Abstract
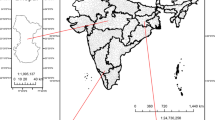
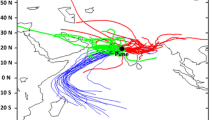
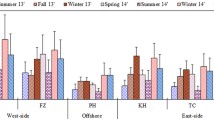
A study has been carried out on water soluble ions, trace elements, as well as PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 elemental and organic carbon samples collected daily from Central Taiwan over a one year period in 2005. A source apportionment study was performed, employing a Gaussian trajectory transfer coefficient model (GTx) to the results from 141 sets of PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 samples. Two different types of PM10 episodes, local pollution (LOP) and Asian dust storm (ADS) were observed in this study. The results revealed that relative high concentrations of secondary aerosols (NO −3 , SO 2−4 and NH +4 ) and the elements Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and As were observed in PM2.5 during LOP periods. However, sea salt species (Na+ and Cl−) and crustal elements (e.g., Al, Fe, Mg, K, Ca and Ti) of PM2.5–10 showed a sharp increase during ADS periods. Anthropogenic source metals, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and As, as well as coarse nitrate also increased with ADS episodes. Moreover, reconstruction of aerosol compositions revealed that soil of PM2.5–10 elevated approximately 12–14% in ADS periods than LOP and Clear periods. A significantly high ratio of non-sea salt sulfate to elemental carbon (NSS-SO 2−4 /EC) of PM2.5–10 during ADS periods was associated with higher concentrations of non-sea-salt sulfates from the industrial regions of China. Source apportionment analysis showed that 39% of PM10, 25% of PM2.5, 50% of PM2.5–10, 42% of sulfate and 30% of nitrate were attributable to the long range transport during ADS periods, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowen, H.J.M.: Environmental chemistry of the elements. Academic Press, London (1979)
Chang, S.C., Lee, C.T.: Assessment of PM10 enhancement by yellow sand on the air quality of Taipei, Taiwan in 2001. Environ. Monit. Assess. 132, 297–309 (2007)
Chen, Y.S., Sheen, P.C., Chen, E.R., Liu, Y.K., Wu, T.N., Yang, C.Y.: Effects of Asian dust storm events on daily mortality in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ. Res. 95, 151–155 (2004)
Cheng, M.T., Lin, Y.C., Chio, C.P., Wang, C.F., Kuo, C.Y.: Characteristics of aerosols collected in central Taiwan during an Asian dust event in spring 2005. Chemosphere 61, 1439–1450 (2005)
Cheng, M.T., Horng, C.L., Su, Y.R., Lin, L.K., Lin, Y.C., Chou, C.C.-K.: Particulate matter characteristics during agricultural waste burning in Taichung city, Taiwan. J. Hazard. Mater. 165, 187–192 (2009)
Chio, C.P., Cheng, M.T., Wang, C.F.: Source apportionment to PM10 in different air quality conditions for Taichung urban and coastal areas, Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 38, 6893–6905 (2004)
Chou, C.C.K., Lee, C.T., Chen, W.N., Chang, S.Y., Chen, T.K., Lin, C.Y., Chen, J.P.: Lidar observations of the diurnal variations in the depth of urban mixing layer: A case study on the air quality deterioration in Taipei, Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 374, 156–166 (2007)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Pritchett, L.C., Pierson, W.R., Frazier, C.A., Purcell, R.G.: The dri thermal optical reflectance carbon analysis system-description, evaluation and application in united-states air-quality studies. Atmos. Environ. 27, 1185–1201 (1993)
Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G., Crow, D., Lowenthal, D.H., Merrifield, T.: Comparison of improve and Niosh carbon measurements. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 34, 23–34 (2001)
CTCI Corporation: Carrying capacity management plan for air pollutants and estimation of emission inventory over Taiwan. Report, Environmental Protection Administration, Taiwan EPA-88-FA31-03-03-1059 (1999) (in Chinese)
CTCI Corporation: Update and management for air pollution emission inventory and estimation for air pollution degradation of GNP. Report, Environmental Protection Administration, Taiwan, EPA-92-FA11-03-D039, 2003. (in Chinese).
Councell, T.B., Duckenfield, K.U., Landa, E.R., Callender, E.: Tire-wear yarticles as a source of zinc to the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4206–4214 (2004)
Dockery, D.W., Pope, C.A., Xu, X., Spengler, J.D., Ware, J.H., Fay, M.E., Ferris, B.G., Speizeer, F.E.: An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 329, 1753–1759 (1993)
Draxler, R.R., Rolph, G.D.: HYSPLIT (Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model access via NOAA ARL READY Website (http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html). NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring, MD. (2003)
Fung, K., Chow, J.C., Watson, J.G.: Evaluation of OC/EC speciation by thermal manganese dioxide oxidation and the improve method. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 52, 1333–1341 (2002)
Hsu, S.C., Liu, S.C., Liu, C.Y., Jeng, W.L., Lin, F.J., Huang, Y.T., Lung, S.C.C., Liu, T.H., Tu, J.Y.: Variations of Cd/Pb and Zn/ Pb ratios in Taipei aerosols reflecting long-range transport or local pollution emissions. Sci. Total Envion. 347, 111–121 (2005)
Hsu, S.C., Liu, S.C., Jeng, W.L., Chou, C.C.K., Hsu, R.T., Huang, Y.T., Chen, Y.W.: Lead isotope ratios in ambient aerosols from Taipei, Taiwan: identifying long-range transport of airborne Pb from the Yangtze Delta. Atmos. Environ. 40, 5393–5404 (2006)
Hsu, S.C., Liu, S.C., Huang, Y.T., Lung, S.C.C., Tsai, F., Tu, J.Y., Kao, S.: A criterion for identifying Asian dust events based on Al concentration data collected from northern Taiwan between 2002 and early 2007. J. Geophys. Res. 113, D18306 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007JD009574
Hwang, J.S., Hu, T.H., Chan, C.C.: Air pollution mix and emergency room visits for respiratory and cardiac diseases in Taipei. J. Data Sci. 2, 311–327 (2004)
Ito, K., Christensen, W.F., Eatough, D.J., Henry, R.C., Kim, E., Laden, F., Lall, R., Larson, T.V., Neas, L., Hopke, P.K., Thurston, G.D.: PM source apportionment and health effects: 2. An investigation of intermethod variability in associations between source-apportioned fine particle mass and daily mortality in Washington, DC. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 16, 300–310 (2006)
Khoder, M.I.: Atmospheric conversion of sulfur dioxide to particulate sulfate and nitrogen dioxide to particulate nitrate and gaseous nitric acid in an urban area. Chemosphere 49, 675–684 (2002)
Kim, H.K., Kang, C.H., Ma, C.J., Lee, J.H., Choi, K.C., Youn, Y.H.: Airborne cadmium in spring season between Asian dust and non-Asian dust periods in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 42, 623–631 (2008)
Kukkonen, J., Härkönen, J., Walden, J., Karppinen, A., Lusa, K.: Evaluation of the CAR-FMI model against measurements near a major road. Atmos. Environ. 35, 949–960 (2001)
Kuo, C.Y., Lin, C.Y., Chiang, W.F., Ko, L.C., Wu, C.W., Shang, W.L.: Variations of chemical compositions in coarse aerosols and fine aerosols in two successive episodes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 25, 2059–2066 (2006)
Kuo, C.Y., Chen, P.T., Lin, Y.C., Lin, C.Y., Chen, H.H., Shih, J.F.: Factors affecting the concentrations of PM10 in central Taiwan. Chemosphere 70, 1273–1279 (2008)
Lee, Y.C., Hill, P.R.: Cool season pollution episodes in Hong Kong, 1996–2002. Atmos. Environ. 37, 2927–2939 (2003)
Lin, T.H.: Long-range transport of yellow sand to Taiwan in spring 2000: observed evidence and simulation. Atmos. Environ. 35, 5873–5882 (2001)
Lin, C.Y., Liu, S.C., Chou, C.C.K., Huang, S.J., Liu, C.M., Kuo, C.H., Young, C.Y.: Long-range transport of aerosols and their impact on the air quality of Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 39, 6066–6076 (2005)
Lin, C.Y., Wang, Z., Chen, W.N., Chang, S.Y., Chou, C.C.K., Sugimoto, N., Zhao, X.: Long-range transport of Asian dust and air pollutants to Taiwan: observed evidence and model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 7, 423–434 (2007)
Ma, C.J., Tohno, S., Kasahara, M., Kasahara, M.: A case study of the size-resolved and individual cloud droplets collected in western Japan during the Asian dust storm event. Atmos. Environ. 39, 739–747 (2005)
Mori, I., Nishikawa, M., Quan, H., Morita, M.: Estimation of the concentration and chemical composition of kosa aerosols at their origin. Atmos. Environ. 36, 4569–4575 (2002)
Mori, I., Nishikawa, M., Tanimura, T., Quan, H.: Change in size distribution and chemical composition of kosa (Asian dust) aerosol during long-range transport. Atmos. Environ. 37, 4253–4263 (2003)
Salvador, P., Artíňano, B., Querol, X., Altastuey, A.: A combined analysis of backward trajectories and aerosol chemistry to characterise long-range transport episodes of particulate matter: The Madrid air basin, a case study. Sci. Total Envion. 390, 495–506 (2008)
Tainio, M., Tuomisto, J.T., Hänninen, O., Aarnio, P., Koistinen, K.J., Jantunen, M.J., Pekkanen, J.: Health effects caused by primary fine particulate matter (PM2.5) emitted from buses in the Helsinki metropolitan area, Finland. Risk Anal. 25, 151–160 (2005)
Thorpe, A., Harrison, R.M.: Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: a review. Sci. Total. Environ. 400, 270–282 (2008)
Tsai, Y.I., Chen, C.L.: Characterization of Asian dust storm and non-Asian dust storm PM2.5 aerosol in southern Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 40, 4734–4750 (2006)
Tsuang, B.J.: A Gaussian plume trajectory model to quantify the source/receptor relationship of primary pollutants and secondary aerosols: Part I. Theory. Atmos. Environ. 37, 3981–3991 (2003)
Tsuang, B.J., Chen, C.L., Lin, C.H., Cheng, M.T., Tsai, Y.I., Chio, C.P., Pan, R.C., Kuo, P.H.: Quantification on the source/receptor relationship of primary pollutants and secondary aerosols by a Gaussian plume trajectory model: Part II. Case Study. Atmos. Environ. 37, 3993–4006 (2003a)
Tsuang, B.J., Lee, C.T., Cheng, M.T., Lin, N.H., Lin, Y.C., Chen, C.L., Peng, C.M., Kuo, P.H.: Quantification on the source/receptor relationship of primary pollutants and secondary aerosols by a Gaussian plume trajectory model: Part III. Asian dust strom periods. Atmos. Environ. 37, 4007–4017 (2003b)
U.S. EPA: Compilation of air pollutant emission factors, Fifth Edition, US Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA. (1995a)
U.S. EPA: Industrial Source Complex (ISC3) Dispersion models-user’s guide II. Description of model algorithms. EPA Publication No. EPA-454/B-95-003b. US Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA. (1995b)
Wang, C.C., Lee, C.T., Liu, S.C., Chen, J.P.: Aerosol characterization at Taiwan’s northern tip during Ace-Asia. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 15, 839–855 (2004)
Wu, P.C., Tsai, J.C., Li, F.C., Lung, S.C., Su, H.J.: Increased levels of ambient fungal spores in Taiwan are associated with dust events from China. Atmos. Environ. 38, 4879–4886 (2004)
Xiu, G., Zhang, D., Chen, J., Huang, X., Chen, Z., Guo, H., Pan, J.: Characterization of major water-soluble inorganic ions in size-fractionated particulate matters in Shanghai campus ambient air. Atmos. Environ. 38, 227–236 (2004)
Yang, C.Y., Chang, C.C., Chung, H.Y., Tsai, S.S., Wu, T.N., Ho, C.K.: Relationship between air pollution and daily mortality in subtropical city: Taipei, Taiwan. Environ. Int. 30, 519–523 (2004)
Yang, C.Y., Chen, Y.S., Chiu, H.F., Goggins, W.B.: Effects of Asian dust storm events on daily stroke admissions in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ. Res. 99, 79–84 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, MT., Chou, WC., Chio, CP. et al. Compositions and source apportionments of atmospheric aerosol during Asian dust storm and local pollution in central Taiwan. J Atmos Chem 61, 155–173 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-009-9131-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-009-9131-8