Abstract
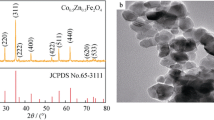
In this research work, magnetic and microwave absorption loss and other response characteristics in cobalt zinc ferrite composite has been studied. Cobalt zinc ferrite with the composition of Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 was prepared via high energy ball milling followed by sintering. Phase characteristics of the as-prepared sample by using XRD analysis shows evidently that a high crystalline ferrite has been formed with the assists of thermal energy by sintering at 1250 °C which subsequently changes the magnetic properties of the ferrite. A high magnetic permeability and losses was obtained from ferrite with zinc content. Zn substitution into cobalt ferrite has altered the cation distribution between A and B sites in spinel ferrite which contributed to higher magnetic properties. Specifically, Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 provides electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics. It was found that cobalt zinc ferrite sample is highly potential for microwave absorber which showed the highest reflection loss (RL) value of − 24.5 dB at 8.6 GHz. This material can potentially minimize EMI interferences in the measured frequency range, and was therefore used as fillers in the prepared composite that is applied for microwave absorbing material.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Luo, Y. Zuo, P. Shen, Z. Yan, K. Zhang, Excellent microwave absorption properties by tuned electromagnetic parameters in polyaniline coated Ba0.9La0.1Fe11.9Ni0.1O19/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 7, 36433–36443 (2017)
Y.B. Feng, T. Qiu, C.Y. Shen, X.Y. Li, Electromagnetic and absorption properties of carbonyl iron/rubber radar absorbing materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 42, 363–368 (2006)
P.J. Bora, K.J. Vinoy, P.C. Ramamurthy, G. Madras, Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of polyaniline-nickel oxide coated cenosphere composite film. Compos. Commun. 4, 37–42 (2017)
H. Wu, S. Qu, K. Lin, Y. Qing, L. Wang, Y. Fan, Q. Fu, F. Zhang, Enhanced low-frequency microwave absorbing property of SCFs@TiO2 composite. Powder Technol. 333, 153–159 (2018)
H. Wu, G. Wu, Y. Ren, X. Li, L. Wang, Multishelled metal oxide hollow spheres: easy synthesis and formation mechanism. Chem.-A Eur. J. 22, 8864–8871 (2016)
H. Wu, G. Wu, L. Wang, Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 269, 443–451 (2015)
H. Wu, G. Wu, Y. Ren, L. Yang, L. Wang, X. Li, Co2+/Co3+ ratio dependence of electromagnetic wave absorption in hierarchical NiCo2O4–CoNiO2 hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 7677–7690 (2015)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Y. Ren, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, H. Wu, Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@C nanorod-carbon sphere composite and its application as microwave absorbing material. J. Alloys Compd. 652, 346–350 (2015)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, F. Xiang, Z. Jia, Q. Xie, G. Wu, H. Wu, Morphology-controlled synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of nanostructured 3D CeO2. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 41, 6–11 (2016)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Q. Xie, Z. Jia, F. Xiang, H. Wu, Facile synthesis of urchin-like ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Mater. Lett. 144, 157–160 (2015)
T. Kagotani, R. Kobayashi, S. Sugimoto, K. Inomata, K. Okayama, J. Akedo, Magnetic properties and microwave characteristics of Ni Zn Cu ferrite film fabricated by aerosol deposition method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 290–291, 1442–1445 (2005)
P.J. Bora, M. Porwal, K.J. Vinoy, P.C. Ramamurthy, G. Madras, Industrial waste fly ash cenosphere composites based broad band microwave absorber. Compos. Part B 134, 151–163 (2018)
T.K. Gupta, B.P. Singh, R.B. Mathura, S.R. Dhakate, Multi-walled carbon nanotube–graphene–polyaniline multiphase nanocomposite with superior electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. Nanoscale 6, 842–851 (2014)
P.J. Bora, G. Lakhani, P.C. Ramamurthy, G. Madras, Poly(vinylbutyral) -polyanilinemagnetically functionalized fly ash cenosphere composite film for electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part B: Eng. 106, 224–233 (2016)
R.C. Handley, Modern magnetic materials: principles and applications.(Wiley-Interscience Publication, Hoboken, 2000)
W. Fu, S. Liu, W. Fan, H. Yang, X. Pang, J. Xu, G. Zou, Hollow glass microspheres coated with CoFe2O4 and its microwave absorption property. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 54–58 (2007)
E. Manova, B. Kunev, D. Paneva, I. Mitov, L. Petrov, Mechanosynthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of nanoparticles of cobalt ferrite, CoFe2O4. Chem. Mater. 16, 5689–5696 (2004)
J. Cao, W. Fu, H. Yang, Q. Yu, Y. Zhang, S. Liu, P. Sun, X. Zhou, Large-scale synthesis and microwave absorption enhancement of actinomorphictubular ZnO/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 4642–4647 (2009)
J. Wan, X. Wang, Y. Wu, M. Zeng, Y. Wang, H. Jiang, W. Zhou, G. Wang, Magnetoelectric CoFe2O4–Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 composite thin films derived by a sol-gel process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 122501 (2005)
S.B. Waje, M. Hashim, W.D.W. Yusoff, Z. Abbas, Sintering temperature dependence of room temperature magnetic and dielectric properties of Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 prepared using mechanically alloyed nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 686–691 (2010)
M.A.N. Ismail, M. Hashim, A. Hajalilou, I. Ismail, M.M.M. Zulkimi, N.H. Abdullah, W.N.A. Rahman, M.S. Abdullah, M. Manap, Magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed cobalt-zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 27, 1293–1298 (2014)
A. Poorbafrani, E. Kiani, Enhanced microwave absorption properties in cobalt–zinc ferrite based nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 416, 10–14 (2016)
I.R. Ibrahim, M. Hashim, R. Nazlan, I. Ismail, W.N.A. Rahman, N.H. Abdullah, F.M. Idris, M.S.E. Shafie, M.M.M. Zulkimi, Grouping trends of magnetic permeability components in their parallel evolution with microstructure in Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 355, 265–275 (2014)
I. Ismail, M. Hashim, K.A. Matori, R. Alias, J. Hassan, Dependence of magnetic properties and microstructure of mechanically alloyed Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 on soaking time. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(16), 2463–2470 (2018)
M.S. Mustaffa, M. Hashim, R.S. Azis, I. Ismail, S. Kanagesan, M.M. Zulkimi, Magnetic phase-transition dependence on nano-to-micron grain-size microstructural changes of mechanically alloyed and sintered Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2 O 4. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 27, 1451–1462 (2014)
A. Verma, T.C. Goel, R.G. Mendiratta, P. Kishan, Magnetic properties of nickel-zinc ferrites prepared by the citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 208, 13–19 (2000)
S.O. Chikazumi, S.H. Charap, Physics of Magnetism (John Wiley, New York, 1964)
L. Neel, Magnetic properties of ferrites: ferrimagnetism and antiferromagnetism. Ann. Phys. 3, 137–198 (1948)
S. Morup, Superparamagnetism and spin glass ordering in magnetic nanocomposites. Europhys. Lett. 28, 671–676 (1994)
R. Adhikari, A. Sarkar, M.V. Limaye, S.K. Kulkarni, A.K. Das, Variation and sign change of magnetostrictive strain as a function of Ni concentration in Ni-substituted ZnFe2O4 sintered nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 073903 (2012)
C.N. Chinnasamy, A. Narayanasamy, N. Ponpandian, K. Chattopadhyay, H. Guerault, J.M. Greneche, Magnetic properties of nanostructured ferrimagnetic zinc ferrite. J. Phys.: Condensed Matter-IOPsci. 12(35), 7795–7805 (2000)
S.S. Kim, S.B. Jo, K.I. Gueon, K.K. Choi, J.M. Kim, K.S. Chun, Complex permeability and permittivity and microwave absorption of ferrite-rubber composite at X-band frequencies. IEEE Trans. Magn. 27, 5462–5464 (1991)
Y. Natio, K. Suetake, Application of ferrite to electromagnetic wave absorber and its characteristics. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 19, 65–72 (1971)
C. Kittel, On the theory of ferromagnetic resonance absorption. Phys. Rev. 73(2), 155–161 (1948)
H. Zou, S. Li, L. Zhang, S. Yan, H. Wu, S. Zhang, Determining factors for high performance silicone rubber microwave absorbing materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1643–1651 (2011)
G.X. Tong, Q. Hu, W.H. Wu, W. Li, H.S. Qian Y. Liang, Submicrometer-sized NiO octahedra: facile one-pot solid synthesis, formation mechanism, and chemical conversion into Ni octahedra with excellent microwave-absorbing properties. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 17494–17504 (2012)
L.J. Deng, P.H. Zhou, J.L. Xie, L. Zhang, Characterization and microwave resonance in nanocrystalline FeCoNi flake composite. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 103916 (2007)
F. Ma, Y. Qin, Y.Z. Li, Enhanced microwave performance of cobalt nanoflakes with strong shape anisotropy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 202507 (2010)
T. Aoyagi, Y. Shimizu, Design of multilayer wave absorber for oblique incidence using the point frequency matching method. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 3, 105–114 (1995)
X. Huang, J. Zhang, S. Xiao, G. Chen, The cobalt zinc spinel ferrite nanofiber: lightweight and efficient microwave absorber. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97(5), 1363–1366 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Material Synthesis Characterization Laboratory, Institute of Advance Technology (ITMA), Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hapishah, A.N., Syazwan, M.M. & Hamidon, M.N. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic and microwave absorbing properties in polycrystalline cobalt zinc ferrite (Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4) composite. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 20573–20579 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0192-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0192-9