Abstract
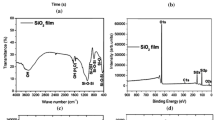
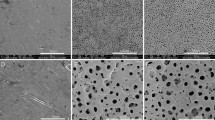
The amorphous phase/TiO2 nanocrystals (APTN) composited coatings were prepared on Ti implants for biomedical applications. The Ti implants without and with the APTN composited coatings both do not cause any adverse effects after implantation into the rabbit tibia. The osseointegration of Ti implants after covering the APTN coatings is improved pronouncedly, greatly increasing the interface bonding strength between the implants and newly formed bones. In addition, it is interesting that the newly formed bone tissues appear in the micro-pores of the APTN coatings, promoting the interface bonding between the implants and new bones by the mechanical interlock. Moreover, the Ti implant with the APTN coatings formed at higher applied voltage exhibit higher shear strength and displacement during the pushing out experiment probably due to its better osseointegration.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yerokhin AL, Nie X, Leyland A, Matthews A, Dowey SJ. Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering. Surf Coat Technol. 1999;122:73–93.
Wei DQ, Zhou Y, Jia DC, Wang YM. Characteristic and in vitro bioactivity of a microarc-oxidized TiO2-based coating after chemical treatment. Acta Biomater. 2007;3:817–27.
Wei DQ, Zhou Y, Jia DC, Wang YM. Effect of heat treatment on the structure and in vitro bioactivity of microarc-oxidized (MAO) titania coatings containing Ca and P ions. Surf Coat Technol. 2007;201:8723–9.
Wei DQ, Zhou Y, Jia DC, Wang YM. Effect of applied voltage on the structure of microarc oxidized TiO2-based bioceramic films. Mater Chem Phys. 2007;104:177–82.
Wei DQ, Zhou Y, Wang YM, Jia DC. Characteristic of microarc oxidized coatings on titanium alloy formed in electrolytes containing chelate complex and nano-HA. Appl Surf Sci. 2007;253:5045–50.
Wei DQ, Zhou Y, Jia DC, Wang YM. Biomimetic apatite deposited on microarc oxidized anatase-based ceramic coating. Ceram Int. 2008;34:1139–44.
Fini M, Cigad A, Rondelli G, Chies R, Giardino R, Giavaresi G, Aldini NN, Torricelli P, Vicentini B. In vitro and in vivo behaviour of Ca- and P-enriched anodized titanium. Biomaterials. 1999;20:1587–94.
Zhu XL, Kim KH, Jeong YS. Anodic oxide films containing Ca and P of titanium biomaterial. Biomaterials. 2001;22:2199–206.
Zhu XL, Ong JL, Kim SY, Kim KH. Surface characteristics and structure of anodic oxide films containing Ca and P on a titanium implant material. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;60:333–8.
Han Y, Hong SH, Xu KW. Structure and in vitro bioactivity of titania-based films by micro-arc oxidation. Surf Coat Technol. 2003;168:249–58.
Frauchiger VM, Schlottig F, Gasser B, Textor M. Anodic plasma-chemical treatment of CP titanium surfaces for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2004;25:593–606.
Li LH, Kong YM, Kim HW. Improved biological performance of Ti implants due to surface modification by micro-arc oxidation. Biomaterials. 2004;25:2867–75.
Song WH, Jun YK, Han Y, Hong SH. Biomimetic apatite coatings on micro-arc oxidized titania. Biomaterials. 2004;25:3341–9.
Cheng S, Wei DQ, Zhou Y. Structure of microarc oxidized coatings containing Si, Ca and Na on titanium and deposition of cefazolin sodium/chitosan composite film. Surf Coat Technol. 2011;205:3798–804.
Zhou R, Wei DQ, Cheng S, Feng W, Li BQ, Wang YM, Jia DC, Zhou Y. MC3T3-E1 cells response of amorphous phase/TiO2 nanocrystals composite coating prepared by microarc oxidation on titanium. Mater Sci Eng C. Revised.
Cheng S, Wei DQ, Zhou Y, Guo HF. Preparation, cell response and apatite-forming ability of microarc oxidized coatings containing Si, Ca and Na on titanium. Ceram Int. 2011;37:2505–12.
Liu XM, Wu SL, Yeung KWK, Chan YL, Hu T, Xu ZS, Liu XY, Chung JCY, Cheung KMC, Chu PK. Relationship between osseointegration and superelastic biomechanics in porous NiTi scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2011;32:330–8.
Schouten C, Meijer GJ, van den Beucken JJJP, Spauwen PHM, Jansen JA. The quantitative assessment of peri-implant bone responses using histomorphometry and micro-computed tomography. Biomaterials. 2009;30:4539–49.
Li Y, Lee IS, Cui FZ, Choi SH. The biocompatibility of nanostructured calcium phosphate coated on micro-arc oxidized titanium. Biomaterials. 2008;29:2025–32.
Jinno T, Kirk SK, Morita S, Goldberg VM. Effects of calcium ion implantation on osseointegration of surface-blasted titanium alloy femoral implants in a canine total hip arthroplasty model. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19:102–9.
Sul YT, Johansson CB, Röser K, Albrektsson T. Qualitative and quantitative observations of bone tissue reactions to anodised implants. Biomaterials. 2002;23:1809–17.
Sul YT, Johansson CB, Jeong Y, Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Resonance frequency- and removal torque analysis of implants with turned and anodized surface oxides. Clin Oral Impl Res. 2002;13:252–9.
Sul YT, Johansson CB, Kang YM, Jeon DG, Albrektsson T. Bone reactions to oxidized titanium implants with electrochemically anion S and P incorporation. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2002;4:478–87.
Ivanoff CJ, Widmark G, Johansson C, Wennerberg A. Histologic evaluation of bone response to oxidized and turned titanium micro-implants in human jawbone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implant. 2003;18:341–8.
Rocci A, Martignoni M, Burgos PM, Gottlow J, Sennerby L. Histology of retrieved immediately and early loaded oxidized implants: light microscopic observations after 5–9 months of loading in the posterior mandible. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5(1):88–98.
Son WW, Zhu X, Shin HI, Ong JL, Kim KH. In vivo histological response to anodized and anodized/hydrothermally treated titanium implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2003;66:520–5.
Li LH, Kong YM, Kim HW, Kim YW, Kim HE, Heo SJ, Koak JY. Improved biological performance of Ti implants due to surface modification by micro-arc oxidation. Biomaterials. 2004;25:2867–75.
Sul YT, Johansson CB, Petronis S, Krozer A, Jeong Y, Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Characteristics of the surface oxides on turned and electrochemically oxidized pure titanium implants up to dielectric breakdown: the oxide thickness, micropore configurations, surface roughness, crystal structure and chemical composition. Biomaterials. 2002;23:491–501.
Hayakawa S, Tsuru K, Ohtsuki C, Osaka A. Mechanism of apatite formation on a sodium silicate class in a simulated body fluid. J Am Ceram Soc. 1999;82:2155–60.
Sul YT, Johansson C, Byon E, Albrektsson T. The bone response of oxidized bioactive and non-bioactive titanium implants. Biomaterials. 2005;26:6720–30.
Svensson S, Suska F, Emanuelsson L, Palmquist A, Norlindh B, Trobos M, Bäckros H, Persson L, Rydja G, Ohrlander M, Lyvén B, Lausmaa J, Thomsen P. Osseointegration of titanium with an antimicrobial nanostructured noble metal coating. Nanomed-Nanotechnol. 2013;9:1048–56.
Rubshtein AP, Trakhtenberg ISh, Makarova EB, Triphonova EB, Bliznets DG, Yakovenkova LI, Vladimirov AB. Porous material based on spongy titanium granules: structure, mechanical properties, and osseointegration. Mater Sci Eng, C. 2014;35:363–9.
Elias CN, Meyers MA, Valiev RZ, Monteiro SN. Ultrafine grained titanium for biomedical applications: an overview of performance. J Mater Res Tech. 2013;2:340–50.
Bryington MS, Hayashi M, Kozai Y, Vandeweghe S, Andersson M, Wennerberg A, Jimbo R. The influence of nano hydroxyapatite coating on osseointegration after extended healing periods. Dent Mater. 2013;29:514–20.
Wang N, Li H, Lü W, Li J, Wang J, Zhang Z, Liu Y. Effects of TiO2 nanotubes with different diameters on gene expression and osseointegration of implants in minipigs. Biomaterials. 2011;32:6900–11.
Laiblin C, Jaeschke G. Clinical chemistry examinations of bone and muscle metabolism under stress in the Gottingen miniature pig-an experimental study. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1979;92:124–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Basic Science Research Program (2012CB933900), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51002039 and 51021002), Fund for the Doctoral Project to new teachers, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. HIT.NSRIF.2014002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, R., Wei, D., Yang, H. et al. Osseointegration of bioactive microarc oxidized amorphous phase/TiO2 nanocrystals composited coatings on titanium after implantation into rabbit tibia. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 1307–1318 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5154-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5154-z