Abstract
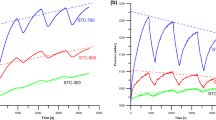
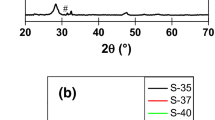
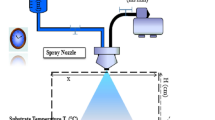
In the present experimentation, the photovoltaic properties of CuS incorporated SiO2 nanocomposites were investigated. The nanocomposite between CuS and SiO2 were prepared by solid state diffusion method. During the process of solid state diffusion, silicic acid was used as source of silicon. The prepared composites characterized by X-ray diffractions, scanning electron microscopy, ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometers, Raman spectroscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy and thermal analysis and photovoltaic measurements. IV characteristics of PV cell shows that performance of cell is sensitive to concentration of CuS in composite. The optimized power conversion efficiency was 1.11% found to be for 15 wt% CuS loaded SiO2 composite having fill factor 0.189 under the power incidence of 0.0104 W/m2.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Saga, Advances in crystalline silicon solar cell technology for industrial mass production. NPG Asia Mater. 2, 96–102 (2010)
H. Rao, W. Sun, S. Ye, W. Yan, Y. Li, H. Peng, Z. Liu, Z. Bian, C. Huang, Solution-processed CuS NPs as an inorganic hole-selective contact material for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 7800–7805 (2016)
M. Kim, A. Ochirbat, H.J. Lee, CuS/CdS quantum dot composite sensitizer and its applications to various TiO2 mesoporous film-based solar cell devices. Langmuir 31, 7609–7615 (2015)
X. Xu, J. Bullock, L.T. Schelhas, E.Z. Stutz, J.J. Fonseca, M. Hettick, V.L. Pool, K.F. Tai, M.F. Toney, X. Fang, A. Javey, L.H. Wong, J.W. Ager, Chemical bath deposition of p-type transparent, highly conducting (CuS)x:(ZnS)1–x nanocomposite thin films and fabrication of Si heterojunction solar cells. Nano Lett. 16, 1925–1932 (2016)
Y. Wu, C. Wadia, W. Ma, B. Sadtler, A.P. Alivisatos, Synthesis and photovoltaic application of copper(I) sulfide nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 8, 2551–2555 (2008)
L. Isac, I. Popovici, A. Enesca, A. Duta, Copper sulfide (CuxS) thin films as possible p-type absorbers in 3D solar cells. Energy Procedia 2, 71–78 (2010)
M. Sabet, M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, Facile one-step microwave to prepare CuInS2/CuS nanocomposite for solar cells. IET Micro Nano Lett. 6, 904–908 (2011)
F. Ghribi, A. Alyamani, Z. Ben Ayadi, K. Djessas, L.E.L. Mir, Study of CuS thin films for solar cell applications sputtered from nanoparticles synthesised by hydrothermal route. Energy Procedia 84, 197–203 (2015)
M.A. Sangamesha, K. Pushpalatha, G.L. Shekar, S. Shamsundar, Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline CuS thin films for dye-sensitized solar cells. ISRN Nanomater. 2013, 829430–829438 (2013)
K.R. Nemade, S.A. Waghuley, Highly responsive carbon dioxide sensing by graphene/Al2O3 quantum dots composites at low operable temperature. Indian J. Phys. 88, 577–583 (2014)
K.R. Nemade, S.A. Waghuley, Band gap engineering of CuS nanoparticles for artificial photosynthesis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 39, 781–785 (2015)
K.R. Nemade, R.V. Barde, S.A. Waghuley, Photocatalytic study of alumina–zirconia ceramic nanocomposite synthesized by spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 41, 4836–4840 (2015)
S. Ou, Q. Xie, D. Ma, J. Liang, X. Hu, W. Yu, Y. Qian, A precursor decomposition route to polycrystalline CuS nanorods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 94, 460–466 (2005)
J. Serrano, A. Cantarero, M. Cardona, N. Garro, R. Lauck, R.E. Tallman, T.M. Ritter, B.A. Weinstein, Raman scattering in β-Zn. Phys. Rev. B 69, 014301–014307 (2004)
S.Y. Wang, W. Wang, Z.-H. Lu, Asynchronous-pulse ultrasonic spray pyrolysis deposition of CuS (x = 1, 2) thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B103, 184–188 (2003)
A. Milekhin, L. Sveshnikova, T. Duda, N. Surovtsev, S. Adichtchev, L. Ding, D.R.T. Zahn, Vibrational spectra of quantum dots formed by Langmuir–Blodgett technique, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 28, C5E22–C5E26 (2010)
M. Nafees, M. Ikram, S. Alia, Thermal behavior and decomposition of copper sulfide nanomaterial synthesized by aqueous sol method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 10, 635–641 (2015)
T. Salmi, M. Bouzguenda, A. Gastli, A. Masmoudi, MATLAB/simulink based modelling of solar photovoltaic cell. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2, 213–218 (2012)
M. Seifi, A. Soh, N. Izzrib. A. Wahab, M.K.B. Hassan, A comparative study of PV models in Matlab/Simulink. Int. J. Electr. Robot. Electron. Commun. Eng. 7, 97–102 (2013)
G.L. Kabongo, P.S. Mbule, G.H. Mhlongo, B.M. Mothudi, K.T. Hillie, M.S. Dhlamini, Photoluminescence quenching and enhanced optical conductivity of P3HT-derived Ho3+-doped ZnO nanostructures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 418–426 (2016)
I. Mora-Sero, S. Gimenez, T. Moehl, F. Fabregat-Santiago, T. Lana-Villareal, R. Gomez, J. Bisquert, Factors determining the photovoltaic performance of a CdSe quantum dot sensitized solar cell: the role of the linker molecule and of the counter electrode. Nanotechnology 19, 424007–442014 (2008)
Acknowledgements
Authors are very much thankful to the Head, Department of Physics, Sant Gadge Baba Amravati University, Amravati, India, for providing necessary facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kute, A.M., Waghuley, S.A. Photovoltaic properties of nanostructured copper sulfide incorporated silicon rich composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 16199–16206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9709-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9709-5