Abstract
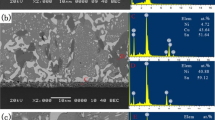
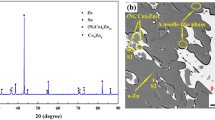
Phase separation mechanism and property changes in In–41Sn–9Zn solder was investigated with the current density of direct current 1.0 × 103 A/cm2. The results indicated that the phase separation was affected by the combination of electron wind force and back stress. The different degree of lattice distortion between different regions was one of the causes of the back stress. In the alloy, In-rich β phases and Sn-rich γ phases were segregated at the cathode side and anode side respectively, while Zn atoms didn’t migrate to the two poles significantly. Sn was the main diffusing atom \(\left( {\left| {{\text{Z}}_{\text{Sn}}^{*} } \right| > \,\left| {{\text{Z}}_{\text{In}}^{*} } \right|} \right)\) in the alloy, so the volume change rates at the anode side was about four times higher than that of the cathode side. After 72 h electromigration, the cathode–anode difference in micro-hardness, melting point, thermal enthalpy and melting interval was about 0.3 Mpa, 2 °C, 4.18 J/g, and 0.9 °C, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others

References
X.S. Liu, R.W. Davis, L.C. Hughes, M.H. Rasmussen, R. Bhat, C. Zah, J. Stradling, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 013104 (2006)
G. Yoo, J.-H. Park, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 65, 960 (2014)
C.-K. Hu, H.B. Huntington, Phys. Rev. B 26, 2782 (1982)
M.L. Huang, Z.J. Zhang, N. Zhao, F. Yang, J. Mater. Res. 30, 3316 (2015)
T.Y. Lee, K.N. Tu, S.M. Kuo, D.R. Frear, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 3189 (2001)
Y. Wang, J. Han, L.M. Ma, Y. Zuo, F. Guo, J. Electron. Mater. 45, 6095 (2016)
Y. Li, A.B.Y. Lim, K. Luo, Z. Chen, F.S. Wu, Y.C. Chan, J. Alloys Compd. 673, 372 (2016)
F.J. Wang, L.L. Zhou, Z.J. Zhang, J.H. Wang, X.J. Wang, M.F. Wu, J. Electron. Mater. 46, 6204 (2017)
J. Sun, G. Xu, F. Guo, Z. Xia, Y. Lei, Y. Shi, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 3544 (2011)
L.T. Chen, C.M. Chen, J. Mater. Res. 21, 962 (2006)
P.S. Ho, T. Kwok, Rep. Prog. Phys. 52, 301 (1989)
H.Y. Liu, Q.S. Zhu, Z.G. Wang, J.D. Guo, J.K. Shang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 211 (2012)
I. Ohnuma, Y. Cui, X.J. Liu, Y. Inohana, S. Ishihara, H. Ohtani, R. Kainuma, K. Ishida, J. Electron. Mater. 29, 1113 (2000)
K.N. Tu, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5451 (2003)
B. Sindam, K.C. James Raju, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 3997 (2015)
Y.F. Liu, X.L. Li, Y. Li, Z.K. Zhao, F.S. Bai, Appl. Phys. A 122, 174 (2016)
J.Z. Wang, D.X. Mao, L. Shi, W. Zhang, X.H. Zhang, J. Electron. Mater. 48, 817 (2018)
I.A. Blech, K.L. Tai, Appl. Phys. Lett. 30, 387 (1977)
I.A. Blech, C. Herring, Appl. Phys. Lett. 29, 131 (1976)
H.W. He, G.C. Xu, F. Guo, J. Mater. Sci. 45, 334 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (Grant Number E201447) and Science and technology research project of Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (Grant Number 11521047). The authors would like to thank Professor Chen and Professor Liu at the center for material analysis and testing, who provided the experimental help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Mao, D., Shi, L. et al. Phase separation mechanism and property changes in In–41Sn–9Zn under the current stressing. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 11676–11681 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01526-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01526-3