Abstract
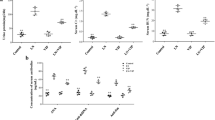
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) has been found to act as a potent anti-inflammatory factor through regulating the production of both anti- and pro-inflammatory mediators and promoting Th2-type responses. In this study, we used myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model in C57BL/6 mice to investigate the potential effects of VIP on multiple sclerosis. Our results showed that in vivo treatment of EAE-induced mice with VIP had great protective benefit at both clinical and histological levels. Disease suppression was associated with the inhibition of T cells proliferation, shifting of the immune response toward a Th2-type response and influencing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IFN-γ, IL-6 and IL-2 as well as chemotactic factors such as RANTES. In conclusion, the study provides evidence that VIP had great protective effect on EAE through its inhibition actions on pathogenic T cells and through a specific effect on the Th1 response.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Said SI, Mutt V: Polypeptide with broad biological activity: Isolation from small intestine. Science 169:1217–1218, 1970.
Blalock JE: The syntax of immune-neuroendocrine communication. Immunol Today 15:504–511, 1994.
Gomariz RP, Martinez C, Abad C, Leceta J, Delgado M: Immunology of VIP: A review and therapeutical perspectives. Curr Pharm Des 7:89–111, 2001.
Pozo D: VIP- and PACAP-mediated immunomodulation as prospective therapeutic tools. Trends Mol Med 9:211–217, 2003.
Delgado M, Pozo D, Ganea D: The significance of vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation. Pharmacol Rev 56:249–290, 2004.
Calvo JR, Pozo D, Guerrero JM: Functional and molecular characterization of VIP receptors and signal transduction in human and rodent immune systems. Adv Neuroimmunol 6:39–47, 1996.
Harmar AJ, Arimura A, Gozes I, Journot L, Laburthe M, Pisegna JR, Rawlings SR, Robberecht P, Said SI, Sreedharan SP, Wank SA, Waschek JA: International Union of Pharmacology. XVIII. Nomenclature of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. Pharmacol Rev 50:265–270, 1998.
Delgado M: VIP: A very important peptide in T helper differentiation. Trends Immunol 24:221–224, 2003.
Abad C, Martinez C, Juarranz MG, Arranz A, Leceta J, Delgado M, Gomariz RP: Therapeutic effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid mice model of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 124:961–971, 2003.
Keino H, Kezuka T, Takeuchi M, Yamakawa N, Hattori T, Usui M: Prevention of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Arch Ophthalmol 122:1179–1184, 2004.
Delgado M, Abad C, Martinez C, Leceta J, Gomariz RP: Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease. Nat Med 7:563–568, 2001.
Giovannoni G, Hartung HP: The immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and Guillain-Barre syndrome. Curr Opin Neurol 9:165–177, 1996.
Zamvil SS, Steinman L: The T lymphocyte in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Annu Rev Immunol 8:579–621, 1990.
Steinman L: Assessment of animal models for MS and demyelinating disease in the design of rational therapy. Neuron 24:511–514, 1999.
Bernard CC, Johns TG, Slavin A, Ichikawa M, Ewing C, Liu J, Bettadapura J: Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein: A novel candidate autoantigen in multiple sclerosis. J Mol Med 75:77–88, 1997.
Wekerle H, Kojima K, Lannes-Vieira J, Lassmann H, Linington C: Animal models. Ann Neurol 36(Suppl):S47–S53, 1994.
Teresi S, Boudard F, Bastide M: Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide and vasoactive intestinal peptide on murine CD4 and CD8 T cell proliferation. Immunol Lett 50:105–113, 1996.
Delgado M, Chorny A, Gonzalez-Rey E, Ganea D: Vasoactive intestinal peptide generates CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in vivo. J Leukoc Biol 78:1327–1338, 2005.
Ersoy E, Kus CN, Sener U, Coker I, Zorlu Y: The effects of interferon-beta on interleukin-10 in multiple sclerosis patients. Eur J Neurol 12:208–211, 2005.
Youssef S, Stuve O, Patarroyo JC, Ruiz PJ, Radosevich JL, Hur EM, Bravo M, Mitchell DJ, Sobel RA, Steinman L, Zamvil SS: The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes a Th2 bias and reverses paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. Nature 420:78–84, 2002.
Delgado M, Munoz-Elias EJ, Gomariz RP, Ganea D: VIP and PACAP inhibit IL-12 production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Subsequent effect on IFNgamma synthesis by T cells. J Neuroimmunol 96:167–181, 1999.
Delgado M, Ganea D: Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit interleukin-12 transcription by regulating nuclear factor kappaB and Ets activation. J Biol Chem 274:31930–31940, 1999.
Delgado M, Leceta J, Gomariz RP, Ganea D: Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide stimulate the induction of Th2 responses by up-regulating B7.2 expression. J Immunol 163:3629–3635, 1999.
Ranger AM, Das MP, Kuchroo VK, Glimcher LH: B7-2 (CD86) is essential for the development of IL-4-producing T cells. Int Immunol 8:1549–1560, 1996.
Ganea D, Delgado M: Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) as modulators of both innate and adaptive immunity. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 13:229–237, 2002.
Delgado M, Leceta J, Ganea D: Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide promote in vivo generation of memory Th2 cells. FASEB J 16:1844–1846, 2002.
Eugster HP, Frei K, Kopf M, Lassmann H, Fontana A: IL-6-deficient mice resist myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 28:2178–2187, 1998.
Ransohoff RM: The chemokine system in neuroinflammation: An update. J Infect Dis 186(Suppl 2):S152–S156, 2002.
Delgado M, Ganea D: Inhibition of endotoxin-induced macrophage chemokine production by vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 167:966–975, 2001.
Gonzalez-Rey E, Fernandez-Martin A, Chorny A, Martin J, Pozo D, Ganea D, Delgado M: Therapeutic effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Down-regulation of inflammatory and autoimmune responses. Am J Pathol 168:1179–1188, 2006.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The helpful advice of Prof. Jingwu Zang was greatly appreciated. This work was supported in part by Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Project 04DZ14902), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (04QMX1423) and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (T0206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Haiyan Li and Yunhua Mei contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Mei, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide Suppressed Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Inhibiting T Helper 1 Responses. J Clin Immunol 26, 430–437 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9042-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9042-2