Abstract
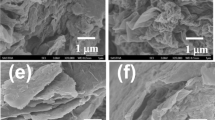
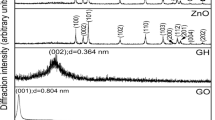
The quality of chemically synthesized few-layered graphene, which is known as reduced graphene oxide (RGO) depends on the oxidation of graphite, effective exfoliation of graphite oxide and complete reduction of graphene oxide. Herein, we report the preparation of nitrogen doped RGO by a modified Hummer’s method using potassium manganate along with potassium permanganate to achieve improved oxidation of graphite and a small amount of bovine serum albumin as a dispersant to avoid restacking of graphene sheets. Besides reducing the agglomeration of graphene layers, bovine serum albumin also serves as a nitrogen dopant. The quality of as-prepared nitrogen doped RGO is examined by morphological and structural studies. While microscopic studies confirm the formation of thin, well dispersed RGO sheets, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies confirm the doping of nitrogen in RGO. A specific surface area of 286 m2 g−1 is obtained for nitrogen doped RGO, which is mainly contributed by the basal planes and ordered mesoporosity of RGO. The capacitance properties of as-prepared nitrogen doped RGO without any conductive additive are evaluated by cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge–discharge cycling. A specific capacitance of 142 F g−1 obtained at a current density 1 A g−1 is almost twice the specific capacitance obtained for commercial graphene platelet aggregates (75 F g−1). The rate performance of as-prepared nitrogen doped RGO is comparable to that of commercial graphene platelet aggregates. It is also found that nitrogen doped RGO electrode can be charged and discharged for at least 2000 cycles without fade in the capacitance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Kim, K.B. Kim, S.M. Park, K.C. Roh, Sci. Rep. 6, 21182 (2016)
J.L. Xia, L.J.H. Chen, N.T. Tao, Nat. Nanotechnol. 4, 505 (2009)
S. Han, D. Wu, S. Li, F. Zhang, X. Feng, Adv. Mater. 26, 849 (2014)
Y. Zhu, S. Murali, M.D. Stoller, K.J. Ganesh, W. Cai, P.J. Ferreira, A. Pirkie, R.M. Wallace, K.A. Cychosz, M. Thommes, D. Su, E.A. Stach, R.S. Ruoff, Science 332, 1537 (2011)
Y. Huang, J. Liang, Y. Chen, Small 8, 1805 (2012)
C. Lee, X.D. Wei, J.W. Kysar, J. Hone, Science 321, 385 (2008)
P. Yu, S.E. Lowe, G.P. Simon, Y.L. Zhong, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 20, 329 (2015)
Y. Wu, B. Wang, Y. Ma, Y. Huang, N. Li, F. Zhang, Y. Chen, Nano Res. 3, 661 (2010)
K.S. Novoselov, V.I. Falko, L. Colombo, P.R. Gellert, M.G. Schwab, K.A. Kim, Nature 490, 192 (2012)
K.S. Kim, Y. Zhao, H. Jang, S.Y. Lee, J.M. Kim, K.S. Kim, J.H. Ahn, P. Kim, J.Y. Choi, B.H. Hong, Nature 457, 706 (2009)
B.C. Brodie, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 149, 249 (1859)
W. Hummers, R. Offeman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339 (1958)
M. Naoki, K. Takuya, N. Yuta, Sci. Rep. 6, 21715 (2016)
J.H. Shin, K.K. Kim, A. Benayad, S.M. Yoon, H.K. Park, I.S. Jung, M.H. Jin, H.K. Jeong, J.M. Kim, J.Y. Choi, Y.H. Lee, Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1987 (2009)
J. Zhang, H. Yang, G. Shen, P. Cheng, J. Zhang, S. Guo, Chem. Commun. 46, 1112 (2010)
J. Zhao, S. Pei, W. Ren, L. Gao, H.M. Cheng, ACS Nano 4, 5245 (2010)
Q. He, S. Wu, S. Gao, X. Cao, Z. Yin, H. Li, P. Chen, H. Zhang, ACS Nano 5, 5038 (2011)
S. Ahadian, M. Estili, V.J. Surya, J.R. Azcon, X. Liang, H. Shiku, M. Ramalingam, T. Matsue, Y. Sakka, H. Bae, K. Nakajima, Y. Kawazoe, Nanoscale 7, 6436 (2015)
C.H. Wen, C. Indranil, D.G. Goodwin, H.W. Matthew, D.F. Howard, B. Dermont, R.G. Zepp, Environ. Sci. Technol. 6, 3435 (2015)
Y. Wang, D.C. Alsmeyer, R.L. McCreery, Chem. Mater. 2, 557 (1990)
F. Tuinstra, J.L. Koenig, J. Chem. Phys. 53, 1126 (1970)
A.C. Ferrari, Solid State Commun. 143, 47 (2007)
J.R. Pels, F. Kapteijn, J.A. Moulijn, Q. Zhu, K.M. Thomas, Carbon 33, 1641 (1995)
P.H. Matter, L. Zhang, U.S. Ozkan, J. Catal. 239, 83 (2006)
S.R. Gajjela, K. Ananthanarayanan, C. Yap, M. Gratzel, P. Balaya, Energy Environ. Sci. 3, 838 (2010)
M. Kruk, M. Jaroniec, Chem. Mater. 13, 3169 (2001)
H. Zhang, T. Kuila, N.H. Kim, D.S. Yu, J.H. Lee, Carbon 69, 66 (2014)
B.E. Conway, Electochemical Supercapacitors (Kluwer Academic Publishers/Plenum Press, New York, 1999), pp. 1–698
J. Wang, B. Ding, L. Xu, L. Shen, H. Dou, X. Zhang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 22284 (2015)
S.S. Balaji, A. Elavarasan, M. Sathish, Electrochim. Acta 200, 37 (2016)
K. Xia, W. Guoxu, H. Zhang, Y. Yu, L. Liu, A. Chen, J. Nanopart. Res. 19, 254 (2017)
B. Jiang, C. Tian, L. Wang, L. Sun, C. Chen, X. Nong, Y. Qiao, H. Fu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 3438 (2012)
P. Bharathidasan, D.W. Kim, S. Devaraj, S.R. Sivakkumar, Electrochim. Acta 204, 146 (2016)
C. Zheng, X.F. Zhou, H.L. Cao, G.H. Wang, Z.P. Liu, RSC Adv. 5, 10739 (2015)
Acknowledgements
Financial support from Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, India (SB/FT/CS-025/2014 & SB/FT/CS-007/2013) and University Grant Commission – Department of Atomic Energy Consortium for Scientific Research, India (CSR/Acctts/2015/1075) are gratefully acknowledged. We thank Dr. V. Ramanathan for Raman spectroscopic studies and SASTRA for infrastructural and instrumental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharathidasan, P., Sridhar, S., Vardhan, P.V. et al. High capacitance and long cycle-life of nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 7661–7667 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8760-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8760-6