Abstract
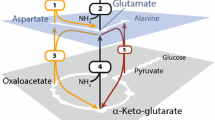
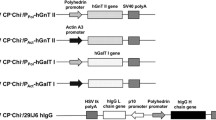
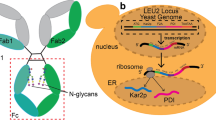
Silkworms serve as promising bioreactors for the production of recombinant proteins, including glycoproteins and membrane proteins, for structural and functional protein analyses. However, lack of methodology for stable isotope labeling has been a major deterrent to using this expression system for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structural biology. Here we developed a metabolic isotope labeling technique using commercially available silkworm larvae. The fifth instar larvae were infected with baculoviruses for co-expression of recombinant human immunoglobulin G (IgG) as a test molecule, with calnexin as a chaperone. They were subsequently reared on an artificial diet containing 15N-labeled yeast crude protein extract. We harvested 0.1 mg of IgG from larva with a 15N-enrichment ratio of approximately 80 %. This allowed us to compare NMR spectral data of the Fc fragment cleaved from the silkworm-produced IgG with those of an authentic Fc glycoprotein derived from mammalian cells. Therefore, we successfully demonstrated that our method enables production of isotopically labeled glycoproteins for NMR studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BmNPV:
-
Bombyx mori nuclleopolyhedrovirus
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- Fuc:
-
Fucose
- Gal:
-
Galactose
- GlcNAc:
-
N-Acetylglucosamine
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- HSQC:
-
Heteronuclear single-quantum coherence
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- LC/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography/mass spectroscopy
- Man:
-
Mannose
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- PTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
References
Aburatani T, Ueda H, Nagamune T (2002) Importance of a CDR H3 basal residue in V(H)/V(L) interaction of human antibodies. J Biochem 132:775–782
Ailor E et al (2000) N-glycan patterns of human transferrin produced in Trichoplusia ni insect cells: effects of mammalian galactosyltransferase. Glycobiology 10:837–847
Breitbach K, Jarvis DL (2001) Improved glycosylation of a foreign protein by Tn-5B1-4 cells engineered to express mammalian glycosyltransferases. Biotechnol Bioeng 74:230–239. doi:10.1002/bit.1112
Cohen SA, Michaud DP (1993) Synthesis of a fluorescent derivatizing reagent, 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate, and its application for the analysis of hydrolysate amino acids via high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 211:279–287. doi:10.1006/abio.1993.1270
de Marco A (2009) Strategies for successful recombinant expression of disulfide bond-dependent proteins in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 8:26. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-8-26
de Wildt RM, Mundy CR, Gorick BD, Tomlinson IM (2000) Antibody arrays for high-throughput screening of antibody–antigen interactions. Nat Biotechnol 18:989–994. doi:10.1038/79494
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
DeLano WL (2002) The PyMOL molecular graphics system DeLano scientific. San Carlos, CA, USA
Demain AL, Vaishnav P (2009) Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol Adv 27:297–306. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.01.008
Dojima T, Nishina T, Kato T, Uno T, Yagi H, Kato K, Park EY (2009) Comparison of the N-linked glycosylation of human beta1, 3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 expressed in insect cells and silkworm larvae. J Biotechnol 143:27–33. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.06.013
Dojima T et al (2010) Improved secretion of molecular chaperone-assisted human IgG in silkworm, and no alterations in their N-linked glycan structures. Biotechnol Prog 26:232–238
Dutta A, Saxena K, Schwalbe H, Klein-Seetharaman J (2012) Isotope labeling in mammalian cells. Methods Mol Biol 831:55–69. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-480-3_4
Goddard T, Kneller D (1993) SPARKY 3. University of California, San Francisco
Harrison RL, Jarvis DL (2006) Protein N-glycosylation in the baculovirus-insect cell expression system and engineering of insect cells to produce “mammalianized” recombinant glycoproteins. Adv Virus Res 68:159–191. doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(06)68005-6
Hirayama C, Konno K, Shinbo H (1996) Utilization of ammonia as a nitrogen source in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Insect Physiol 42:983–988
Hiyoshi M, Kageshima A, Kato T, Park EY (2007) Construction of a cysteine protease deficient Bombyx mori multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus bacmid and its application to improve expression of a fusion protein. J Virol Methods 144:91–97. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2007.04.005
Hollister JR, Jarvis DL (2001) Engineering lepidopteran insect cells for sialoglycoprotein production by genetic transformation with mammalian beta 1,4-galactosyltransferase and alpha 2,6-sialyltransferase genes. Glycobiology 11:1–9
Hollister J, Grabenhorst E, Nimtz M, Conradt H, Jarvis DL (2002) Engineering the protein N-glycosylation pathway in insect cells for production of biantennary, complex N-glycans. Biochemistry 41:15093–15104
Horie Y, Watanabe K, Ito T (1966) Nutrition of the silkworm, Bombyx mori XIV. Futher stuides on the requirements for B vitamins. Bull Seric Exp Sta 20:393–409
Jarvis DL (2009) Baculovirus-insect cell expression systems. Methods Enzymol 463:191–222. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(09)63014-7
Kamiya Y, Yanagi K, Kitajima T, Yamaguchi T, Chiba Y, Kato K (2013) Application of metabolic 13C labeling in conjunction with high-field nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for comparative conformational analysis of high mannose-type Oligosaccharides. Biomolecules 3:108–123. doi:10.3390/biom3010108
Kamiya Y, Satoh T, Kato K (2014) Recent advances in glycoprotein production for structural biology: toward tailored design of glycoforms. Curr Opin Struct Biol 26:44–53. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2014.03.008
Kato K, Yamaguchi Y (2011) Glycoproteins and antibodies: solution NMR studies. In: Encyclopedia of magnetic resonance, vol (in press). Wiley, Chichester. DOI:10.1002/9780470034590
Kato K, Yamaguchi Y, Arata Y (2010a) Stable-isotope-assisted NMR approaches to glycoproteins using immunoglobulin G as a model system. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 56:346–359
Kato T, Kajikawa M, Maenaka K, Park EY (2010b) Silkworm expression system as a platform technology in life science. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:459–470. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2267-2
Matsumiya S et al (2007) Structural comparison of fucosylated and nonfucosylated Fc fragments of human immunoglobulin G1. J Mol Biol 368:767–779. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.034
Motohashi T, Shimojima T, Fukagawa T, Maenaka K, Park EY (2005) Efficient large-scale protein production of larvae and pupae of silkworm by Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus bacmid system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326:564–569
Ohki S, Dohi K, Tamai A, Takeuchi M, Mori M (2008) Stable-isotope labeling using an inducible viral infection system in suspension-cultured plant cells. J Biomol NMR 42:271–277. doi:10.1007/s10858-008-9283-x
Palmberger D, Rendic D, Tauber P, Krammer F, Wilson IB, Grabherr R (2011) Insect cells for antibody production: evaluation of an efficient alternative. J Biotechnol 153:160–166. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.02.009
Park EY, Abe T, Kato T (2008) Improved expression of fusion protein using a cysteine- protease- and chitinase-deficient Bombyx mori (silkworm) multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus bacmid in silkworm larvae. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 49:135–140
Park EY, Ishikiriyama M, Nishina T, Kato T, Yagi H, Kato K, Ueda H (2009) Human IgG1 expression in silkworm larval hemolymph using BmNPV bacmids and its N-linked glycan structure. J Biotechnol 139:108–114. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.09.013
Sasaki K et al (2009) Silkworm expression and sugar profiling of human immune cell surface receptor, KIR2DL1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:575–580. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.065
Saxena K, Dutta A, Klein-Seetharaman J, Schwalbe H (2012) Isotope labeling in insect cells. Methods Mol Biol 831:37–54. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-480-3_3
Skrisovska L, Schubert M, Allain FH (2010) Recent advances in segmental isotope labeling of proteins: NMR applications to large proteins and glycoproteins. J Biomol NMR 46:51–65. doi:10.1007/s10858-009-9362-7
Takahashi N, Kato K (2003) GALAXY(glycoanalysis by the three axes of MS and chromatography):a web application that assists structural analyses of N-glycans. Trends Glycosci Glycotech 15:235–251
Takahashi H, Shimada I (2010) Production of isotopically labeled heterologous proteins in non-E. coli prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. J Biomol NMR 46:3–10. doi:10.1007/s10858-009-9377-0
Vranken WF et al (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59:687–696
Yagi H, Yamamoto M, Yu SY, Takahashi N, Khoo KH, Lee YC, Kato K (2010) N-Glycosylation profiling of turtle egg yolk: expression of galabiose structure. Carbohydr Res 345:442–448. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2009.12.002
Yagi H, Saito T, Yanagisawa M, Yu RK, Kato K (2012) Lewis X-carrying N-glycans regulate the proliferation of mouse embryonic neural stem cells via the Notch signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 287:24356–24364. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.365643
Yagi H, Zhang Y, Yagi-Utsumi M, Yamaguchi T, Iida S, Yamaguchi Y, Kato K (2014) Backbone 1H, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments of the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin G glycoprotein. Biomol NMR Assign. doi:10.1007/s12104-014-9586-7
Yagi H et al (2015) NMR-based structural validation of therapeutic antibody produced in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell Rep. doi:10.1007/s00299-015-1757-1
Yamaguchi Y, Kato K (2010) Dynamics and interactions of glycoconjugates probed by stable-isotope-assisted NMR spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol 478:305–322
Yamaguchi Y, Kim H, Kato K, Masuda K, Shimada I, Arata Y (1995) Proteolytic fragmentation with high specificity of mouse immunoglobulin G Mapping of proteolytic cleavage sites in the hinge region. J Immunol Methods 181:259–267
Yamaguchi Y et al (2006) Glycoform-dependent conformational alteration of the Fc region of human immunoglobulin G1 as revealed by NMR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:693–700. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.10.002
Zhu J (2012) Mammalian cell protein expression for biopharmaceutical production. Biotechnol Adv 30:1158–1170. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.08.022
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the Program for the Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (NIBIO) and by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (24249002, 25102008, and 25860053) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). This study was partly also supported by the Nanotechnology Platform Program (Molecule and Material Synthesis) of MEXT. We also thank Ms. Kiyomi Senda and Ms. Kumiko Hattori (Nagoya City University) for their help in purification of IgG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagi, H., Nakamura, M., Yokoyama, J. et al. Stable isotope labeling of glycoprotein expressed in silkworms using immunoglobulin G as a test molecule. J Biomol NMR 62, 157–167 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-015-9930-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-015-9930-y