.
Poveda, K., Steffan-Dewenter, I., Scheu, S., and Tscharntke, T. 2005. Effects of decomposers and herbivores on plant performance and aboveground plant–insect interactions. Oikos 108:503–510.
Soler, R., Bezemer, T. M., Van der Putten, W. H., Vet, L. E. M., and Harvey, J. A. 2005. Root herbivore effects on above-ground herbivore, parasitoid and hyperparasitoid performance via changes in plant quality. J. Anim. Ecol. 74:1121–1130.
Soler, R., Harvey, J. A., Kamp, A. F. D., Vet, L. E. M., Van der Putten, W. H., Van Dam, N. M., Stuefer, J. F., Gols, R., Hordijk, C. A., and Bezemer, T. M. 2007. Root herbivores influence the behavior of an aboveground parasitoid through changes in plant-volatile signals. Oikos 116:367–376.
Staley, J. T., Hodgson, C. J., Mortimer, S. R., Morecroft, M. D., Masters, G. J., Brown, V. K., and Taylor, M. E. 2007. Effects of summer rainfall manipulations on the abundance and vertical distribution of herbivorous soil macro-invertebrates. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 43:189–198.
Van Dam, N. M., and Raaijmakers, C. E. 2006. Local and systemic induced responses to cabbage root fly larvae (Delia radicum) in Brassica nigra and B. oleracea. Chemoecology 16:17–24.
Van Dam, N. M., Harvey, J. A., Wäckers, F. L., Bezemer, T. M., Van der Putten, W. H., and Vet, L. E. M. 2003. Interactions between aboveground and belowground induced responses against phytophages. Basic Appl. Ecol. 4:63–77.
Van Dam, N. M., Raaijmakers, C. E., and Van der Putten, W. H. 2005. Root herbivory reduces growth and survival of the shoot feeding specialist Pieris rapae on Brassica nigra. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 115:161–170.
Van der Putten, W. H., Vet, L. E. M., Harvey, J. A., and Wäckers, F. L. 2001. Linking above- and belowground multitrophic interactions of plants, herbivores, pathogens, and their antagonists. TREE 16:547–554.
Willinger, G., and Dobler, S. 2001. Selective sequestration of iridoid glycosides from their host plants in Longitarsus flea beetles. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 29:335–346.
Wurst, S., and Van der Putten, W. H. 2007. Root herbivore identity matters in plant-mediated interactions between root and shoot herbivores. Basic Appl. Ecol. 8:491–499.
Wurst, S., Dugassa-Gobena, D., Langel, R., Bonkowski, M., and Scheu, S. 2004. Combined effects of earthworms and vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizas on plant and aphid performance. New Phytol. 163:169–176.
Acknowledgments
We thank Wiecher Smant for analyzing plant N and C concentrations, Sander Van Beersum for determining the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonization of the roots, and Kees Hordijk for the gas chromatography–mass spectrometry measurements. The study was financed by the EU-funded Marie-Curie training network BIORHIZ (“Biotic Interactions in the Rhizosphere as Structuring Forces for Plant Communities,” MRTN-CT-2003-505090). Publication 4324 Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wurst, S., Van Dam, N.M., Monroy, F. et al. Intraspecific Variation in Plant Defense Alters Effects of Root Herbivores on Leaf Chemistry and Aboveground Herbivore Damage. J Chem Ecol 34, 1360–1367 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-008-9537-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-008-9537-9