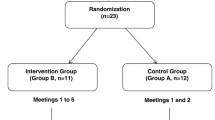
Although both diabetes and the efficacy of medical management are international issues, psycho-educational interventions might be culturally bound. Blood Glucose Awareness Training (BGAT) is a psycho-educational program for patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It is focused on improving recognition and management of extreme blood glucose levels, and is the best documented American psycho-educational program for this purpose. A randomized controlled clinical trial of BGAT's long-term benefits in a non-American setting has been lacking. One hundred and eleven adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus from Switzerland and Germany participated. After a 6 months baseline assessment, subjects were randomly assigned to receive either 2 months of BGAT (n = 56) or a physician-guided self-help control intervention (n = 55). BGAT improved recognition of low (p = 0.008), high (p = .03), and overall blood glucose (p = 0.001), and reduced frequency of severe hypoglycemia (p = 0.04), without compromising metabolic control. BGAT reduced both the external locus of control (p < 0.02) and fear of hypoglycemia (p < 0.02). BGAT was efficacious in reducing adverse clinical events and achieving clinically desirable goals in a European, as well as American setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BGAT:
-
Blood Glucose Awareness Training
- T0:
-
baseline
- T1:
-
1–6 months after intervention
- T2:
-
7–12 months after intervention
REFERENCES
Bradley, C. (1994). The well-being questionnaire. In Bradley, C. (Ed.), Handbook of Psychology and Diabetes: A Guide to Psychological Measurement in Diabetes Research and Practice, Harwood Academic Press, Chur, pp. 89–109.
Broers, S., le Cessie, S., van Vliet, K. P., Spinhoven, P., van der Ven, N. C., and Radder, J. K. (2002). Blood glucose awareness training in dutch type 1 diabetes patients. Short-term evaluation of individual and group training. Diabet. Med. 19(2): 157–161.
Clarke, W., Cox, D., Gonder-Frederick, L., Carter, W., and Pohl, S. (1987). Evaluating clinical accuracy of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care 10: 622–628.
Clarke, W. L., Cox, D. J., Gonder-Frederick, L. A., Julian, D., Schlundt, D., and Polonsky, W. (1995). Reduced awareness of hypoglycemia in adults with IDDM. A prospective study of hypoglycemic frequency and associated symptoms. Diabetes Care 18(4): 517–522.
Cox, D., Carter, W., Gonder-Frederick, L., Clarke, W., and Pohl, S. (1988). Blood glucose discrimination training in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. Biofeedback Self-Regul. 13: 201–217.
Cox, D., Gonder-Frederick, L., Julian, D., and Clarke, W. (1994a). Long-term follow-up evaluation of blood glucose awareness training. Diabetes Care 17: 1–5.
Cox, D., Gonder-Frederick, L., Julian, D., Cryer, P., Lee, J., Richards, F., and Clarke, W. (1991). Intensive vs. standard blood glucose awareness training (BGAT) with insulin dependent diabetes: Mechanisms and ancillary effects. Psychosom. Med. 53: 453–462.
Cox, D., Gonder-Frederick, L., Lee, J., Julian, D., Carter, W., and Clarke, W. (1989). Effects and correlates of blood glucose awareness training among patients with IDDM. Diabetes Care 12: 313–318.
Cox, D., Gonder-Frederick, L., Polonsky, W., Schlundt, D., Julian, D., and Clarke, W. (1995). A multi center evaluation of Blood Glucose Awareness Training-II. Diabetes Care 18: 523–528.
Cox, D., Gonder-Frederick, L., Polonsky, W., Schlundt, D., Julian, D., Kovatchev, B., and Clarke, W. (2001). Blood Glucose Awareness Training (BGAT-2): Long term benefits. Diabetes Care 24: 637–642.
Cox, D., Penberthy, J., Zrebiec, J., Weinger, K., Aikens, J., Stetson, B., DeGroot, M., Trief, P., Schaechinger, H., and Hermanns, H. (2003). Diabetes and driving: International survey of frequency and correlates. Diabetes Care 26: 2329–2334.
Cox, D. J., Kovatchev, B. P., Julian, D. M., Gonder-Frederick, L. A., Polonsky, W. H., Schlundt, D. G., and Clarke, W. L. (1994b). Frequency of severe hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus can be predicted from self-monitoring blood glucose data. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 79(6): 1659–1662.
Cryer, P. (1994). Banting lecture. Hypoglycemia: The limiting factor in the management of IDDM. Diabetes 43: 1378–1378.
Dahlbert, C. (1992). Subjective well being of young adults. Theoretical and empirical analyses of structure and stability. Zeitschrift für Differentielle und Diagnostische Psychologie 13: 207–220.
Gold, A. E., Frier, B. M., McLeod, K. M., and Deary, I. J. (1997). A structural equation model for predictors of severe hypoglycemia in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 14: 309–315.
Gonder-Frederick, L., Clarke, W., and Cox, D. (1997a). The emotional, social, and behavioral implications of insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Semin. Clin. Neuropsychiatry 2: 57–65.
Gonder-Frederick, L., Cox, D., Kovatchev, B., Julian, D., and Clarke, W. (1997b). The psychosocial impact of severe hypoglycemic episodes on spouses of patients with IDDM. Diabetes Care 20: 1543–1546.
Irvine, A., Cox, D., and Gonder-Frederick, L. (1994). The Fear of Hypoglycaemia Scale. In Bradley, C. (Ed.), Handbook of Psychology and Diabetes. Routledge, London, pp. 133–155.
Kinsley, B., Weinger, K., Bajaj, M., Levy, C., Quigley, M., Simonson, D., Cox, D., and Jacobson, A. (1999). Blood Glucose Awareness Training and epinephrine responses to hypoglycemia during intensive treatment in Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 22: 1022–1028.
Kohlmann, C., Petrak, F., Schuler, M., Krohne, H., Kuestner, E., and Beyer, J. (1995). Diabetes-specific control beliefs: Are changes dependent on critical life events? In Kohlmann, C. and Kulzer, B. (Eds.), Diabetes And Psychology. Diagnostic Approaches. Huber, Bern, pp. 111–118.
Kovatchev, B. P., Cox, D. J., Gonder-Frederick, L. A., Young-Hyman, D., Schlundt, D., and Clarke, W. (1998). Assessment of risk for severe hypoglycemia among adults with IDDM: validation of the low blood glucose index. Diabetes Care 21(11): 1870–1875.
Muhlhauser, I., Sawicki, P., Blank, M., Overmann, H., Richter, B., and Berger, M. (2002). Reliability of causes of death in persons with Type I diabetes. Diabetologia 45: 1490–1497.
Paschalides, C., Wearden, A. J., Dunkerley, R., Bundy, C., Davies, R., and Dickens, C. M. (2004). The associations of anxiety, depression and personal illness representations with glycaemic control and health-related quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Psychosom. Res. 57(6): 557–564.
Sovik, O., and Thordarson, H. (1999). Dead-in-bed syndrome in young diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 22(Suppl. 2): B40–B42.
Stahl, W., Berger, W., Schaechinger, H., and Cox, D. (1998). Spouse's worries concerning diabetic partner's possible hypoglycemia. Diabet. Med. 15: 619–620.
Tattersall, R. (1999). Frequency, causes, and treatment of hypoglycemia. In Frier, B., and Fisher, B. (Eds.), Hypoglycemia in Clinical Diabetes, Wiley, Chichester, UK, pp. 55–87.
ter Braak, E., Appelman, A., van de Laak, M., Stolk, R., van Haeften, T., and Erkelens, D. (2000). Related articles, links free full text clinical characteristics of type 1 diabetic patients with and without severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 23: 1467–1471.
The DCCT Research Group (1988). Reliability and validity of a diabetes quality-of-life measure for the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes Care 11: 725–732.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by the Swiss National Diabetes Foundation (SDG), Basel Diabetes Foundation (DGRBB), Walter-und Margarethe von Lichtenstein Foundation, Freie Akademische Gesellschaft Basel, Lilly Inc., Switzerland, and Astra-Fonds. We thank Prof. Dr. Wolf Langewitz and Dr. Brigitta Wössmer, who helped with clinical supervision and advice. We also thank the following diabetes nurses, who were actively engaged in motivating and referring patients: Cornelia Müller, Vreni Bättig, Regula Schinz, Marco Pavan (all Basel) and Bettina Blaser (Luzern).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The following centers participated in the study: Basel University Hospital (HS, KH, WB and UK), diabetes outpatient center practice, Olten (MS), diabetes clinic, Bad Mergentheim (NH), diabetes outpatient center practice, Solothurn (Ernst Iff), diabetes outpatient center practice, Aarau (Jürg Lareida), diabetes outpatient center practice, Winterthur (Elisabeth Nützi), diabetes outpatient center practice, Luzern (Frank Ackermann), and Kantonspital Luzern (Christoph Henzen).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schachinger, H., Hegar, K., Hermanns, N. et al. Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Blood Glucose Awareness Training (BGAT III) in Switzerland and Germany. J Behav Med 28, 587–594 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-005-9026-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-005-9026-3