Abstract
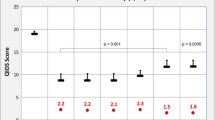
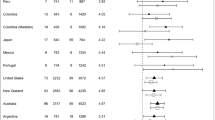
Psychological distress states have been related to rate of disease progression among HIV-positive individuals. However, the measures that have been used in this research as well as the treatment context of the populations studied are highly variable, making it challenging for clinicians to incorporate such measures into screening batteries. The present study examined the association of two summary scales of the Millon Behavioral Medicine Diagnostic (MBMD; Millon et al., Millon Behavioral Medicine Diagnostic. NCS Assessments, Minneapolis, 2001), with markers of HIV disease status (CD4 and CD8 cell counts, viral load) among an ethnically diverse sample of 147 HIV-positive individuals (52 men who have sex with men, 34 men who have sex with women, and 51 women) who had recently initiated Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART). After controlling for age and months since HIV diagnosis, we found that higher scores on the overall MBMD Psych Referral Summary Scale, reflecting a need for mental health treatment, were related to greater HIV viral load but did not relate to CD4 or CD8 cell counts. Subgroup analyses revealed that Psych Referral scores were related to greater HIV viral load only for the men who have sex with men (MSM) subgroup. These results suggest that the MBMD may help in identifying psychosocial characteristics associated with some markers of disease status in persons with HIV and perhaps may also be useful in identifying individual differences in response to treatment and eventual disease outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoni, M., Carrico, A., Durán, R., Spitzer, S., Penedo, F., Ironson, G., et al. (2006). Randomized clinical trial of cognitive behavioral stress management on human immunodeficiency virus viral load in gay men treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. Psychosomatic Medicine, 68, 143–151.
Beaudin, C. L., & Chambre, S. M. (2006). HIV/AIDS as a chronic disease: Emergence from the plague model. American Journal of Behavioral Science, 39, 684–706.
Carrico, A., & Antoni, M. H. (2008). The effects of psychological interventions on neuroendocrine hormone regulation and immune status in HIV-positive persons: A review of randomized controlled trials. Psychosomatic Medicine, 70, 575–584.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2007a). HIV/AIDS fact sheet. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/resources/factsheets/index.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2007b). HIV/AIDS among men who have sex with men. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/topics/msm/resources/factsheets/msm.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2007c). HIV/AIDS among women. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/topics/women/resources/factsheets/women.htm
Cole, S. (2008). Psychosocial influences on HIV-1 disease progression: Neural, endocrine, and virologic mechanisms. Psychosomatic Medicine, 70, 562–568.
Cruess, D. G., Douglas, S. D., Petitto, J. M., Have, T. T., Getttes, D., Dube, B., et al. (2005). Association of resolution of major depression with increased natural killer cell activity among HIV-seropositive women. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162, 2125–2130.
Cruess, D. G., Localio, A. R., Platt, A. B., Brensinger, C. M., Christie, J. D., Gross, R., et al. (2009). Patient attitudinal and behavioral factors associated with Warfarin non-adherence at outpatient anticoagulation clinics. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 17, 33–42.
Cruess, D. G., Minor, S., Antoni, M. G., & Millon, T. (2007). Utility of the Millon Behavioral Medicine Diagnostic (MBMD) to predict adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) medication regimens among HIV-positive men and women. Journal of Personality Assessment, 89, 277–290.
Dowshen, N., Binns, H. J., & Garofalo, R. (2009). Experiences of HIV-related stigma among young men who have sex with men. AIDS Patient Care and STDs, 23, 371–376.
First, M. B., Spitzer, R. L., Miriam, G., & Williams, J. B. W. (2001). Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders, Research Version, Patient Edition (SCID-I/P). New York: Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute.
Gallant, J. E., & Hoffman, C. (2010). CD4 cell count. In HIV Guide; Management; Laboratory Testing. Retrieved July 27, 2010, from http://www.hopkins-hivguide.org
Golin, C., Marks, G., Wright, J., Gerkovich, M., Tien, H., Patel, S. N., et al. (2009). Psychosocial characteristics and sexual behaviors of people in care for HIV infection: An examination of men who have sex with men, hetersexual men and women. AIDS and Behavior, 13, 1129–1142.
Ickovics, J. R., Hamburger, M. E., Vlahov, D., Schoenbaum, E. E., Schuman, P., Boland, R. J., et al. (2001). Mortality, CD4 cell count decline, and depressive symptoms among HIV-seropositive women: Longitudinal analysis from the HIV epidemiology research study. JAMA, 285, 1460–1465.
Ickovics, J. R., Milan, S., Boland, R., Schoenbaum, E., Schuman, P., & Vlahov, D. (2006). Psychological resources protect health: 5-year survival and immune function among HIV-infected women from four US cities. AIDS, 20, 1851–1860.
Ironson, G., Balbin, E., Stuetzle, R., Fletcher, M. A., O’Cleirigh, C., Laurenceau, J. P., et al. (2005a). Dispositional optimism and the mechanisms by which it predicts slower disease progression in HIV: Proactive behavior, avoidant coping, and depression. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 12, 86–97.
Ironson, G., & Hayward, H. (2008). Do positive psychosocial factors predict disease progression in HIV? A review of the evidence. Psychosomatic Medicine, 70, 546–554.
Ironson, G., O’Clerigh, C., Fletcher, M. A., Laurenceau, J. P., Balbin, E., Klimas, N., et al. (2005b). Psychosocial factors predict CD4 and viral load change in men and women with human immunodeficiency virus in the era of highly active antiretroviral treatment. Psychosomatic Medicine, 67, 1013–1021.
Ironson, G., Weiss, S., Lydston, D., Ishii, M., Jones, D., Asthana, D., et al. (2005c). The impact of improved self-efficacy on HIV viral load and distress in culturally diverse women living with AIDS: The SMART/EST women’s project. Self-efficacy and HIV viral load in women with AIDS. AIDS care, 17, 222–236.
Israelski, D. M., Prentiss, D. E., Lubega, S., Balmas, G., Garcia, P., Muhammad, M., et al. (2007). Psychiatric co-morbidity in vulnerable populations receiving primary care for HIV/AIDS. AIDS Care, 19, 220–225.
Jaffe, H. W., Valdiserri, R. O., & De Cock, K. M. (2007). The reemerging HIV/AIDS epidemic in men who have sex with men. JAMA, 298, 2412–2414.
Klimas, N., Koneru, A., & Fletcher, M. (2008). Overview of HIV. Psychosomatic Medicine, 70, 523–530.
Leserman, J. (2003). HIV disease progression: Depression, stress, and possible mechanisms. Biological Psychiatry, 54, 295–306.
Leserman, J. (2008). Role of depression, stress, and trauma in HIV disease progression. Psychosomatic Medicine, 70, 539–545.
Leserman, J., Petitto, J. M., Golden, R. N., Gaynes, B. N., Gu, H., Perkins, D. O., et al. (2000). Impact of stressful life events, depression, social support, coping, and cortisol on progression to AIDS. American Journal of Psychiatry, 157, 1221–1228.
Leserman, J., Petitto, J. M., Gu, H., Gaynes, B. N., Barroso, J., Golden, R. N., et al. (2002). Progression to AIDS, a clinical AIDS condition, and mortality: Psychosocial and physiological predictors. Psychological Medicine, 32, 1059–1073.
Mellors, J. W., Rinaldo, C. R., Gupta, P., White, R. M., Todd, J. A., & Kingsley, L. A. (1996). Prognosis in HIV-1 infection predicted by the quantity of virus in plasma. Science, 24, 1167–1170.
Millon, T., Antoni, M., Millon, C., Meagher, S., & Millon, G. S. (2001). Millon Behavioral Medicine Diagnostic. Minneapolis: NCS Assessments.
Nilsson, J., Kinloch-de-Loes, S., Granath, A., Sonnerborg, A., Goh, L. E., & Andersson, J. (2007). Early immune activation in gut-associated and peripheral lymphoid tissue during acute HIV infection. AIDS, 21, 565–574.
Pence, B. W., Miller, W. C., Whetten, K., Eron, J. J., & Gaynes, G. N. (2006). Prevalence of DSM-IV-defined mood, anxiety, and substance use disorders in an HIV clinic in the Southeastern United States. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, 42, 298–306.
Power, C., Selnes, O. A., Grim, J. A., & McArthur, J. C. (1995). HIV dementia scale: A rapid screening test. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome—Human Retrovirology, 8, 273–278.
Rinaldo, C., Huang, X. L., Fan, Z. F., Ding, M., Beltz, L., Logar, A., et al. (1995). High levels of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) memory cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity and low viral load are associated with lack of disease in HIV-1-infected long-term nonprogressors. Journal of Virology, 69, 5838–5842.
Sloan, E. K., Collado-Hidalgo, A., & Cole, S. (2007). Psychobiology of HIV infection. In R. Ader (Ed.), Psychneuroimmunology, 4th ed (Vol. 2, pp. 1053–1076). Burlington, MA: Elsevier Academic Press.
Ternoshok, L., Wald, R. L., Synowski, S., & Garzino-Demo, A. (2008). Coping as a multi-system construct that influences pathways mediating HIV-relevant immune function and disease progression. Psychosomatic Medicine, 70, 555–561.
UNAIDS. (2007). AIDS Epidemic Update. Available at http://data.unaids.org/pub/EPISlides/2007/2007_epiupdate_en.pdf
Weaver, K. E., Llabre, M. M., Duran, R. E., Antoni, M. H., Ironson, G., Penedo, F. J., et al. (2005). A stress and coping model of medication adherence and viral load in HIV-positive men and women on highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Health Psychology, 24, 385–392.
Whetten, K., Leserman, J., Lowe, K., Stangl, D., Theilman, N., Swartz, M., et al. (2006). Prevalence of childhood sexual abuse and physical trauma in an HIV-Positive sample from the deep south. American Journal of Public Health, 96, 1028–1030.
Wilkinson, G. S. (1993). Wide Range Achievement Test–Revision 3. Wilmington, DE: Jastak Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burbridge, C., Cruess, D.G., Antoni, M.H. et al. Using the Millon Behavioral Medicine Diagnostic (MBMD) to Evaluate the Need for Mental Health Services in Association with Biomarkers of Disease Status Among HIV Positive Men and Women. J Clin Psychol Med Settings 18, 30–38 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10880-011-9231-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10880-011-9231-x