Abstract
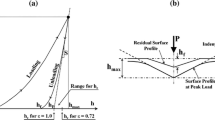
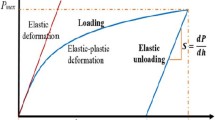
Microindentation is an investigational tool often used to determine hardness and other derived material properties of the material bone. This study explored the variation of microindentation hardness results with five independent variables. The variables were: applied mass, dwell time, drying time, time between indentation and measurement, and distance between the center of an indentation and the edge of other indentations and pores. These variables were selected because they represented a reasonable range of specimen investigational steps. We also investigated the cross sections of typical indentation residual impressions to determine the degree of material pile-up at the edges of the impressions. We found that microindentation hardness varied with applied mass and with distance between the indentation and neighboring indentations and pores but not with the other variables. Our recommended minimum applied mass is 0.10 kg versus a previously published value of 0.05 kg. We also found no discernable material pile-up at the residual impression edges, in contrast to reports of others.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. HUJA, T. KATONA and W. ROBERTS, in “Mechanical testing of bone and the bone-implant interface” (CRC Press, Boca Raton (FL), 2000) p. 247.
M. RAMRAKHIANI, D. PAL and T. MURTY, Acta Anat. 103 (1979) 358.
P. RICHES, N. EVERITT, A. HEGGIE and D. MCNALLY, J. Biomech. 30(10) (1997) 1059.
E. AMITAY-SADOVSKY and H. WAGNER, Poly. Commun. 39(11) (1998) 2387.
B. LAWN, A. EVANS and D. MARSHALL, J. Am. Ceram. Soci. 63(9–10) (1980) 574.
S. LUM and W. DUNCAN-HEWITT, Pharma. Res. 13(11) (1996) 1739.
D. MARSHALL, T. NOMA and A. EVANS, Commun. Am. Ceram. Soci. 65 (1982) 175.
J. CURREY and K. BREAR, J. Mat. Sci. Mat. Med. 1 (1990) 14.
N. MEREDITH, M. SHERRIF, D. SETCHELL and S. SWANSON, Arch. Oral. Bio. 40(6) (1996) 539.
H. XU, D. SMITH, S. JAHANMIR, E. ROMBERG, J. KELLY, V. THOMPSON and E. REKOW, J. Dent. Res. 77(3) (1998) 472.
S. COWIN, in “Bone Mechanics”. (CRC Press, 2001) p. 6–12–6–19.
G. VANDER VOORT and G. LUCAS, Advan. Mater. Pro. 154(3) (1998) 21.
R. AMPRINO, Acta Anat. 34 (1958) 161.
J. RHO and G. PHARR, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 10 (1999) 485.
A. RAPOFF, O. FONTANEL and S. VENKATARAMAN. Heterogeneous orthotropic elasticity about a nutrient foramen via microindentation. in 51st Bioengineering Division Conference of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers., Key Biscayne, FL 2003.
MITUTOYO, Instruction manual for micro hardness testing machine model: HM-112. Mitutoyo: Japan 1998.
L. RIESTER, T. BELL and A. FISCHER-CRIPPS, J. Mater. Res. 16(6) (2001) 1660.
MATWEB, The On-line Materials Information Source. Available from http://www.matweb.com Site last visited January 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, W.M., Rapoff, A.J. Microindentation in bone: Hardness variation with five independent variables. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 18, 591–597 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-2306-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-2306-4