Abstract
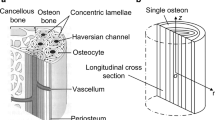
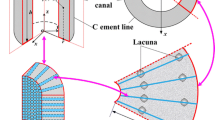
Cortical bone is a composite material consisting of a porous elastic solid and viscous fluid. It is well known that the intraosseous fluid circulates as a result of a bone fluid pressure gradient in the porous space of the cortical bone. When a time-dependent mechanical load is applied to the bone, intraosseous fluid flow occurs through the interconnected pore space in the bone. Bone fluid flow leads to a strain generated streaming potential (SGP). However, there is no experimental study on the relationship between the generation of intraosseous pressure and the SGP. The purpose of this study was to obtain the relationship between SGP and intraosseous pressure generations in cortical bone. In order to understand the issue, a drained, one-dimensional experimental setup for fluid-filled cortical bone samples with four different strain rates was used to simultaneously measure the intraosseous pressure and SGP. The results revealed a significant correlation (r = 0.98, p = 0.02) between the generation of the SGP and the intraosseous pressure, which indicates that an intraosseous pressure gradient produces a SGP in cortical bone.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. C. COWIN, J. Biomech. 32 (1999) 217
J. D. BRYANT, T. DAVID, P. H. GASKEIL, S. KING and G. LOND, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. [H]: J. Eng. Med. 203 (1989) 11
K. PIEKARSKI and M. MUNRO, Nature 269 (1977) 80
A. F. MAK, D. T. HUANG, J. D. ZHANG and P. TONG, J. Biomech. 30 (1997) 11
T. H. LIM and J. H. HONG, J. Musculoskeletal Res. 2 (1998) 167
J. L. NOWINSKI and F. C. DAVIS, Math. Biosci. 8 (1970) 397
J. L. NOWINSKI, Acta Mech. 13 (1972) 281
J. A. OCHOA, A. P. SANDERS, D. A. HECK and B. M. HILLBCRRY, J. Biomech. Eng. 113 (1991) 259
J. A. OCHOA and B. M. HILLBERRY, Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc. 17 (1992) 163
S. WEINBAUM, S. C. COWIN and Y. ZENG, in “Advances in Bioengineering”, edited by R. Vanderby Jr. (American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, 1991) p. 317
D. ZHANG and S. C. COWIN, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 42 (1994) 1575
S. HUGHES, R. DAVIES, R. KHAN and P. KELLY, Clinl. Orthop. Relat. Res. 134 (1978) 332
J. NAGATOMI, B. P. ARULANANDAM, D. W. METZGER, A. MEUNIER and R. BIZIOS, J. Biomech. Eng. 123 (2002) 308
T. M. L. KNOTHE and U. KNOTHE, J. Biomech. 33 (2000) 247
L. WANG, C. CIANI, S. B. DOTY and S. P. FRITTON, Bone 34 (2004) 499
S. WEINBAUM, S. C. COWIN and Y. ZENG, J. Biomech. 27 (1994) 339
R. M. DILLAMAN, R. D. ROER and D. M. GAY, J. Biomech. 24(S1) (1991) 163
S. C. COWIN, L. MOSS-SALENTIJN and M. L. MOSS, J. Biomech. Eng. 113 (1991) 191
J. A. SPADARO, in “Bone”, edited by B. K. Hall (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1993) p. 37
D. GROSS and W. S. WILLIAMS, J. Biomech. 15 (1982) 277
D. PIENKOWSKI and S. R. POLLACK, J. Orthop. Res. 1 (1983) 30
S. R. POLLACK, in “Bone Mechanics Handbook”, edited by S. C. Cowin (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2001) pp. 21–24
C. A. BASSETT and R. O. BECKER, Science 137 (1962) 1063
R. B. BORGENS, Science 225 (1984) 478
T. P. HARRIGAN and J. J. HAMILTON, J. Biomech. 26 (1993) 183
L. A. MACGINITIE, G. D. STANLEY, W. A. BIEBER and D. D. WU, J. Biomech. 30 (1997) 1133
B. R. BECK, Y-X. QIN, K. J. MCLEOD and M. W. OTTER, Calcif. Tissue Int. 71 (2002) 335
T. M. KEAVENY, X. E. GUO, E. F. WACHTEL, T. A. MCMAHON and W. C. HAYES, J. Biomech. 27 (1994) 1127
K. WATANABE, T. WATANABE, H. WATANABE, H. ANDO, T. ISHIKAWA and K. KOBAYASHI, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 52 (2005) 2100
J. H. HONG, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. [H]: J. Eng. Med. 218 (2004) 375
R. R. COOPER, J. W. MILGRAM and R. A. ROBINSON, J. Bone Joint Surg. 48A (1966) 1239
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the Special Research Center Support Program of Medical Devices and Supplies Development Grants (A020603) of Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J., Ko, S.O., Khang, G. et al. Intraosseous pressure and strain generated potential of cylindrical bone samples in the drained uniaxial condition for various loading rates. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 2589–2594 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3241-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-3241-0