Abstract
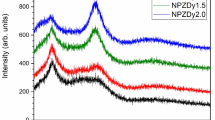
The Eu3+ co-doped Y2O3: Dy3+ phosphors were synthesized by solid-state reaction method, also known as a ceramic route. The properties of synthesized phosphors were studied with the help of PXRD, SEM, EDX, FTIR, Photoluminescence (PL) spectra, CIE coordinates and Thermoluminescent (TL) spectra. The PL spectra exhibit emissions at 486, 588, 596, 610, 681 and 693 nm due to the energy transfer between dopant ions. The blue emission is dominated due to dysprosium ions. The TL spectra were recorded for synthesized phosphors irradiated by UV and γ radiation. For UV irradiated phosphors, TL glow peaks were obtained at 455, 490 and 549 K whereas for γ irradiated phosphors TL glow peaks were obtained at 470 and 650 K. Using deconvoluted TL curves, kinetic parameters were computed by peak shape method. Second order kinetics were obtained with activation energy values varying from 7.553 × 10− 1 to 11.10 × 10− 1 eV for UV irradiated phosphors and 11.152 × 10− 1 to 15.252 × 10− 1 eV for γ irradiated phosphors.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhao, D. Wang, D. Meng, Synthesis and VUV photoluminescence of Y2O3:Eu3+ by doping different Ions”. Optik-Int. J. Light Electron Optics. 156, 8–12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.10.140
H. Eilers, Effect of particle/grainsizeon theoptical properties of Y2O3: Er,Yb., J. Alloys Compd. 474(1–2), 569–572 (2009)
S.H. Shin, J.H. Kang, D.Y. Jeon, S.H. Choi, S.H. Lee, Y.C. You, D.S. Zang, Cathodo-luminescence change of Y2O3: Eu phosphors by incorporation of Zn ions. Solid State Commun. 135, 30–33 (2005)
S. Liu, J. Zhang, Z. Wang, Z. Shi, Y. Zhou, X. Ren, Q. Yan, Refinement and homogenization of M7C3 carbide in hypereutectic Fe-Cr-C coating by Y2O3 and TiC. Mater. Charact. 132, 41–45, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60469-5
S. Wanchang, Z. Pei, L.I. Pan, S.H.E. Xiaolin, Z.H.A.O. Kun, Phase evolution, microstructure and properties of Y2O3-doped TiCN-based cermets. J. Rare Eearth 33(8), 867 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60498-1
T. lgarashi, M. Ihara, M. Kusunoki, M. Ohno, Relationship between optical properties and crystallinity of nanometer Y2O3: Eu phosphor. J I. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1549 (2000)
K. Gupta, R.M. Kadam, N.S. Dhoble, S.P. Lochab, S.J. Dhoble, A comparative comparative investigation of Ce3+–/Dy3+– and Eu2+– doped LiAlO2 phosphors for high dose radiation dosimetry: explanation of defect recombination mechanism using PL,TL and EPR study. J. Lumin. 188, 81–95 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.03.046
W.T. Carnall, P.R. Fields, K. Rajnak, Electronic energy levels in the trivalent lanthanide Aquo ions. I. Pr3+, Nd3+, Pm3+, Sm3+, Dy3+, Ho3+, Er3+, and Tm3+. J. Chem. Phys. 49, 4424–4442 (1968)
Q. Liu, Y. Liu, Z. Yang, Y. Han, X. Li, G. Fu, Multi wavelength excited white-emitting phosphor Dy3+ activated Ba3Bi(PO4)3. J. Alloys Compd. 515, 16–19 (2012)
S. Dutta, S. Som, S.K. Sharma, Luminescence and photometric characterization of K+ compensated CaMoO4:Dy3+ nanophosphors. Dalton Trans. 42, 54 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt50780g
Z. Ming, L.I. Xin-hai, H. Qi-yang, W. Zhi-xing, G.Hua-jun. Preparation methods of novel structural Y2O3:Eu3+. Rare Metal Mate. Eng. 37(1), 2065–2068 (2008)
S. Jayasudha, K. Madhukumar, C.M.K. Nair, G. Rashmi, S. Nair.Rajesh, T.S. Elias, TL dosimetric characterization of gamma irradiated SrSO4:Eu phosphors. J. Lumin. 183, 259–265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.11.044
S. Ghorbania, M.R. Loghman-Estarkib, R. Shoja Razavib, A. Alhaji, A new method for the fabrication of MgO- Y2O3 composite nanopowder at low temperature based on bioorganic material. Ceram. Int. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.025
Y. Li, Y.M. Zhang, G.Y. Hong, Y Yu. Upconversion luminescence of Y2O3: Er3+, Yb3+ nanoparticles prepared by a homogeneous precipita- tion method. J. Rare Earths 26, 450 (2008)
S. Katyayan, S. Agrawal, Investigation of spectral properties of Eu3+ and Tb3+ doped strontium zirconium trioxide orthorhombic perovskite for optical and sensing applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 18442–18454 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7791-8
J.A. Capobianco, F. Vetrone, T. D’Alesio, G. Tessari, A. Speghini, M. Bettinelli, Optical spectroscopy of nanocrystalline cubic Y2O3: Er3+ obtained by combustion. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2, 3203–3207 (2000)
S. Som, M. Chowdhury, S.K. Sharma, Band gap and trapping parameters of color tunable Yb3+ /Er3+ codoped Y2O3 upconversion phosphor synthesized by combustion route. J Mater Sci. 49, 858–867 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7769-8
S. Som, P. Mitra, V. Kumar, V. Kumar, J.J. Terblans, H.C. Swart, S.K. Sharma, The energy transfer phenomena and colour tunability in Y2O3S: Eu3+/Dy3+ micro-fibers for white emission in solid state lighting applications. Dalton Trans. 43(26), 9860–9871 (2014)
P.A. Raymundo-Pereira, D.A. Ceccato, A.G.B. Junior, M.F.S. Teixeira, S.A.M. Lima, A.M. Pires, Study on the structural and electrocatalytic properties of Ba2+-and Eu3+-doped silica xerogels as sensory platforms. RSC Adv. 6, 104529–104536 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA22508J
C. Zhong, H. Ji, R. Li, J. Wang, Z. Li, X. Sun, Facile preparation and fluorescence enhancement of yolk-like Ag@Y2O3:Yb3+,Tm3+ hollow structured composite. RSC Adv. Compos. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra45464a.
F. Yang, L. Qiao, H. Ren, F. Yan, Z. Xie, “Synthesis and luminescence properties of color-tunable Dy3+/Eu3+: CeAlON phosphors. Ceram. Int. 43(11), 8406–8410 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.03.187
Y. Liu, G. Liu, X. Dong, J. Wang, W. Yu, Tunable photoluminescence and magnetic properties of Dy3+ and Eu3+ doped GdVO4 multifunctional phosphors. Phys. Chem.Chem. Phys. 17, 2663 (2015)
Y. Zhu, G. Zheng, Z. Dai, L. Zhang, J. Mu, Core–shell structure and luminescence of SrMoO4:Eu3+(10%) phosphors. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 1361–1371 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2016.04.018
Y.N. Zhu, G.H. Zheng, X. Xin, R. Zhuang, L.Y. Zhang, Strong luminescence enhancement of Li doped Y2O3:5%Eu3 + phosphors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 1485–1488 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5685-9
V.M. Lojpur, M.D. PSAhrenkiel, Dramićanin, Color-tunableup-conversion emission inY2O3: Yb3+,Er3+nanoparticlesprepared by polymer complex solutionmethod. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 131 (2013)
S. Katyayan, S. Agrawal, Dynamics of concentration quenching in Eu3+ and Tb3+ doped calcium dioxide-oxo-zirconium perovskite. J Mater Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8156-z
L.Y. Zhang, W.W. Fu, G.H. Zheng, Z.X. Dai, Y.N. Zhu, J.J. Mu, Morphology and luminescent properties of SrMoO4:Eu3+, Dy3+. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 5164–5174 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4409-5
L. Tingqiao, L.H.R. Hussin, Z. Ibrahim, K. Deraman, H.O. Lintang, Effects of Eu3+ and Dy3+ doping or co-doping on optical and structural properties of BaB2Si2O8 phosphor for white LED applications. J. Rare Earths 34(1), 21 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60573-1
L. Yongqiang, Z. Lingyun, D. Zhenxiang, Z. Ganhong, Z. Yanan, M. Yongqing, Effect of li content, deposition time and solution concentration on morphology and photoluminescence properties of Y 2 O 3: 5%Eu 3+, x %Li+ thin film. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 46, 1524–1529 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(17)30158-3
T.S. Atabaev, Y.H. Hwang, H.K. Kim, Color-tunable properties of Eu3+ and Dy3+-codoped Y2O3 phosphor particles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7(1), 556 (2012)
D.L. Dexter, A theory of sensitized luminescence in solids. J. Chem. Phys. 21, 836–850 (1953)
V.R. Bandi, B.K. Grandhe, H.J. Woo, K.W. Jang, D.S. Shin, S.S. Yi, J.H. Jeong, Luminescence and energy transfer of Eu3+ or/and Dy3+ co-doped inSr3AlO4F phosphors with NUV excitation for WLEDs. J. Alloy. Compd. 538, 85–90 (2012)
V. Dubey, J. Kaur, S. Agrawal, N.S. Suryanarayana, K.V.R. Murthy, Effect of Eu3+ concentration on photoluminescence and thermoluminescence behavior of YBO3: Eu3+ phosphor. Superlattices Microstruct. 67, 156–171 (2014)
C.S. McCamy, Correlated color temperature as an explicit function of chromaticity coordinates. Color Res. Appl. 17, 142e4 (1992)
R. Chen, S.W.S. McKeever, Theory of Thermoluminescence and Related Phenomena. (World Scientific, Singapore, 1997)
D.V. MChandrasekhar, N. Sunitha, H. Dhananjaya, S.C. Nagabhushana, B.M. Sharma, C. Nagabhushana, Shivakumara, R.P.S. Chakradhar, Thermoluminescence response in gamma and UV irradiated Dy2O3 nanophosphor. J. Lumin. 132(7), 1798–1806 (2012)
S. Som, M. Chowdhury, S.K. Sharma, Kinetic parameters of g-irradiated Y2O3 phosphors: effect of doping/codoping and heating rate. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 110, 51–58 (2015)
N.J. Shivaramu, K.R. Nagabhushana, B.N. Lakshminarasappa, F. Singh, Synthesis characterization and luminescence studies of gamma irradiated nanocrystalline yttrium oxide. Spectrochimica Acta A 154, 220–231 (2016)
D Afouxenidi, G.S. Polymeris, N.C. Tsirliganis, G. Kitis, Computerised curve deconvolution of TL/OSL curves using a popular spreadsheet program. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncr315
M. Chowdhury, S.K. Sharma, S.P. Lochab, Thermoluminescence glow curve analysis of g-irradiated Eu3+ doped SnO2 composites. Ceram. Int. 42, 5472–5478 (2016)
J. Botterman, J.J. Joos, P.F. Smet, Trapping and detrapping inSrAl2O4:Eu,Dy persistent phosphors: influence of excitation wavelength and temperature. Phys. Rev. B 90, 085147 (2014)
D. Hagemann, S. Lovy, S. Yoon, N. Pokrant, B. Gartmann, J. Walfort, Bierwagen, Wavelength dependent loading of traps in the persistent phosphor SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+. J. Lumin. 170, 299–304 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2015.10.035
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, T., Agrawal, S. Luminescent properties of Eu3+ co-doped Y2O3: Dy3+ phosphors synthesized via ceramic route. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 7832–7841 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8782-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8782-0