Abstract
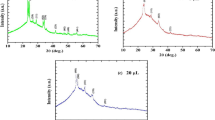
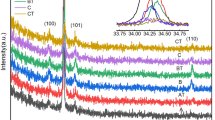
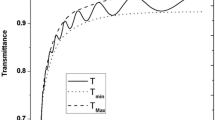
Thin films of Ti-doped ZnO (TZO) were prepared by RF magnetron sputtering using targets prepared with sintering temperatures in the range 1100–1500 °C; the microstructures and optoelectronic properties of the TZO targets and films were characterized by SEM, XRD, Hall Effect analysis, UV–VIS spectrophotometry and physical property measurement system. Results indicated that the target sintering temperature affected both the TZO targets and films. The Ti/Zn atomic ratios in the targets decreased progressively with increasing sintering temperature, but by a smaller amount in films prepared from them. XRD patterns showed that all films were preferentially oriented along the c axis at 2θ ~ 34° in their XRD patterns. The films sputtered with targets sintered at above 1300 °C were relatively smooth, and had larger average grain size. The target sintered at 1450 °C had the highest density. The best optoelectronic properties were found with the film sputtered from the target sintered at 1300 °C; this sample had superior crystal properties, high average optical transmittance (88.9%), and the lowest resistivity (8.47 × 10−4 Ω cm). Furthermore, the resistivity of all the films changed with temperature between 10 and 350 K, they experienced an initial decrease followed by an increase as the temperature was raised.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Onwona-Agyeman, M. Nakao, T. Kohno, D. Liyanage, K. Murakami, T. Kitaoka, Chem. Eng. J. 219, 273 (2013)
Q. Huang, Y.F. Wang, S. Wang, D.K. Zhang, Y. Zhao, X.D. Zhang, Thin Solid Films 520, 5960 (2012)
M.H. Jiang, X.Y. Liu, H. Wang, Surf. Coat. Technol. 203, 3750 (2009)
J.Y. Kao, C.Y. Hsu, G.C. Chen, D.C. Wen, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23, 1352 (2012)
Q.B. Ma, H.P. He, Z.Z. Ye, L.P. Zhu, J.Y. Huang, Y.Z. Zhang, B.H. Zhao, J. Solid State Chem. 181, 525 (2008)
S. Okuda, T. Matsuo, H. Chiba, T. Mori, K. Washio, Thin Solid Films 557, 197 (2014)
L.P. Peng, L. Fang, X.F. Yang, Q.L. Huang, F. Wu, Y.C. Cao, M.W. Li, C.Y. Kong, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 25, 995 (2011)
L.P. Peng, L. Fang, X.F. Yang, H.B. Ruan, Y.J. Li, Q.L. Huang, C.Y. Kong, Phys. E.: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 41, 1819 (2009)
H. Qin, H.F. Liu, Y.Z. Yuan, Surf. Eng. 29, 70 (2013)
S. Wang, J. Shen, Z.J. Zhang, X.L. Yang, Q. Zhang, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 28, 1 (2008)
H.W. Wu, R.Y. Yang, C.M. Hsiung, C.H. Chu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 166 (2013)
J.W. Xu, H. Wang, M.H. Jiang, X.Y. Liu, Bull. Mater. Sci. 33, 119 (2010)
H.F. Zhang, R.J. Liu, H.F. Liu, Q.S. Chen, X.F. Wang, Y.X. Mei, J. Synth. Cryst. 39, 766 (2010)
H.X. Chen, W.G. Guo, J.J. Ding, S.Y. Ma, Superlattices Microstruct. 51, 544 (2012)
Y.C. Lin, C.Y. Hsu, S.K. Hung, D.C. Wen, Ceram. Int. 39, 5795 (2013)
S.S. Lin, J.L. Huang, D.F. Lii, Mater. Chem. Phys. 90, 22 (2005)
H.P. Chang, F.H. Wang, J.C. Chao, C.C. Huang, H.W. Liu, Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, S185 (2011)
F.H. Wang, H.P. Chang, J.C. Chao, Thin Solid Films 519, 5178 (2011)
J. Liu, S.Y. Ma, X.L. Huang, L.G. Ma, F.M. Li, F.C. Yang, Q. Zhao, X.L. Zhang, Superlattices Microstruct. 52, 765 (2012)
K. Bergum, P.A. Hansen, H. Fjellvag, O. Nilsen, J. Alloys Compd. 616, 618 (2014)
W.S. Liu, S.Y. Wu, C.H. Tseng, C.Y. Hung, Thin Solid Films 570, 568 (2014)
L. Gao, Y. Zhang, J.M. Zhang, K.W. Xu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2498 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Dr. Bernard A. Goodman for his helpful discussions. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.112650020 and 11675043), and Foundation of Xingjian College of Guangxi of University China (Grant No. 2016ZKA01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Li, F., Chen, X. et al. Influence of sintering temperatures of ceramic targets on microstructures and photoelectric properties of titanium-doped ZnO nano-films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 4654–4660 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6104-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6104-y