Abstract
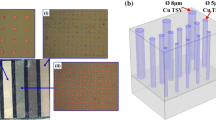
As through-silicon vias (TSVs) are key structural elements of 3D integration and packaging, creep deformation, which causes TSV-Cu protrusion, is critical for TSV reliability. Here, the effect of the diffusion creep behavior on the TSV-Cu protrusion morphology is analyzed using experiment and simulation. The protrusion morphology of TSV-Cu after annealing treatment is examined using a white light interferometer. The diffusion creep mechanism of TSV-Cu is determined by observation of the TSV-Cu microstructure using a scanning electron microscopy and a focused ion beams. The TSV-Cu grain size is measured using an electron backscatter diffraction system. The diffusion creep rate model of TSV-Cu is deduced based on the energy balance theory and is introduced into the finite element model to clarify the influence of diffusion creep on TSV-Cu protrusion. It is determined that the diffusion creep of TSV-Cu is mainly caused by grain boundary diffusion and grain boundary sliding. The diffusion creep strain rate is positively correlated with the ambient temperature and the external load but negatively correlated with the grain size. The amount of TSV-Cu protrusion increases with decreasing grain size. The simulation results show that the “donut”-shaped protrusion morphology is more likely to occur in TSV-Cu with smaller grain sizes near the sidewall region of the via.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.P. Dow et al., Highly selective Cu electrodeposition for filling through silicon holes. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 14, D63 (2011)
F. Che et al., Development of wafer-level warpage and stress modeling methodology and its application in process optimization for TSV wafers. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2, 944 (2012)
K.H. Lu et al., (2010), Thermal stress induced delamination of through silicon vias in 3-D interconnects, In: Proceedings of the electronic components and technology conference (ECTC), 2010, Las Vegas, pp 40
H.Y. Tsai et al., Thermal stress and failure location analysis for through silicon via in 3D integration. J. Mech. 32, 47 (2016)
H.H. Chang et al., The effect of mechanical stress on electromigration behavior. J. Mech. 31, 441 (2015)
S. Chen et al., Protrusion of electroplated copper filled in through silicon vias during annealing process. Microelectron. Reliab. 63, 183 (2016)
N. Ranganathan et al., A study of thermo-mechanical stress and its impact on through-silicon vias. J. Micromech. Microeng. 18, 075018 (2008)
C.C. Lee et al., Impact of high density TSVs on the assembly of 3D-ICs packaging. Microelectron. Eng. 107, 101 (2013)
S.P. Murarka, Multilevel interconnections for ULSI and GSI era. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 19, 87 (1997)
I. De Wolf et al., Cu pumping in TSVs: effect of pre-CMP thermal budget. Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 1856 (2011)
F.X. Che et al., Study on Cu protrusion of through-silicon via. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 3, 732 (2013)
A. Heryanto et al., Effect of copper TSV annealing on via protrusion for TSV wafer fabrication. J. Electron. Mater. 41, 1 (2012)
S.Y. Chang et al., Nanomechanical response and creep behavior of electroless deposited copper films under nanoindentation test. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 423, 52 (2006)
K. Zhang et al., The influence of time, temperature, and grain size on indentation creep in high-purity nanocrystalline and ultrafine grain copper. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 5197 (2004)
V. Srivastava et al., The effect of low stresses on creep and surface profiles of thin copper wires. Acta Mater. 51, 4611 (2003)
W. Wu et al., A study of creep behavior of TSV-Cu based on nanoindentaion creep test. J. Mech. 32, 717 (2016)
F.R.N. Nabarro (1947), Dislocations in a simple cubic lattice. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1947, 256
C. Herring, Diffusional viscosity of a polycrystalline solid. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 437 (1950)
R.L. Coble, A model for boundary diffusion controlled creep in polycrystalline materials. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1679 (1963)
D. Hull et al., The growth of grain-boundary voids under stress. Philos. Mag. 4, 673 (1959)
C. Okoro et al., Impact of the electrodeposition chemistry used for TSV filling on the microstructural and thermo-mechanical response of Cu. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 3868 (2011)
G.S. Was (1993), The role of grain boundary chemistry and structure in the environmentally-assisted intergranular cracking of nickel-base alloys, Technical Report
S. Onaka et al., Kinetics of diffusional creep discussed by energy dissipation and effect of grain-size distribution on the rate equations. Acta Mater. 49, 2161 (2001)
T. Mori et al., Steady-state creep of a composite analyzed by an energy balance method. Philos. Mag. Lett. 78, 331 (1998)
T. Mori et al., Overview no. 126 Stress relaxation by plastic flow, interfacial sliding and diffusion in an inclusion bearing material. Acta Mater. 45, 429 (1997)
R. Sandström et al., The role of creep in stress strain curves for copper. J. Nucl. Mater. 422, 51 (2012)
S. Onaka et al., Kinetics of stress relaxation caused by the combination of interfacial sliding and diffusion: two-dimensional analysis. Acta Mater. 46, 3821 (1998)
W. Wu et al., Experimental and numerical investigation of mechanical properties of electroplating copper filled in through silicon vias. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 6, 23 (2016)
S. Deser et al., Three-dimensional Einstein gravity: dynamics of flat space. Ann. Phys. 152, 220 (1984)
R.A. Carolan et al., Effect of grain boundary sliding on the creep micro-deformation of copper. Mater. Trans. JIM 32, 67 (1991)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) No. 11502006, Beijing Natural Science Foundation No. 2182011, National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) No. 11672009, and the Beijing Key Laboratory of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, T., Qin, F., Chen, S. et al. The effect of the diffusion creep behavior on the TSV-Cu protrusion morphology during annealing. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 16305–16316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9720-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9720-x