Abstract
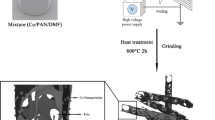
Aiming to tailor microwave absorption properties of furan resin derived carbon (FRC) which is expected using as matrix in carbon/carbon composites (C/C) for microwave absorption, SiO2 doped furan resin derived carbon (SFRC) particles were prepared and their dielectric behavior and microwave absorption capability were investigated. Results indicated that compared with pure FRC particles, complex permittivity of SFRC particles decreases significantly, which is mainly ascribed to the greatly decreased electrical conductivity. Due to improved microwave impedance and relative high dielectric loss, FRC particles doped by 20 wt% SiO2 show enhanced microwave absorption performance. However, when SiO2 is increased to 40 wt%, the microwave absorption property is weakened because of low attenuation capability. SFRC could potentially be used as a suitable carbon matrix to prepare C/C with favorable microwave absorption capability.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Chen, C. Xu, C. Ma, W. Ren, H. Cheng, Adv. Mater. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204196
A.K. Singh, A. Shishkin, T. Koppel, N. Gupta, Compos. B (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.05.027
S.E. Zakiyan, H. Azizi, I. Ghasemi, Compos. Sci. Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.02.002
H. Wu, S. Qu, K. Lin, Powder Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.04.015
A. Kolanowska, D. Janas, A.P. Herman, R.G. Jędrysiak, T. Giżewski, S. Boncel, Carbon (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.09.078
M. Letellier, J. Macutkevic, P. Kuzhir, J. Banys, V. Fierro, A. Celzard, Carbon (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.06.080
H. Wu, G. Wu, Y. Ren, L. Yang, L. Wang, X. Li, J. Mater. Chem. C (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TC01716E
D. Lan, M. Qin, R. Yang, J. Colloid Interface Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.108
C. Mao-Sheng, Y. Jian, S. Wei-Li, Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/am3021069
W.-L. Song, M.-S. Cao, M.-M. Lu, J. Liu, J. Yuan, L.-Z. Fan, J. Mater. Chem. C (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TC00494A
W.L. Song, X.T. Guan, L.Z. Fan, Carbon (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.01.002
H. Wu, G. Wu, L. Wang, Powder Technol. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.09.045
B. Wen, M. Cao, M. Lu, Adv. Mater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201400108
X.-F. Lu, P. Xiao, Carbon (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.03.007
X. Luo, D.D.L. Chung, Compos. B (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-8368(98)00065-1
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Y. Ren, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, H. Wu, J. Alloy. Compd. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.08.236
Y. Wang, W. Wang, J. Sun, C. Sun, Y. Feng, Z. Li, Carbon (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.04.026
X. Wang, X. Bao, X. Zhou, G. Shi, J. Alloy. Compd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.150
Y. Wei, J. Yue, X.-Z. Tang, Z. Du, X. Huang, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.079
W. Zhou, L. Long, P. Xiao, Ceram. Int. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.01.095
M. Gholampoor, F. Movassagh-Alanagh, H. Salimkhani, Solid State Sci. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2016.12.005
H. Salimkhani, A. Motei Dizaji, E. Hashemi, P. Palmeh, G. Sabeghi, S. Salimkhani, Ceram. Int. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.185
E. Savage, Carbon (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1586-5
W. Zhou, P. Xiao, Y. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.03.107
H.L. Ding, Y.X. Zhang, S. Wang, J.M. Xu, S.C. Xu, G.H. Li, Chem. Mater. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm302828d
Y. Wang, Y. Lai, S. Wang, W. Jiang, Ceram. Int. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.148
B. Wen, M.-S. Cao, Z.-L. Hou, Carbon (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.07.110
C. Ge, L. Wang, G. Liu, T. Wang, J. Alloy. Compd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.081
Y. Liu, Y. Li, F. Luo, J. Alloy. Compd. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.04.301
M.-S. Cao, X.-L. Shi, X.-Y. Fang, Appl. Phys. Lett. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2803764
X. Yuan, L. Cheng, L. Zhang, J. Alloys Compd. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.309
X. Yuan, L. Cheng, S. Guo, L. Zhang, Ceram. Int. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.151
X. Ji, W. Zhang, W. Jia, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.07.013
W. Song, M. Cao, Z. Hou, X. Fang, X. Shi, J. Yuan, Appl. Phys. Lett. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3152764
M.-S. Cao, W.-L. Song, Z.-L. Hou, B. Wen, J. Yuan, Carbon (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.10.028
J.E. Atwater, J.R.R. Wheeler, Appl. Phys. A (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-003-2329-8
W. Zhou, P. Xiao, Y. Li, L. Zhou, Ceram. Int. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.01.090
R.C. Che, L.M. Peng, X.F. Duan, Q. Chen, X.L. Liang, Adv. Mater. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200306460
Z.W. Li, G.Q. Lin, Y.P. Wu, L.B. Kong, IEEE Trans. Magn. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2008.2007757
F. Qin, C. Brosseau, J. Appl. Phys. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3688435
M. Cao, X. Wang, W. Cao, X. Fang, B. Wen, J. Yuan, Small (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201800987
W. Cao, X. Wang, J. Yuan, W. Wang, M. Cao, J. Mater. Chem. C (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TC02185E
T. Inui, K. Konishi, K. Oda, IEEE Trans. Magn. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/20.801110
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51604107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, L., Zhou, W., Xiao, P. et al. Microwave absorption properties of SiO2 doped furan resin derived carbon particles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 3359–3364 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00609-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00609-x