Abstract
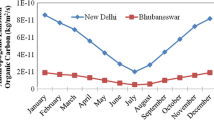
Sampling of particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter cut off at 2.5 μm (PM2.5) has been carried out over a semi urban site of Pune and an urban site of Hyderabad. Analysis of elemental Carbon (EC) and Organic Carbon (OC) present in PM2.5 was carried out using advanced Desert Research Institute’s (DRI) Thermal/Optical Carbon Analyzer operated on IMPROVE_ A (Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environments_ A) protocol. It is found that average concentration of EC and OC both at Pune and Hyderabad was highest during winter season and lowest during monsoon season. Winter high is mainly controlled by inversion, whereas monsoon low is due to rain-out and wash-out process. OC/EC ratio showed higher variation over Pune compared to that over Hyderabad in different seasons, indicating divergent sources of emission of OC and EC at Pune. Formation of Secondary Organic Carbon (SOC) has also been identified as one of the reasons for wide variation in OC/EC ratio value in different seasons over both the sites.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACE-Asia: Asian Pacific Regional Aerosol Characterization Experiment: http://saga.pmel.noaa.gov/aceasia/ (1999).
Kaushar, A., Budhavant, K.B., Safai, P.D., Rao, P.S.P.: Seasonal factors influencing in chemical composition of total suspended particles at Pune, India. Sci. Tot. Environ. 414, 257–267 (2012)
Begum, B.A., Hossain, A., Nahar, N., Markwitz, A., Hopke, P.K.: Organic and black carbon in PM2.5 at an urban site at Dhaka, Bangladesh. Aerosol Air Qual. Res 12, 1062–1072 (2012)
Bond, T.C., Streets, D.G., Yarber, K.F., Nelson, S.M., Woo, J.H., Klimont, Z.: A technology based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from Combustion. J. Geophys. Res. 109, D14203 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003JD003697
Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Ho, K.F., et al.: Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in Pearl River Delta Region, China during 2001 winter period. Atmos. Environ. 37, 1451–1460 (2003)
Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Ho, K.F., Zou, S.C., Fung, K., Li, Y., Watson, J.G., Chow, J.C.: Spatial and seasonal variations of atmospheric organic carbon and elemental carbon in Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Environ. 38, 4447–4456 (2004)
Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Ho, K.F., Fung, K., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G.: Characterization of roadside fine particulate carbon and its eight fractions in Hong Kong. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 6, 106–122 (2006)
Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Ho, K.F., Zhang, R.J., Jin, Z.D., Shen, Z.X., Chen, G.C., Kang, Y.M., Zou, S.C., Zhang, L.Z., Qi, S.H., Dai, M.H., Cheng, Y., Hu, K.: Spatial and seasonal distributions of carbonaceous aerosols over China. J. Geophys. Res. 112, D22S11 (2007). doi:10.1029/ 2006JD 008205
Cao, J.J., Wu, F., Chow, J.C., Lee, S.C., Li, Y., Chen, S.W., An, Z.S., Fung, K.K., Watson, J.G., Zhu, C.S., Liu, S.X.: Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 5, 3127–3137 (2005)
Castro, L.M., Pio, C.A., Harrison, R.M., Smith, D.J.T.: Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 33, 2771–2781 (1999)
Chan, C.Y., Xu, X.D., Li, Y.S., Wong, K.H., Ding, G.A., Chan, L.Y., Cheng, X.H.: Characteristics of vertical profiles and sources of PM2.5, P M10 and carbonaceous species in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 39, 5113–5124 (2005)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Chen, L.W.A., Arnott, W.P., Moosmuller, H., Fung, K.K.: Equivalence of elemental carbon by thermal/optical reflectance and transmittance with different temperature protocols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4414–4422 (2004)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Chen, L.W.A., Chang, M.C.O., Robinson, N.F., Trimble, D., Kohl, S.: The IMPROVE_A Temperature Protocol for Thermal/Optical Carbon Analysis: Maintaining Consistency with a Long-Term Database. J. Air & Waste Manage. Assoc. 57, 1014–1023 (2007). doi:10.3155/1047-3289.57.9.1014
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Robles, J., Wang, X., Chen, L.W.A., Trimble, D.L., Kohl, S.D., Tropp, R.J., Fung, K.K.: Quality assurance and quality control for thermal/optical analysis of aerosol samples for organic and elemental carbon. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. (2011). doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5103-3
Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change, Climate Change: The scientific basis, 5, aerosols, their direct and indirect effects, pp. 289–348. Cambridge University Press, London (2001)
Cooke, W.F., Liousse, C., Cachier, H., Feichter, J.: Construction of a 1° × 1° fossil fuel emission data set for carbonaceous aerosol and implementation and radiative impact in the ECHAM4 model. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 137–22 (1999)
Dan, M., Zhuang, G.S., Lia, X.X., et al.: The characteristics of carbonaceous species and their sources in PM2.5 in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 38, 3443–3452 (2004)
Feng, Y., Chen, Y., Guo, H., Zhi, G., Xiong, S., Li, J., Sheng, G., Fu, J.: Characteristics of organic and elemental carbon in PM2.5 samples in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Res. 92, 434–442 (2009)
Gu, J., Bai, Z., Liu, A., Wu, L., Xie, Y., Li, W., Dong, H., Zhang, H.: Characterization of atmospheric organic carbon and element carbon of PM2.5 and PM10 at Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 10, 167–176 (2010)
Gundel, L.A., Guyot-Sionnest, N.S., Novakov, T.: A study of the interaction of NO2 with carbon particles. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 10, 343–351 (1989)
Holler, R., Tohnoa, S., Kasaharaa, M., et al.: Long-term characterization of carbonaceous aerosol in Uji, Japan[J]. Atmos. Environ. 36, 1267–1275 (2002)
Holm, T.: Aspects of the mechanism of the flame ionization detector; review. J. Chromatogr. Abstr. 842, 221–227 (1999)
Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Summary for policymakers, in Climate change 2007: The scientific Basis Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment Report of the Intergovernmental panel on climate change, edited by S. Solomon et al., Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1–18 (2007)
Jacobson, M.Z.: Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 409, 695–697 (2001)
Ke, L., Ding, X., Tanner, R.L., Schauer, J.J., Zheng, M.: Source contributions to carbonaceous aerosols in the Tennessee Valley Region. Atmos. Environ. 41, 8898–8923 (2007)
Kim, E., Hopke, P.K.: Improving source identification of fine particles in a rural Northeastern US area utilizing temperature resolved carbon fractions. J. Geophys. Res. 109, D09204 (2004)
Kim, Y.P., Moon, K.C., Lee, J.H., Baik, N.J.: Concentrations of carbonaceous species in particles at Seoul and Cheju in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 33, 2751–2758 (1999)
Kim, Y.P., Moon, K.C., Lee, J.H.: Organic and elemental carbon in fine particles at Kosan, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 34, 3309–3317 (2000)
Kim, E., Hopke, P.K., Edgerton, E.S.: Source identification of Atlanta aerosol by positive matrix factorization. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 53, 731–739 (2003)
Kim, K.H., Sekiguchi, K., Kudo, S., Sakamoto, K.: Characteristics of atmospheric elemental carbon (Char and Soot) in ultrafine and fine particles in a roadside environment, Japan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 11, 1–12 (2011)
Kumar, K.R., Sivakumar, V., Reddy, R.R., Rama Gopal, K.: Ship-borne measurements of columnar and surface aerosol loading over the Bay of Bengal during W-ICARB campaign: role of airmass transport, latitudinal and longitudinal gradients. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 13, 818–837 (2013). doi:10.4209/aaqr.2012.08.0225
Kumar, R., Barth, M.C., Nair, V.S., Pfister, G.G., Suresh Babu, S., Satheesh, S.K., Krishna Moorthy, K., Carmichael, G.R., Lu, Z., Streets, D.G.: Sources of black carbon aerosols in South Asia and surrounding regions during the Integrated Campaign for Aerosols, Gases and Radiation Budget (ICARB). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 15, 5415–5428 (2015). doi:10.5194/acp-15-5415-2015
Lin, J.J., Tai, H.S.: Concentrations and distributions of carbonaceous species in ambient particles in Kaohsiung City. Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 35, 2627–2636 (2001)
Meng, Z.Y., Jiang, X.M., Yan, V., Lin, W.L., Zhang, H.D., Wang, Y.: Characteristics and sources of PM2.5 and carbonaceous species during winter in Taiyuan, China. Atmos. Environ. 41, 6901–6908 (2007)
Molnar, A., Meszaros, E., Hansson, H.C., et al.: The importance of organic and Elemental carbon in the fine atmospheric aerosol particles. Atmos. Environ. 33, 2745–2750 (1999)
Neusu, ß.,.C., Gnauk, T., Plewka, A., Herrmann, H., Quinn, P.K.: Carbonaceous aerosol over the Indian Ocean: OC/EC fractions and selected specifications from size- segregated onboard samples. J. Geophys. Res. 107(D19), 8031 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JD000327
Novakov, T., Penner, E.J.: Large contribution of organic aerosols to cloud condensation nuclei concentrations. Nature 365, 823–826 (1993)
Nunes, T.V., Pio, C.A.: Carbonaceous aerosols in industrial and coastal atmospheres. Atmos. Environ. 27, 1339–1346 (1993)
Panicker, A.S., Pandithurai, G., Safai, P.D., Dipu, S., Lee, D.I.: On the contribution of black carbon to the composite aerosol radiative forcing over an urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 44, 3066–3070 (2010)
Pavese, G., Calvello, M., Esposito, F.: Black carbon and organic components in the atmosphere of Southern Italy: comparing emissions from different sources and production processes of carbonaceous particles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 12, 1146–1156 (2012)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M.: Spatio-temporal variability in atmospheric abundances of EC, OC and WSOC over Northern India. J. Aerosol Sci. 41, 88–98 (2010a)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M.: Day-night variability of EC, OC, WSOC and inorganic ions in urban environment of Indo-Gangetic Plain: implications to secondary aerosol formation. Atmos. Environ. 45, 460–468 (2010b)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M., Hegde, P.: Atmospheric abundances of primary and secondary carbonaceous species at two high-altitude sites in India: sources and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 42, 6785–6796 (2008)
Ram, K., Sarin, M.M., Sudheer, A.K., Rengarajan, R.: Carbonaceous and secondary inorganic aerosols during wintertime fog and haze over urban sites in the indo-gangetic plain. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 12, 359–370 (2012)
Ramanathan, V., Crutzen, P.J., Kiehl, J.T., Rosenfeld, D.: Atmosphere: aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 294, 2119–2124 (2001)
Rosen, H., Novakov, T.: Raman scattering and the characterization of atmospheric aerosol particles. Nature 266, 708–710 (1977)
Saarikoski, S., Timonen, H., Saarnio, K., Aurela, M., Jarvi, L., Keronen, P., et al.: Sources of organic carbon in fine particulate matter in northern European urban air. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 8, 6281–6295 (2008)
Sahu, L.K., Kondo, Y., Miyazaki, Y., Pongkiatkul, P., Kim Oanh, N.T.: Seasonal and diurnal variations of black carbon and organic carbon aerosols in Bangkok. J. Geophys. Res. 116, D15302 (2011). doi:10.1029/2010JD015563
Satsangi, A., Pachauri, T., Singla, V., Lakhani, A., Kumari, K.M.: Organic and elemental carbon aerosols at a suburban site. Atmos. Res. 113, 13–21 (2012)
Saxena, P., Hildeman, L.M., McMurry, P.H., Seinfeld, J.H.: Organics alter hygroscopic behavior of atmospheric particles. J. Geophys. Res. 100(D9), 18,755–18,770 (1995). doi:10.1029/95JD01835
Schauer, J.J., Kleeman, M.J., Cass, G.R., Simoneit, B.R.T.: Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 5. C1–C32 organic compounds from gasoline-powered motor vehicles. Environ. Sci. Tech. 36, 1169–1180 (2002)
Schauer, J.J., Kleeman, M.J., Cass, G.R., Simoneit, B.R.T.: Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 2. C1 through C30 organic compounds from medium duty diesel trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 33, 1578–1587 (1999)
Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.: Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change[M], pp. 705–707. Wiley, New York (1998)
Shakya, K.M., Ziemba, L.D., Griffin, R.J.: Characteristics and sources of carbonaceous, ionic, and isotopic species of wintertime atmospheric aerosols in Kathmandu Valley. Nepal. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. (2009). doi:10.4209/aaqr. 2009.10.0068
Streets, D.G., et al.: An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 108(D21), 8809 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002JD003093
Turpin, B.J., Huntzicker, J.J.: Identification of secondary aerosol episodes and quantification of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during CAQS. Atmos. Environ. 29, 3527–3544 (1995)
Vedal, S.: Critical review—ambient particles and health: lines that divide. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 47(5), 551–581 (1997)
Viidanoja, J., Sillanp, M., Laakia, J., Kerminen, V.M., Hillamo, R., Aarnio, P., Koskentalo, T.: Organic and black carbon in PM2.5 and PM10: 1 year of data from an urban site in Helsinki, Finland. Atmos. Environ. 36, 3183–3193 (2002)
Watson, J.G.: Visibility: Science and regulation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 52(6), 628–713 (2002)
Watson, J.G., Chow, J.C., Chen, L.-W.A., Frank, N.H.: Methods to assess carbonaceous aerosol sampling artifacts for IMPROVE and other long-term networks. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 59, 898–911 (2009)
Zhang, M.G.: Modeling of organic carbon aerosol distributions over East Asia in the springtime. China Particuology 2(5), 192–195 (2004)
Zhang, M.G., Xu, Y.Y., Zhang, R.J., et al.: Emission and concentration distributions of black carbon aerosol in East Asia during the spring time. Chin. J. Geophys. 48(1), 55–61 (2005)
Zhang, Y., Shao, M., Zhang, Y., Zeng, L., He, L., Zhu, B., Wei, Y., Zhu, X.: Source profiles of particulate organic matters emitted from cereal straw burnings. J. Environ. Sci. 19, 167–175 (2007a)
Zhang, R.J., Cao, J.J., Lee, S.C., Shen, Z.X., Ho, K.F.: Carbonaceous aerosols in PM10 and pollution gases in winter in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 19, 564–571 (2007b)
Zhu, C.S., Cao, J.J., Shen, Z.X., Liu, S.X., Zhang, T., Zhao, Z.Z., Xu, H.M., Zhang, E.K.: Indoor and outdoor chemical components of PM2.5 in the rural areas of Northwestern China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 12, 1157–1165 (2012)
Acknowledgments
Authors sincerely acknowledge Prof. B.N. Goswami, Director, IITM, Pune for his continuous support, encouragement and guidance to carry out this study. The assistance provided by Mr. Naveed Shaikh in the analysis of OC and EC is also acknowledged with thanks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, K., Panicker, A.S., Beig, G. et al. Carbonaceous aerosols over Pune and Hyderabad (India) and influence of meteorological factors. J Atmos Chem 73, 1–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-015-9314-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-015-9314-4