Abstract
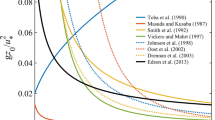
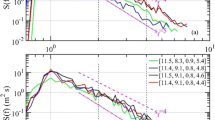
Surface waves are the roughness element of the ocean surface. The parameterization of the drag coefficient of the ocean surface is simplified by referencing to wind speed at an elevation proportional to the characteristic wavelength. The dynamic roughness is analytically related to the drag coefficient. Under the assumption of fetch limited wave growth condition, various empirical functions of the dynamic roughness can be converted to equivalent expressions for comparison. For datasets covering a wide range of the dimensionless frequency (inverse wave age), it is important to account for the variable rate of wave development at different wave ages. As a result, the dependence of the Charnock parameter on wave age is nonmonotonic. Finally, the analysis presented here suggests that the significant wave steepness is a sensitive property of the ocean surface and a single variable normalization of the dynamic roughness using a wavelength or wave height parameter actually produces more robust functions than bi-variable normalizations using wave height and wave slope.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anctil, F. and M. A. Donelan (1996): Air-water momentum flux observed over shoaling waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 26, 1344–1353.
Babanin, A. V. and Y. P. Soloviev (1998): Field investigation of transformation of the wind wave frequency spectrum with fetch and the stage of development. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 28, 563–576.
Banner, M. L. and W. K. Melville (1976): On the separation of air flow over water waves. J. Fluid Mech., 77, 825–842.
Burling, R. W. (1959): The spectrum of waves at short fetches. Dtsch. Hydrogr. Z., 12, 96–117.
Charnock, H. (1955): Wind stress on a water surface. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc., 81, 639.
Dobson, F., W. Perrie and B. Toulany (1989): On the deep-water fetch laws for wind-generated surface gravity waves. Atmos.-Ocean, 27, 210–236.
Donelan, M. A. (1979): On the fraction of wind momentum retained by waves. p. 141–159. In Marine Forecasting, ed. by J. C. J. Nihoul, Elsevier.
Donelan, M. A. (1990): Air-sea interaction. p. 239–292. In The Sea—Volume 9: Ocean Engineering Science, ed. by B. LeMehaute and D. M. Hanes, Wiley Interscience.
Donelan, M. A., J. Hamilton and W. H. Hui (1985): Directional spectra of wind-generated waves. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond., A315, 509–562.
Donelan, M. A., F. W. Dobson, S. D. Smith and R. J. Anderson (1993): On the dependence of sea surface roughness on wave development. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 23, 2143–2149.
Hasselmann, K. et al. (1973): Measurements of wind-wave growth and swell decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP). Dtsch. Hydrogr. Z., Suppl. A, 8, 12, 95 pp.
Hwang, P. A. (2004): Influence of wavelength on the parameterization of drag coefficient and surface roughness. J. Oceanogr., 60, 835–841.
Hwang, P. A. (2005): Comparison of the ocean surface wind stress computed with different parameterization functions of the drag coefficient. J. Oceanogr., 61, 91–107.
Hwang, P. A. and D. W. Wang (2004): Field measurements of duration limited growth of wind-generated ocean surface waves at young stage of development. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 34, 2316–2326. (Corrigendum, 35, 268–270, 2005.)
Janssen, J. A. M. (1997): Does wind stress depend on sea-state or not?—A statistical error analysis of HEXMAX data. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 83, 479–503.
Jones, I. S. F. and Y. Toba (eds.) (2001): Wind Stress over the Ocean. Cambridge Univ. Press, 307 pp.
Kahma, K. K. and C. J. Calkoen (1992): Reconciling discrepancies in the observed growth of wind-generated waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 22, 1389–1405.
Kawai, S. (1982): Structure of air flow separation over wind wave crests. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 23, 503–521.
Kawai, S., K. Okada and Y. Toba (1977): Support of the 3/2-power law and the guσ−4-spectral form for growing wind waves with field observation data. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan, 33, 137–150.
Keller, M. R., W. C. Keller and W. J. Plant (1992): A wave tank study of the dependence of X band cross sections on wind speed and water temperature. J. Geophys. Res., 97, 5771–5792.
Kitaigorodskii, S. A. (1973): The Physics of Air-Sea Interaction. Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem (English translation), 237 pp.
Kitaigorodskii, S. A. and Y. A. Volkov (1965): On the roughness parameter of the sea surface and the calculation of momentum flux in the near surface layer of the atmosphere. Izv., Atmos. Oceanic Phys., 1, 973–988.
Makin, V. K. (2003): A note on a parameterization of the sea drag. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 106, 593–600.
Makin, V. K. and V. N. Kudryavtsev (1999): Coupled sea surface-atmosphere model. 1. Wind over waves coupling. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 7613–7623.
Makin, V. K. and V. N. Kudryavtsev (2002): Impact of dominant waves on sea drag. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 103, 83–99.
Merzi, N. and W. H. Graf (1985): Evaluation of the drag coefficient considering the effects of mobility of the roughness elements. Ann. Geophys., 3, 473–478.
Miles, J. W. (1957): On the generation of surface waves by shear flow. J. Fluid Mech., 3, 185–204.
Oost, W. A., G. J. Komen, C. M. J. Jacobs and C. Van Oort (2002): New evidence for a relation between wind stress and wave age from measurements during ASGAMAGE. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 103, 409–438.
Phillips, O. M. (1977): The Dynamics of the Upper Ocean. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, U.K., 336 pp.
Schlichting, H. (1968): Boundary-Layer Theory, translated by J. Kestin. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 748 pp.
Smith, S. D., R. J. Anderson, W. A. Oost, C. Kraan, N. Maat, J. DeCosmo, K. B. Katsaros, K. L. Davidson, K. Bumke, L. Hasse and H. M. Chadwick (1992): Sea surface wind stress and drag coefficients: The HEXOS results. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 60, 109–142.
Stewart, R. W. (1974): The air-sea momentum exchange. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 6, 151–167.
Taylor, P. K. and M. J. Yelland (2001): The dependence of sea surface roughness on the height and steepness of the waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 31, 572–590.
Toba, Y., N. Iida, H. Kawamura, N. Ebuchi and I. S. F. Jones (1990): Wave dependence of sea-surface wind stress. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 20, 705–721.
Ueno, K. and M. Deushi (2003): A new empirical formula for the aerodynamic roughness of water surface waves. J. Oceanogr., 59, 819–831.
Volkov, Y. (2001): The dependence on wave age. p. 206–217. In Wind Stress over the Ocean, ed. by I. S. F. Jones and Y. Toba, Cambridge Univ. Press, New York.
Young, I. R. (1999): Wind Generated Ocean Waves. Elsevier, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 288 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, P.A. Drag Coefficient, Dynamic Roughness and Reference Wind Speed. J Oceanogr 61, 399–413 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-005-0050-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-005-0050-2