Abstract
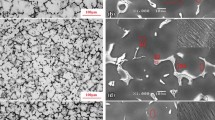
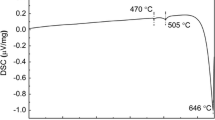
In this research, binary Mg–Zn (up to 3 wt% Zn) and ternary Mg–Zn–Gd (up to 3 wt% Gd, 3 wt% Zn) alloys were prepared by induction melting in an argon atmosphere. The structures of these alloys were characterized using light and scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrometry, X-ray diffraction and X-ray fluorescence. In addition, Brinell hardness measurements were taken to supplement these studies. Corrosion behavior was evaluated by immersion tests and potentiodynamic measurements in a physiological solution (9 g/l NaCl). Depending on the composition, structures of the as-cast alloys contained α-Mg dendrites, MgZn, Mg5Gd and Mg3Gd2Zn3 phases. Compared to pure Mg, zinc improved the corrosion resistance of binary Mg–Zn. Gadolinium also improved the corrosion resistance in the case of Mg–1Zn–3Gd alloy. The highest corrosion rate was observed for Mg–3Zn–3Gd alloy. Our results improve the understanding of the relationships between the structure and corrosion behavior of our studied alloy systems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song G. Control of biodegradation of biocompatable magnesium alloys. Corros Sci. 2007;49(4):1696–701.
Seal CK, Vince K, Hodgson MA. Biodegradable surgical implants based on magnesium alloys – a review of current research. IOP Conference Ser Mater Sci Eng. 2009;4(1):012011.
Davis JR. Handbook of materials for medical devices. Materials Park: ASM International; 2003.
Wang X, Lu HM, Li XL, Li L, Zhenh YF. Effect of cooling rate and composition on microstructures and properties of Zn–Mg alloys. Trans Nonferr Met Soc China. 2007;17:S122–5.
Jürgen V. Magnesium: nutrition and metabolism. Mol Aspects Med. 2003;24(1–3):27–37.
Staiger MP, Pietak AM, Huadmai J, Dias G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials. 2006;27(9):1728–34.
Zeng R, Dietzel W, Witte F, et al. Progress and challenge for magnesium alloys as biomaterials, vol. 8. Weinheim: Wiley; 2008.
Witte F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: a review. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1680–92.
Pereda MD, Alonso C, Burgos-Asperilla L, del Valle JA, Ruano OA, Perez P, et al. Corrosion inhibition of powder metallurgy Mg by fluoride treatments. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1772–82.
Gray-Munro JE, Seguin C, Strong M. Influence of surface modification on the in vitro corrosion rate of magnesium alloy AZ31. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;91A(1):221–30.
Hiromoto S, Shishido T, Yamamoto A, Maruyama N, Somekawa H, Mukai T. Precipitation control of calcium phosphate on pure magnesium by anodization. Corros Sci. 2008;50(10):2906–13.
Chun-Yan Z, Rong-Chang Z, Cheng-Long L, Jia-Cheng G. Comparison of calcium phosphate coatings on Mg–Al and Mg–Ca alloys and their corrosion behavior in Hank’s solution. Surf Coat Technol. 2010;204(21–22):3636–40.
Erbel R, Di Mario C, Bartunek J, Bonnier J, de Bruyne B, Eberli FR, et al. Temporary scaffolding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: a prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2007;369(9576):1869–75.
Di Mario C, Griffiths HUW, Goktekin O, Peeters N, Verbist JAN, Bosiers M, et al. Drug-eluting bioabsorbable magnesium stent. J Interv Cardiol. 2004;17(6):391–5.
Peeters P, Bosiers M, Verbist J, Deloose K, Heublein B. Preliminary results after application of absorbable metal stents in patients with critical limb ischemia. J Endovasc Ther. 2005;12(1):1–5.
Chang J, Guo X, He S, Fu P, Peng L, Ding W. Investigation of the corrosion for Mg–xGd–3Y–0.4Zr (x = 6,8,10,12 wt%) alloys in a peak-aged condition. Corros Sci. 2008;50(1):166–77.
Rokhlin LL, Nikitina NI. Recovery after ageing of Mg–Y and Mg–Gd alloys. J Alloy Comp. 1998;279(2):166–70.
Hänzi AC, Gerber I, Schinhammer M, Löffler JF, Uggowitzer PJ. On the in vitro and in vivo degradation performance and biological response of new biodegradable Mg–Y–Zn alloys. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1824–33.
Hort N, Huang Y, Fechner D, Stormer M, Blawert C, Witte F, et al. Magnesium alloys as implant materials-principles of property design for Mg–RE alloys. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1714–25.
Xin Y, Hu T, Chu PK. In vitro studies of biomedical magnesium alloys in a simulated physiological environment: a review. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(4):1452–9.
Zhang S, Zhang X, Zhao C, Li J, Song Y, Xie C, et al. Research on an Mg–Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(2):626–40.
Witte F, Hort N, Vogt C, Cohen S, Kainer KU, Willumeit R, et al. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2008;12(5–6):63–72.
http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/. Accessed 19 Dec 2012.
Li Z, Gu X, Lou S, Zheng Y. The development of binary Mg–Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone. Biomaterials. 2008;29(10):1329–44.
Zhang EL, Yang L, Xu JW, Chen HY. Microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion properties of Mg–Si(–Ca, Zn) alloy for biomedical application. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1756–62.
Zhang E, Yang L. Microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion properties of Mg–Zn–Mn–Ca alloy for biomedical application. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;497(1–2):111–8.
Gu XN, Zheng W, Cheng Y, Zheng YF. A study on alkaline heat treated Mg–Ca alloy for the control of the biocorrosion rate. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(7):2790–9.
Huan Z, Leeflang M, Zhou J, Fratila-Apachitei L, Duszczyk J. In vitro degradation behavior and cytocompatibility of Mg–Zn–Zr alloys. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(9):2623–35.
Gu X, Zheng Y, Zhong S, Xi T, Wang J, Wang W. Corrosion of, and cellular responses to Mg–Zn–Ca bulk metallic glasses. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6):1093–103.
Zberg B, Uggowitzer PJ, Loffler JF. MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants. Nat Mater. 2009;8(11):887–91.
Zhang E, He W, Du H, Yang K. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion properties of Mg–Zn–Y alloys with low Zn content. Mat Sci Eng A. 2008;488(1–2):102–11.
Nie JF, Gao X, Zhu SM. Enhanced age hardening response and creep resistance of Mg–Gd alloys containing Zn. Scripta Mater. 2005;53(9):1049–53.
Yuan G, Kato H, Amiya K, Inoue A. Excellent creep properties of Mg-Zn-Cu-Gd-based alloy strengthened by quasicrystals and Laves phases. J Mater Res. 2005;20(5):1278–86.
Liu Y, Yuan G, Ding W, Lu C. Deformation behavior of Mg–Zn–Gd-based alloys reinforced with quasicrystal and Laves phases at elevated temperatures. J Alloy Comp. 2007;427(1–2):160–5.
Massalski B, Okamoto H. Binary alloys phase diagrams. 2nd ed. Materials Park: ASM International; 1996.
Liu Y, Yuan GY, Lu C, Ding WJ. Progress in light metals, aerospace materials and superconductors. Mat Sci Forum. 2007;546–549:323–6.
Xu DK, Tang WN, Liu L, Xu YB, Han EH. Effect of Y concentration on the microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J Alloy Comp. 2007;432(1–2):129–34.
Liu K, Zhang J, Rokhlin LL, Elkin FM, Tang D, Meng J. Microstructures and mechanical properties of extruded Mg–8Gd–0.4Zr alloys containing Zn. Mater Sci Eng A. 2009;505(1–2):13–9.
Wu S, Gao JC, Qiao LY, Wang Y. Corrosion behavior of Mg and Mg–Zn alloys in simulated body fluid. Trans Nonferr Met Soc China. 2008;18(3):588–92.
Wu D, Chen RS, Han EH. Excellent room-temperature ductility and formability of rolled Mg–Gd–Zn alloy sheets. J Alloy Comp. 2011;509(6):2856–63.
Friedrich HE, Mordike BL. Magnesium technology. Berlin: Springer; 2006.
Yang J, Wang L, Wang L, Zhang H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of the Mg–4.5Zn–xGd (x = 0, 2, 3 and 5) alloys. J Alloy Comp. 2008;459(1-2):274–80.
Millazo G, Caroli S, Sharma VK. Tables of standart electrode potentials. Chichester: Wiley; 1978.
Qi HY, Huang GX, Bo H, Xu GL, Liu LB, Jin ZP. Experimental investigation and thermodynamic assessment of the Mg–Zn–Gd system focused on Mg-rich corner. J Mater Sci. 2011;47(3):1319–30.
Balasubramani N, Pillai UTS, Pai BC. Effect of Zn concentration on the microstructure and phase formation of Mg–5Gd alloy. J Alloy Comp. 2008;460(1–2):L6–10.
Chen R, Liang S, Wu D, Han E. Consideration of castability and formability for new magnesium alloys. Open J Met. 2012;2(1):8–17.
Liu Y, Yuan G, Lu C, Ding W. Stable icosahedral phase in Mg–Zn–Gd alloy. Scripta Mater. 2006;55(10):919–22.
Yong L, Guangyin Y, Song Z, Xinping Z, Chen L, Wenjiang D. Effects of Zn/Gd ratio and content of Zn, Gd on phase constitutions of Mg alloys. Mater Trans. 2008;49(5):941–4.
Li JH, Schumacher P. Solidification and age hardening behaviour of Mg–Zn–Gd Alloys. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. 2012;27(1):012021.
Song Y, Han E-H, Shan D, Yim CD, You BS. The effect of Zn concentration on the corrosion behavior of Mg–xZn alloys. Corros Sci. 2012;65:322–30.
Song Y, Han E-H, Shan D, Yim CD, You BS. The role of second phases in the corrosion behavior of Mg–5Zn alloy. Corros Sci. 2012;60:238–45.
Shi Z, Liu M, Atrens A. Measurement of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys using Tafel extrapolation. Corros Sci. 2010;52(2):579–88.
Atrens A, Liu M, Zainal Abidin NI. Corrosion mechanism applicable to biodegradable magnesium implants. Mater Sci Eng B. 2011;176(20):1609–36.
Zhao M-C, Schmutz P, Brunner S, Liu M, Song G-l, Atrens A. An exploratory study of the corrosion of Mg alloys during interrupted salt spray testing. Corros Sci. 2009;51(6):1277–92.
Gale WF, Totemeier TC. Smithells metals reference book. 8th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2004.
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank the Czech Science Foundation (Project no. P108/12/G043) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubásek, J., Vojtěch, D. Structural characteristics and corrosion behavior of biodegradable Mg–Zn, Mg–Zn–Gd alloys. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 24, 1615–1626 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4916-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4916-3