Abstract
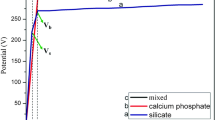
The release of titanium and calcium species to a simulated body fluid (SBF) at 37°C has been investigated for titanium treated by dc plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) in three different electrolytes, namely phosphate, silicate and calcium- and phosphorus-containing. The average rate of release of titanium over a 30 day period in immersion tests, determined by solution analysis, was in the range ~1.5–2.0 pg cm−2 s−1. Calcium was released at an average rate of ~11 pg cm−2 s−1. The passive current densities, determined from potentiodynamic polarization measurements, suggested titanium losses of a similar order to those determined from immersion tests. However, the possibility of film formation does not allow for discrimination between the metal releases due to electrochemical oxidation of titanium and chemical dissolution of the coating.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishra AK, Davidson JA, Poggie RA, Kovacs P, FitzGerald TJ. Mechanical and tribological properties and biocompatibility of diffusion hardened Ti–13Nb–13Zr—a new titanium alloy for surgical implants. ASTM Spec Tech Publication. 1996;1272:96–112.
Latour RA Jr. Future materials for foot surgery. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 1995;12:519–44.
Hübler R. Hardness and corrosion protection enhancement behaviour of surgical implant surfaces treated with ceramic thin films. Surf Coat Technol. 1999;116–119:1111–5.
Khan MA, Williams RL, Williams DF. Titanium alloys—corrosion and wear studies in-vitro. Trans Annual Meet Soc Biomater. 1996;2:480–5.
Gil FJ, Fernandez E, Manero JM, Planell JA, Sabria J, Cortada M, et al. A study of the abrasive resistance of metal alloys with applications in dental prosthetic fixators. Bio-med Mater Eng. 1995;5:161–7.
Yoshinari M, Oda Y, Kato T, Okuda K. Influence of surface modifications to titanium on antibacterial activity in vitro. Biomaterials. 2001;22:2043–8.
Heidenau F, Mittelmeier W, Detsch R, Haenle M, Stenzel F, Ziegler G, et al. A novel antibacterial titania coating: metal ion toxicity and in vitro surface colonization. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2005;16:883–8.
Petrini P, Arciola CR, Pezzali I, Bozzini S, Montanaro L, Tanzi MC, et al. Antibacterial activity of zinc modified titanium oxide surface. Int J Artif Organs. 2006;29:434–42.
Gopal J, Muraleedharan P, George P, Khatak HS. Investigation of the antibacterial properties of an anodised titanium alloy. Trends Biomater Artif Organs. 2003;17:13–8.
Giordano C, Visai L, Pedeferri MP, Chiesa R, Cigada A. Antibacterial treatments on titanium for implantology. In: Proceed Biomed Pharmacotherapy Int Congress, Pisa, October 10–13, vol. 60, 2006. p. 472–6.
Frauchiger VM, Schlottig F, Gasser B, Textor M. Anodic plasma-chemical treatment of CP titanium surfaces for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2004;25:593–606.
Wei D, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Jia D. Characteristic of microarc oxidized coatings on titanium alloy formed in electrolytes containing chelate complex and nano-HA. Appl Surf Sci. 2007;253:5045–50.
Wei D, Zhou Y, Jia D, Wang Y. Characteristic and in vitro bioactivity of a microarc-oxidized TiO2-based coating after chemical treatment. Acta Biomater. 2007;3:817–27.
Liu F, Wang F, Shimizu T, Igarashi K, Zhao L. Formation of hydroxyapatite on Ti–6Al–4V alloy by microarc oxidation and hydrothermal treatment. Surf Coat Technol. 2005;199:220–4.
Nie X, Leyland A, Matthews A. Deposition of layered bioceramic hydroxyapatite/TiO2 coatings on titanium alloys using a hybrid technique of micro-arc oxidation and electrophoresis. Surf Coat Technol. 2000;125:407–14.
Matykina E, Monfort F, Berkani A, Skeldon P, Thompson GE, Gough J. Characterization of spark-anodized titanium for biomedical applications. J Electrochem Soc. 2007;154:C279–85.
Matykina E, Montuori M, Gough J, Monfort F, Berkani A, Skeldon P, et al. Spark anodizing of titanium for biomedical applications. Trans Inst Met Finish. 2006;84:125–33.
Bianchi G, Malaguzzi S. Cathodic reduction of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide on titanium. In: Proceed 1st Int Congr Metallic Corr. 1961. p. 78–83.
Matykina E, Skeldon P, Thompson GE. Fundamental and practical evaluation of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings of titanium. Surf Eng. 2007;23:412–4
Shukla AK, Balasubramaniam R. Effect of surface treatment on electrochemical behavior of CP Ti, Ti–6Al–4V and Ti–13Nb–13Zr alloys in simulated human body fluid. Corros Sci. 2006;48:1696–720.
Ibris N, Mirza Rosca JC. EIS study of Ti and its alloys in biological media. J Electroanal Chem. 2002;526:53–62.
Reclaru L, Meyer J-M. Effects of fluorides on titanium and other dental alloys in dentistry. Biomaterials. 1998;19:85–92.
Solar RJ, Pollack SR, Korostoff E. In vitro corrosion testing of titanium surgical implant alloys: an approach to understanding titanium release from implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 1979;13:217–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Matykina, E., Skeldon, P. et al. Calcium and titanium release in simulated body fluid from plasma electrolytically oxidized titanium. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 21, 81–88 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3850-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3850-x